The new year may have brought with it some signs of progress toward a comprehensive deal between world powers and Iran, lending credence to one of Graham Fuller’s 2015 predictions for the Middle East. However, any movement toward a nuclear agreement must now contend with a potentially game-changing complication: the desire of a new and more hawkish Republican-led Congress to impose additional sanctions on Iran regardless of how the talks are progressing.
The Associated Press reported on Friday that the P5+1 (the US, UK, France, Germany, Russia, and China) had reached a tentative agreement with Iranian negotiators on a plan to have Tehran ship some portion of its stockpiled low enriched uranium (LEU) to Russia. The agreement would presumably be along the lines of the arrangement that was first reported by IPS’s Gareth Porter in October whereby Iran’s stockpiled LEU, as well as much of its newly enriched LEU, would be converted by the Russians into fuel for its Bushehr civilian nuclear facility.
If the AP report is accurate, the deal could represent a major breakthrough in one of the core areas of dispute between the parties: the size of Iran’s uranium enrichment program. The P5+1 have sought to limit the number of centrifuges that Iran would be allowed to operate under the terms of a deal in order to lengthen the amount of time it would take the Iranians to produce enough highly enriched uranium (HEU) for a single nuclear bomb if it chose to pursue one (Iran’s “breakout time”). But Iran has balked at the idea of reducing its centrifuge program. However, another element in the “breakout time” calculation (part of the so-called “Rubik’s Cube” of a final nuclear deal) is the amount of LEU that Iran has stockpiled. Were Iran to agree to ship its LEU (which can be fairly easily enriched to levels required for weaponization) to Russia for conversion into fuel rods (which cannot be easily converted to a weaponizable form), then Iran’s “breakout time” could be extended with only a relatively minor –and perhaps even no — reduction in Iran’s current centrifuge capacity.
It should be noted that the AP report contained no specifics, saying simply that “both sides in the talks are still arguing about how much of an enriched uranium stockpile to leave Iran.” It also offered no indication that the deal would motivate the US/P5+1 negotiators to alter their demand that Iran cut its current number of operating centrifuges by over 50%, to 4500, under a final deal. In addition, Iran’s foreign ministry quickly dismissed the AP report, with spokeswoman Marzieh Afkham saying that “no agreement has been reached yet on any of the issues [being discussed] during nuclear talks,” although that denial could reflect diplomatic posturing on Iran’s part.
Other news out of Tehran, however, has offered a more encouraging sign that the sides may be moving closer to a deal. Iranian President Hassan Rouhani on Sunday argued that Iran should be prepared to accept some limits on its uranium enrichment program if doing so could help achieve a larger aim:
Speaking to an economic conference in Tehran, Rouhani both countered hard-line critics worried Iran will give up too much while also attempting to signal his administration remains open to negotiation with the six-nation group leading the talks.
If “we are ready to stop some types of enrichment which we do not need at this time, does it mean we have compromised our principles and cause?” Rouhani asked.
He responded: “Our cause is not linked to a centrifuge. It is connected to our heart and to our willpower.”
Rouhani’s remarks caused a bit of a social media storm, with some reputable analysts, including Suzanne Dimaggio who heads the Iran initiative at the New American Foundation, suggesting that a final deal is on the horizon.
Important speech by #Iran‘s @HassanRouhani today: “Our ideals are not bound to centrifuges.” Preparing for a deal. http://t.co/f9CB66RT9G
— Suzanne DiMaggio (@suzannedimaggio) January 4, 2015
Additionally, Rouhani seemed to suggest that he could put the terms of a final nuclear deal to a national referendum, possibly in order to bypass potential opposition from hardliners in the Majles (Iran’s parliament) and higher up the country’s religious and political hierarchy. As Juan Cole notes, the results of such a referendum could still be overruled by Iran’s Supreme Leader, Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, but Khamenei may be reluctant to overrule the will of a majority of the Iranian public.
