This is the second in a series of primers on the fast-moving situation in Ukraine, and covers events from March 2 through March 9. For more background on the situation, please see part 1.
Summary of Recent Events
This week saw sporadic military activity on the Crimean peninsula, in [...]]]>
This is the second in a series of primers on the fast-moving situation in Ukraine, and covers events from March 2 through March 9. For more background on the situation, please see part 1.
Summary of Recent Events
This week saw sporadic military activity on the Crimean peninsula, in particular a reported attack by pro-Russian gunmen on a Ukrainian air force base in Sevastopol that ended when the gunmen retreated. Diplomatic efforts seem to have stalled, as Russia refused to speak directly with the new Ukrainian government, which it regards as illegitimate, and threatened that any sanctions against Russia would “boomerang” against the United States. The week’s biggest development was that Crimea’s parliament has voted to begin the process of seceding from Ukraine and joining Russia, a vote that the governments of Ukraine, the United States, and the European Union all termed “illegal.”
Secession movement
On March 6 the Crimean parliament voted to secede from Ukraine and become part of Russia, pending the approval of the Russian government and the results of a referendum now scheduled for March 16. Although Russian President Vladimir Putin had said earlier in the week that he “did not foresee” Russia annexing Crimea, the leaders of both houses of Russia’s parliament publicly welcomed the Crimean assembly’s vote and pledged to honor the wishes of the Crimean people as expressed in the referendum. The draft referendum, which Kyiv Post revealed, offers two options: “joining Crimea with the Russian Federation” or “restoration of 1992 Crimean Constitution” (which declared Crimean independence, then was amended to declare its autonomy within Ukraine).
Ukraine’s interim Prime Minister Arseniy Yatsenyuk criticized the Crimean vote as “illegitimate,” and its interim President, Oleksandr V. Turchynov, termed the vote “a farce.” Leaders of Crimea’s sizable Tatar minority also expressed opposition to the vote. Their sentiments were echoed by American and European leaders. US President Barack Obama characterized the vote as illegal under both the Ukrainian constitution and international law, and the EU envoy to Ukraine, Jan Tombinski, argued that a referendum on secession that was restricted to Crimea would violate Ukrainian law.
Attack on Ukrainian base, questions about the Russian forces
On Monday Ukrainian military sources reported that the commander of Russia’s Black Sea Fleet, based in Sevastopol, had given Ukrainian forces in Crimea until early Tuesday morning to surrender or face an attack. Russian officials denied that any such ultimatum had been issued, and the deadline passed without incident. On Friday, however, armed pro-Russian forces stormed a Ukrainian air force base in Sevastopol and occupied parts of it for several hours as they demanded the surrender of the Ukrainian soldiers inside. When the Ukrainian soldiers refused to surrender, the gunmen withdrew; thus far, both Ukrainian and Russian forces have not fired on one another. Russia continued to deny that the pro-Russian forces in Crimea were Russian military, insisting that they are local “self-defense units,” but considerable evidence has been found suggesting that they are, in fact, Russian military forces. The Ukrainian border guard service contended that roughly 30,000 Russian troops are now on the peninsula, and photographs allegedly taken near the southern Ukrainian city of Chonhar appear to show a freshly dug minefield along the approach from the Ukrainian mainland to Crimea. Deputy Crimean Prime Minister Rustam Temirgaliev stated that Russian troops are the only legal soldiers in Crimea, suggesting that Ukrainian soldiers still on their bases are considered illegal by the Crimean government. On Saturday, March 8, a bus carrying international observers from the Organisation for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) attempted to enter Crimea, but it turned back at the northern Crimean city of Armyansk when “warning shots” were fired at it.
Diplomacy sputters amid looming threat of sanctions from both sides
President Vladimir Putin gave a press conference on Tuesday that appeared to “hit pause” on the Crimea situation, though this characterization was obviously premature given events later in the week. Putin described the events that forced Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych from office as “an anti-constitutional coup” and claimed that Russian intervention was necessary to safeguard the ethnic Russians who are concentrated in Crimea and in major cities in the eastern part of Ukraine, though he reiterated the official Russian position that there has not been an invasion. US Secretary of State John Kerry traveled to Kiev to offer the interim government $1 billion in loan guarantees, and while there he, in remarks that were echoed by Obama, accused Putin of “hiding behind falsehoods” to justify Russia’s actions, and called on him to return Russian forces to their barracks. Kerry failed in his efforts to arrange a meeting between Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov and his Ukrainian counterpart, with Lavrov refusing to recognize the legitimacy of the Kiev government, but on Saturday one of Russia’s deputy foreign ministers did meet with the Ukrainian ambassador to Russia in Moscow.
Sanctions both by and against Russia were already being imposed by week’s end. On Thursday, President Obama ordered the imposition of sanctions against “individuals and entities” that were involved in Russia’s move into Crimea, which followed an earlier decision to suspend all US military cooperation with Russia. European Union leaders suspended talks with Russia on economic and travel issues but did not yet appear to be prepared to go any further. European leaders expressed concern that a Russian response could damage economies across Europe, and Lavrov warned that sanctions could “boomerang” against the United States and Europe. Russia announced that it was considering pulling out of arms control treaties with the US and the OSCE in response to American actions. More urgently, the Russian firm Gazprom hinted Friday that it may suspend gas shipments to Ukraine (and thus, potentially, through Ukraine and on to the rest of Europe) due to Kiev’s outstanding debt, which Gazprom estimates to be $1.89 billion.