Unfortunately, these positive developments take place amid the rise of a new threat to the ongoing negotiations, not from hardliners in Iran’s parliament but rather from hardliners in the newly installed (as of Saturday) US Congress. Senator Lindsey Graham (R-SC) visited Israel late last month and told Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu that there would be a vote on the previously stymied Kirk-Menendez bill (to impose additional sanctions on Iran) sometime in January, and that the new Congress would “follow [Netanyahu’s] lead” on dealing with Iran and the nuclear talks. Putting aside the astonishing sight of a US senator pledging allegiance to a foreign leader, sanctions are a clearly decisive issue for Tehran. The imposition of another round of broad US sanctions, even if they are made conditional on Iran abandoning the talks or breaking its obligations under the existing negotiating framework, would strengthen hardliners in Tehran who have long argued that Washington cannot be trusted. The Obama administration has pledged to veto any additional sanctions on Iran so long as talks are ongoing, but that may not matter; Senator Marco Rubio (R-FL) told reporters last week that he expects the new Congress to pass a new sanctions bill with veto-proof majorities in both the House and the Senate.
The most recent extension of the talks called for a final framework to be in place by March 1 and for a full deal to be reached by July 1. It seems likely that most Republicans in Congress will do their best to scuttle the talks before either of those deadlines can be reached, putting negotiators (who will meet again Jan 15. in Geneva) on an even tighter timeframe.
]]>by Mitchell Plitnick
Some days, it must be really difficult to be the State Department’s spokesperson. It doesn’t seem like a bad job to have at all, but on certain questions it’s impossible to not look like an idiot. A lot of those questions are connected to de facto policies which differ [...]]]>
by Mitchell Plitnick
Some days, it must be really difficult to be the State Department’s spokesperson. It doesn’t seem like a bad job to have at all, but on certain questions it’s impossible to not look like an idiot. A lot of those questions are connected to de facto policies which differ from de jure ones. And there is no better example of that than US policy on Israeli settlements.
Back in the early years after the 1967 war, the United States made it clear that the settlements were illegal according to international law. As recently as 1978, the State Department legal adviser confirmed that all Israeli settlements beyond the Green Line are illegal, and through the Carter administration, this was explicit US policy. That policy has never been explicitly revoked, but beginning with the Reagan administration, de facto policy has been ambiguous. Reagan began the trend when he stated that while the settlements were ill-advised, provocative and that further settlement was not necessary for Israel’s security “I disagreed when, the previous Administration refereed to them as illegal, they’re not illegal. Not under the U.N. resolution that leaves the West Bank open to all people—Arab and Israeli alike, Christian alike.”
The problematic nature of Reagan’s statement — implying that “Arab” equals “Muslim” and “Israeli” equals “Jew”, and more importantly, citing the “U.N. Resolution”, which is not the basis for the illegality of the settlements (the Fourth Geneva Convention is) — notwithstanding, this was the beginning of the US’ refusal to label settlements illegal, terming them instead, at most, “illegitimate.”
The problem for spokespeople arises when they have to parse what that means. Last Monday, in Colombia, Secretary of State John Kerry made what turned out to be an interesting statement. “As the world, I hope, knows, the United States of America views all the settlements as illegitimate,” Kerry said. The use of the word “all” might have worked in Reagan’s day, even in Bill Clinton’s. But today, when the US has allowed Israel to assert that certain settlements are essentially guaranteed (the so-called “settlement blocs” of Gush Etzion, Ariel and Ma’ale Adumim) that little word carries heavy implications.
Israel insists that it’s okay to build in the settlement blocs and the Palestinians should have no problem with that because they’re going to keep them anyway. Israel bases its case on the fact that they have repeatedly stated this publicly without being contradicted and on George W. Bush’s letter to Ariel Sharon in 2004. While that letter did not explicitly state that Israel should keep the blocs, it profoundly altered the diplomatic landscape by promising that the borders between Israel and the envisioned Palestinian state would not be the same as those that existed in 1967 and that alterations would reflect the changed demographics in those, at that time, 37 years. Israel took that to mean it would keep the blocs, and no one, other than some Palestinians (and not the lead spokespeople at the time) said otherwise.
So, when Kerry said all the settlements were illegitimate, it prompted AP reporter Matthew Lee to enter into the following exchange with spokeswoman Jen Psaki:
QUESTION: He said the United States doesn’t see all of the settlement activity as legitimate. Is it correct that – is that correct, that all settlement activity is illegitimate? And I don’t want to get into this illegitimate or illegal, because as far as I’m concerned it’s a distinction without a difference. Does the United States believe that all Israeli settlement activity along – and we can include in that East Jerusalem construction – is all of it illegitimate?
MS. PSAKI: Well, our position on Jerusalem has been clear and has been consistent for some time, which is that we believe it is a final status issue in terms of the discussion of that – of Jerusalem, right?
QUESTION: Mm-hmm.
MS. PSAKI: That is part of the discussion. We have, of course, expressed concerns about construction in East Jerusalem. That hasn’t changed. Our position on settlements we have stated a number of times, and I just stated, and that has not changed either.
QUESTION: Okay. So you do not regard the construction in East Jerusalem as illegitimate. Is that correct?
MS. PSAKI: Well, I think I just stated what we – what our longstanding position has been on construction.
…
QUESTION: But it’s not – hold on, Said. But it’s not that it’s illegitimate?
MS. PSAKI: I don’t have anything more than what I just stated.
QUESTION: Because it is a final status issue?
MS. PSAKI: It is a final status issue that we discussed and worked through.
QUESTION: So one of the questions – okay. So one of the questions that I had that Marie said she would take yesterday –
MS. PSAKI: Mm-hmm.
QUESTION: – was about the 900 homes that were announced for construction in East Jerusalem. Is it fair to say you do not regard those as illegitimate?
MS. PSAKI: Well, we – in terms of those specific – that specific announcement –
QUESTION: Right.
MS. PSAKI: – you know we oppose any unilateral action. Certainly we would include this, that attempt to prejudge final status issues, including the status of Jerusalem. That’s where that building is taking place. That’s our view on it.
QUESTION: Okay. So you’re opposed to it, but you don’t say that it’s illegitimate?
MS. PSAKI: I think you know our position.
QUESTION: Okay. So in terms of illegitimacy then, this legitimacy issue, are existing settlements illegitimate in the eyes of the Administration in the West Bank? Settlements in the West Bank that currently exist now, are they illegitimate, meaning that they should not be part of Israel once there is a peace agreement?
MS. PSAKI: Well, obviously, the question of borders will be worked through and is part of the discussion that will take place and will be ongoing in the weeks and months ahead.
QUESTION: So are existing settlements illegitimate?
MS. PSAKI: Well, we have concerns about ongoing continued settlement activity.
QUESTION: Okay. Do you understand that there’s a serious problem here? Because if you talk about – if all you’re prepared to say is that you don’t accept the legitimacy of continued settlement activity, you are only calling illegitimate settlements that have not been announced, settlements that are, say, a twinkle in the Housing Minister or whoever’s eye. Once they are actually announced or built, you stop calling them illegitimate, and they – and you start saying that that’s a – that’s something to be decided between the parties. Okay?
MS. PSAKI: Well, this has been our position for a number of years.
QUESTION: That’s – well, right. But –
MS. PSAKI: So –
QUESTION: And I’m surprised that no one, and especially me, has picked up on this before, because you have essentially – you don’t oppose settlements at all, because once they’re built or once they’re announced, once plans for them – plans to build them are announced, you’re not opposed to them anymore, because it’s something for the parties to decide whether they’re legitimate or not.
MS. PSAKI: Well, certainly it will be – a big part of the discussion will be that process moving forward.
QUESTION: Right. Do you understand the problem? Do you understand the –
MS. PSAKI: I understand what you’re conveying, Matt. I’m happy to talk back with our team and see if there’s any more clarification we can provide.
QUESTION: Okay. So tell me, am I wrong in thinking that the United States has no position at all except that it is to be decided by the parties on the legitimacy or illegitimacy of settlements that exist in the West Bank today?
MS. PSAKI: I believe you are wrong, Matt. We’ll get you some more clarification.
QUESTION: You believe I’m wrong? Okay.
MS. PSAKI: We’ll get you some more clarification.