Questions over legitimacy
Earlier this week Obama stressed that “[a]ny discussion about the future of Ukraine must include the legitimate government of Ukraine,” but the standoff is being driven in part by a disagreement over what the “legitimate” government of Ukraine actually is. Russia still recognizes Viktor Yanukovych as the legitimate president of Ukraine, and claims that Yanukovych asked for Russian military assistance when he was ousted. The United States, on the other hand, has recognized the interim government in Kiev and says that Yanukovych’s actions in office “undermined” his claim to authority despite the fact that he was a democratically-elected leader. Russia’s continued refusal to deal directly with Kiev is couched in terms of the new government’s illegitimacy, at least in Russia’s view. Aid from the United States and from Europe is being offered to help stabilize the government in Kiev.
]]>by Derek Davison
On February 27 gunmen seized control of government buildings in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea in Ukraine and raised a Russian flag over the headquarters of the Crimean Parliament in the regional capital Simferopol. This began a series of events that has resulted in Crimea under Russian control and [...]]]>
by Derek Davison
On February 27 gunmen seized control of government buildings in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea in Ukraine and raised a Russian flag over the headquarters of the Crimean Parliament in the regional capital Simferopol. This began a series of events that has resulted in Crimea under Russian control and furious diplomatic efforts underway between Ukraine, the European Union, the United Nations, NATO, Russia, and the United States. This primer will offer some background to the (rapidly changing) events currently taking place in Ukraine and some idea as to where things may proceed from here.
What is Crimea and why is it important to Russia?
Crimea is a peninsula that extends from the southern part of Ukraine into the Black Sea. Formerly controlled by the Crimean Khanate (whose Tatar subjects were forcibly relocated out of the peninsula by Josef Stalin in 1944), it was annexed into the Russian Empire in 1783 and immediately became home to Russia’s Black Sea naval fleet, based in the southern city of Sevastopol. The fleet was sunk during the Crimean War (1853-1856) when Sevastopol was besieged by a combined French, British, and Ottoman army, but was rebuilt after the war. In 1921 Crimea became the Crimean Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, part of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, but in 1954, it became part of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic to streamline post-WWII reconstruction. Crimea briefly declared self-government when the Soviet Union collapsed in 1992, but agreed to remain part of the newly independent Ukraine.
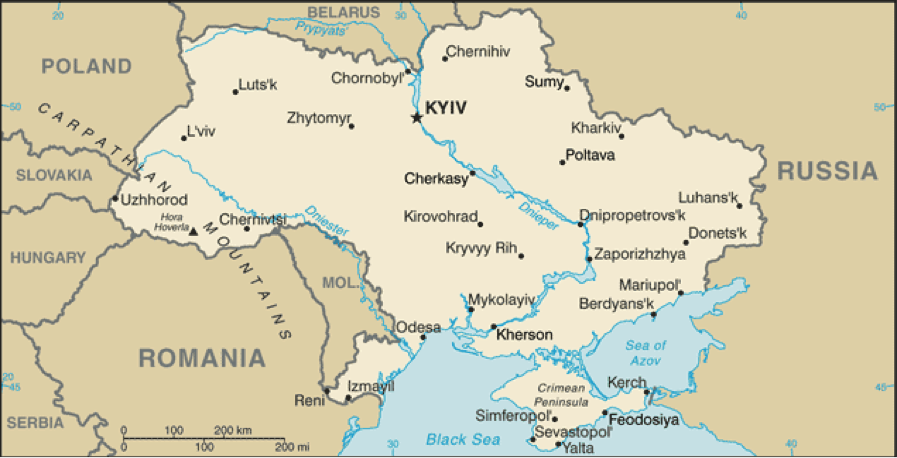 Ukraine, including Crimea to the south (Credit: CIA World Factbook)
Ukraine, including Crimea to the south (Credit: CIA World Factbook)
All of Ukraine has value to Russia, but Crimea is especially important. Crimea has only been part of an independent Ukraine for 20 years, a fraction of the time it was part of Russia, and ethnic Russians are actually almost 60% of the peninsula’s population, according to the most recent census (2001). More crucially, the Russian Black Sea Fleet is based at Sevastopol, part of a post-Soviet deal between the two countries to divide the former Soviet fleet and to lease part of the base to Russia, and so Russia has military/strategic reasons to ensure that it retains access to that base.
Why did Russian forces invade Crimea now?
Beginning in late-November 2013, a series of protests, known as Euromaidan, began in the Ukrainian capital, Kiev, against the government of then-President Viktor Yanukovych, a close ally of Russian President Vladimir Putin. Dueling pro- and anti-government protests, and clashes with security forces, continued through January 2014, when the Yanukovych government announced new draconian anti-protest laws. What had been an occasionally violent protest movement turned into a full-blown revolution, culminating in a series of clashes on February 18-20. Casualty reports vary, but as many as 100 people may have been killed in the violence.