QUESTION: Jen –
MS. PSAKI: Mm-hmm.
QUESTION: – in fact, your longstanding position, going back all the way to 1967, and through George Herbert Walker Bush when he was representative at the United Nations, and on to Andrew Young, and on and on and on, that the settlement, that Jerusalem – East Jerusalem, the West Bank, all territory occupied is contrary to the Fourth Geneva Convention, and any alteration stands contrary to that, that you will not support. That is your position, not to reconcile yourself to the facts on the ground, as has been suggested.
Earlier, Lee said to Psaki “Back in 1978, President Carter said that, quote, ‘We don’t see these settlements as being legal.’ Why can’t you say that they aren’t legal?” Psaki, of course, had no answer.
Ultimately, the only people making the argument that the settlements are legal are the Israelis and a handful of apologists who try to bend and twist international law into an interpretation that fits their needs. Otherwise, there is virtually universal agreement that all settlements beyond the Green Line are illegal. Technically, that is also the US position, since there has never been any official statement from a government representative charged with understanding and interpreting international law to reverse the conclusion reached in 1978. But in reality, the political upheaval that would ensue from re-stating that position makes it impossible to do so.
This was made even more interesting when, on August 12, the Washington Post’s internet edition apparently misquoted Kerry saying that the settlements were illegal, rather than illegitimate. When I saw the original version I almost fell over. Had that occurred, it would have been a major game-changer. Quickly, however, the Post corrected the error. I’m sure it was, indeed, an error, because I cannot imagine Kerry actually saying that.
Yes, I cannot imagine the US’ Secretary of State stating what remains the official legal interpretation as set forth by the State Department’s legal adviser and which, outside the US and Israel, is nearly an absolute consensus view. Interesting, even the most pro-Israel of Presidents, be it Reagan, George W. Bush, Bill Clinton or Barack Obama, has seen the settlements as a serious problem. They would all have liked to see Israel put a halt to them. But when George H.W. Bush, who, during his time as Ambassador to the UN, explicitly stated the settlements were illegal and acted to slow them, he was called anti-Israel. And we can all recall what happened when Obama asked Benjamin Netanyahu to freeze settlements so peace talks could continue (and, no, despite Bibi’s statements, the freeze never really happened — as Lara Friedman of Americans for Peace Now explains here).
These are the results of a schizophrenic policy, where the policy as enacted nearly opposes official statements of it. Good luck to Jen Psaki trying to explain it.
Photo: A new neighbourhood under construction in the West Bank’s Ariel settlement. Credit: Pierre Klochendler/IPS
]]>The suspect graph of a nuclear explosion reportedly provided to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as evidence of Iranian computer modeling of nuclear weapons yields appears to have been adapted from a very similar graph in a scholarly journal article published in January 2009 and available on the internet.
[...]]]>The suspect graph of a nuclear explosion reportedly provided to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as evidence of Iranian computer modeling of nuclear weapons yields appears to have been adapted from a very similar graph in a scholarly journal article published in January 2009 and available on the internet.

Graph published by the scholarly journal Nuclear Engineering and Design, Volume 239, Issue 1, January 2009, Pages 80–86.
The graph, published in a Nov. 27 Associated Press story but immediately found to have a mathematical error of four orders of magnitude, closely resembles a graph accompanying a scholarly article modeling a nuclear explosion. It provides a plausible explanation for the origins of the graph leaked to AP, according to two nuclear physicists following the issue closely.
The graph in the scholarly journal article was well known to the IAEA at the time of its publication, according to a knowledgeable source.
That means that the IAEA should have been able to make the connection between the set of graphs alleged to have been used by Iran to calculate yields from nuclear explosions that the agency obtained in 2011 and the very similar graph available on the internet.
The IAEA did not identify the member countries that provided the intelligence about the alleged Iran studies. However, Israel provided most of the intelligence cited by the IAEA in its 2011 report, and Israeli intelligence has been the source of a number of leaks to the AP reporter in Vienna, George Jahn.

Graph published by the Associated Press on Nov. 27, 2012, reportedly as evidence of Iranian computer modeling of nuclear weapons yields.
The graph accompanying an article in the January 2009 issue of the journal Nuclear Engineering and Design by retired Swiss nuclear engineer Walter Seifritz displayed a curve representing power in a nuclear explosion over fractions of a second that is very close to the one shown in the graph published by AP and attributed by the officials leaking it to an Iranian scientist.
Both graphs depict a nuclear explosion as an asymmetrical bell curve in which the right side of the curve is more elongated than the left side. Although both graphs are too crudely drawn to allow precise measurement, it appears that the difference between the two sides of the curve on the two graphs is very close to the same in both graphs.
The AP graph appears to show a total energy production of 50 kilotonnes taking place over about 0.3 microseconds, whereas the Seifritz graph shows a total of roughly 18 kilotonnes produced over about 0.1 microseconds.
The resemblance is so dramatic that two nuclear specialists who compared the graphs at the request of IPS consider it very plausible that the graph leaked to AP as part of an Iranian secret nuclear weapons research programme may well have been derived from the one in the journal article.
Scott Kemp, an assistant professor of nuclear science and engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), told IPS he suspects the graph leaked to AP was “adapted from the open literature”. He said he believes the authors of that graph “were told they ought to look into the literature and found that paper, copied (the graph) and made their own plot from it.”
Yousaf Butt, a nuclear scientist at the Monterey Institute, who had spotted the enormous error in the graph published by AP, along with his colleague Ferenc Dalnoki-Veress, said in an interview with IPS that a relationship between the two graphs is quite plausible, particularly given the fact they both have similar asymmetries in the power curve.
“Someone may just have taken the Seifritz graph and crudely adapted it to a 50-kilotonne yield instead of the 18 kilotonnes in the paper,” Butt said.
He added that “it’s not even necessary that an actual computer model was even run in the production of the AP graph.”
Apparently anticipating that the Seifriz graph would soon be discovered, the source of the graph given to AP is quoted in a Dec. 1 story as acknowledging that “similar graphs can be found in textbooks, the internet and other public sources.”
Butt said that he doesn’t know whether the AP graph is genuine or not, but that it could well be a forgery.
“If one wanted to plant a forgery,” he wrote, “it would make sense to manufacture something that looked like the output from the many unclassified ‘toy-models’ available on-line or in academic journals, rather than leak something from an actual high-fidelity classified study.”
The Seifritz graph came to the attention of the IAEA secretariat soon after it was published and was referred to the staff specialist on nuclear weapons research, according to a source familiar with the IAEA’s handling of such issues.
The source, who refused to be identified, told IPS the reaction of the official was that the graph represented fairly crude work on basic theory and was therefore not of concern to the agency.
The agency was given the alleged Iranian graph in 2011, and a “senior diplomat” from a different country from the source of the graph said IAEA investigators realised the diagramme was flawed shortly after they received it, according to the Dec. 1 AP story.
The IAEA’s familiarity with the Seifritz graph, two years before it was given graphs that bore a close resemblance to it and which the agency knew contained a huge mathematical error, raise new questions about how the IAEA could have regarded the Israeli intelligence as credible evidence of Iranian work on nuclear weapons.
Yukiya Amano, the director-general of the IAEA, refused to confirm or deny in an appearance at the Council on Foreign Relations in Washington Dec. 6 that the graph published by AP was part of the evidence of Iranian “activities” related to nuclear weapons cited by the agency in its November 2011 report. .
Amano responded to a question on the graph, “I can’t discuss this specific information.”
In its November 2011 report, the IAEA said it had “information” from two member states that Iran had conducted “modeling studies” aimed at determining the “nuclear explosive yield” associated with components of nuclear weapon. It said the “information” had identified “models said to have been used in those studies and the results of these calculations, which the Agency has seen”.
The “senior diplomat” quoted by AP said the IAEA also had a spreadsheet containing the data needed to produce the same yield as shown on the graph – 50 kilotonnes – suggesting that the spreadsheet is closely related to the graph.
Butt observed, however, that the existence of the spreadsheet with data showing the yield related to a 50 kilotonne explosion does not make the graph any more credible, because the spreadsheet could have been created by simply plugging the data used to produce the graph.