On February 21, Yanukovych reached a deal with opposition leaders to end the violence, but the protesters refused to accept it, and the following day Yanukovych fled Kiev. Yanukovych has been impeached and removed from office by the Ukrainian Parliament, an act that he rejects, and is considered a fugitive for his role in the deadly February violence. After Yanukovych was impeached, officials in Putin’s government suggested that the Russian military could intervene in Ukraine if it was deemed necessary in order to “protect” Crimea. On March 1, the Federation Council, the upper house of the Russian Parliament, voted unanimously to give Putin authority to deploy Russian troops into Ukraine, and the Russian military seized near-total control of Crimea.
What were the Ukrainian protests about?
Ukraine’s economy has been in crisis for some time. Many Ukrainians supported the adoption of an Association Agreement with the European Union as a way to boost the economy, but Yanukovych’s government suspended talks over the proposed agreement and instead pursued entry into the Eurasian Customs Union, alongside Russia, Belarus, and Kazakhstan. Polls indicated that a slim plurality of Ukrainians favored the EU deal over the customs union. The name of the protest movement, “Euromaidan,” reflects its initial demand (closer integration with Europe) and the fact that it began in Maidan Nezalezhnosti (“Independence Square”) in downtown Kiev.
The dispute over whether to gravitate toward Europe or back toward Russia exacerbated an already existing ethnic and linguistic split between the largely Ukrainian, pro-Europe western half of the country and the more Russian-oriented eastern half. But this division has been overemphasized as a “cause” of the protests, when the principal causes were Ukraine’s weak economy and Yanukovych’s decisions to reject the EU and then try to violently suppress the initial protests. Even in the eastern, “pro-Russian” part of Ukraine, the majority of the population is ethnic Ukrainian and, according to a 2011 poll, a majority in every province (even Crimea) sees Ukraine as its mother country.
Does Russia have designs on the rest of Ukraine?
The Federation Council resolution authorizing Russian military intervention in Ukraine pointedly allows deployment anywhere in Ukraine, not just Crimea. There are several reasons why Russia wants to retain influence in all of Ukraine, if not to outright control it. Russian history and national pride is inextricably tied to Ukraine, since Russians trace their origins to the 9th-13th century Rus’ people, whose capital and principle city was Kiev. Economically, it would be a blow to Russia if Ukraine were to choose EU membership over joining the Eurasian Customs Union, and Russia also depends on Ukrainian pipelines to ship its natural gas to the rest of Europe. Pro-Russian protests have taken place in eastern Ukrainian cities outside of Crimea, with Russian flags also being raised in several places there.
On the other hand, Russia continues to deny that it has even sent troops into Crimea, let alone the rest of Ukraine, since the fighters who have taken control of Crimea appear to be Russian private paramilitaries rather than official Russian soldiers.
Do the Crimeans want (or need) Russian “protection”?
It does seem that Crimean Russians, worried that the new government in Kiev might be hostile to them, have welcomed the arrival of Russian troops. New Crimean Prime Minister Sergey Aksyonov refused to recognize Yanukovych’s removal from office and asked Putin to send Russian forces to help him “ensure peace” in Crimea. It is worth noting that one of the first acts of the new Ukrainian government was to abolish a 2012 law allowing Russian to be used as a second official language in some parts of the country, and it is also true that the Euromaidan movement included some far-right Ukrainian nationalist groups. However, Crimea is also home to large populations of ethnic Ukrainians and Tatars (who started returning to Crimea after the fall of the USSR), and these groups do not support the Russian invasion.
How have Ukraine and the rest of the world responded to Russia’s invasion?
The Ukrainian government has mobilized its military, though it seems to be on a purely defensive posture. At the UN Security Council, the United States and Ukraine accused Russia of violating Ukraine’s sovereignty, in particular the 1994 Budapest Memorandum in which the US, UK, and Russia pledged to honor Ukraine’s territorial integrity. Russia has countered that American and European involvement in Euromaidan (an accusation for which it has yet to produce any evidence) was itself a violation of Budapest and made Russian intervention necessary. Presidents Barack Obama and Putin held a “testy” phone conversation in which Putin asserted Russia’s right to defend ethnic Russians in Ukraine, while Obama called on Putin to draw his forces back. There are diplomatic levers that the US and the EU can push, including sanctions against Russia and Russian politicians, but there is likely nothing powerful enough to force Putin to withdraw. Kiev has options it can pursue as well; Crimea is, for example, dependent on the mainland for its water and electricity, and while Ukraine relies on Russia for its natural gas, Russia also relies on Ukrainian pipelines to get that gas to European markets, so Putin cannot punish Kiev by just turning the gas off. Still, these options are unlikely to force Russia to withdraw.
Russia may simply order its forces out of Crimea after extracting concessions from Kiev, something akin to the outcome of the Russia-Georgia War in 2008, but it is possible that Putin will attempt to carve eastern Ukraine and Crimea off into a new state, which could lead to a military confrontation.
]]>