Kemp of MIT agreed with Butt’s assessment. “If it’s simply data points plotted in the graph, it means nothing,” he told IPS.
After Butt and Dalnoki-Veress identified the fundamental error in the graph AP had published as evidence of Iranian work on a 50-kilotonne bomb, the Israeli source of the graph and an unidentified “senior diplomat” argued that the error must have been intentionally made by the Iranian scientist who they alleged had produced the graph.
A “senior diplomat” told AP the IAEA believed the scientist had changed the units of energy used by orders of magnitude, because “Nobody would have understood the original….”
That explanation was embraced by David Albright, who has served as unofficial IAEA spokesman in Washington on several occasions. But neither Albright nor the unidentified officials quoted by Jahn offered any explanation as to why an accurate graph would have been more difficult for Iranian officials to understand than one with such a huge mathematical error.
Further undermining the credibility of the explanation, Jahn’s sources suggested that the Iranian scientist whom they suspected of having devised the graph was Dr. Majid Shahriari, the nuclear scientist assassinated by the Israeli intelligence agency Mossad in 2010.
No evidence has been produced to indicate that Shahriari, who had a long record of publications relating to nuclear power plants and basic nuclear physics, had anything to do with nuclear weapons research.
*Gareth Porter, an investigative historian and journalist specialising in U.S. national security policy, received the UK-based Gellhorn Prize for journalism for 2011 for articles on the U.S. war in Afghanistan.
]]>Beginning with a reference to a contentious report by the AP that used an alleged Iranian document provided by an “unnamed country” to suggest “that Iran is working on a bomb,” Mark Hibbs, a senior associate in Carnegie’s Nuclear Policy Program, writes that increasing reliance by the International [...]]]>
Beginning with a reference to a contentious report by the AP that used an alleged Iranian document provided by an “unnamed country” to suggest “that Iran is working on a bomb,” Mark Hibbs, a senior associate in Carnegie’s Nuclear Policy Program, writes that increasing reliance by the International Atomic Energy Association (IAEA) on third-party data can compromise the agency’s political credibility:
The true significance of this document is that it landed in our e-mailboxes in the midst of renewed internal debate about how the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) should determine whether member states are in compliance with their nonproliferation obligations. Beginning two decades ago, the IAEA started relying less on information it gathers during its own field inspections alone and more on information that others provide, most of which is open-source, but some of which is not. This third-party data has become central to the IAEA’s work, and it is about to become even more so. The leak of the graph to the AP underscores that if this data isn’t rigorously vetted and handled carefully, the IAEA’s technical and political credibility will be seriously compromised.
Meanwhile the Guardian reports that the IAEA has attempted to tighten internal security by “narrowing the circle of officials and analysts who deal with the most sensitive material.” The measures apparently include prohibiting any Persian speakers from working in the safeguards department to fulfil the imperative task of analyzing documents about Iran’s nuclear program.
]]>That Associated Press story displaying a graph alleged to be part of an Iranian computer simulation of a nuclear explosion — likely leaked by Israel with the intention of reinforcing the media narrative of covert Iranian work on nuclear weapons – raises serious questions about the International Atomic [...]]]>
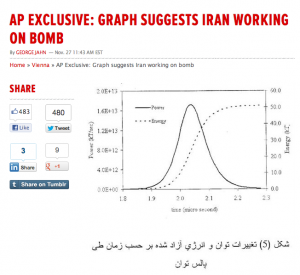 That Associated Press story displaying a graph alleged to be part of an Iranian computer simulation of a nuclear explosion — likely leaked by Israel with the intention of reinforcing the media narrative of covert Iranian work on nuclear weapons – raises serious questions about the International Atomic Energy Association’s (IAEA) claim that it has credible evidence of such modeling work by Iran.
That Associated Press story displaying a graph alleged to be part of an Iranian computer simulation of a nuclear explosion — likely leaked by Israel with the intention of reinforcing the media narrative of covert Iranian work on nuclear weapons – raises serious questions about the International Atomic Energy Association’s (IAEA) claim that it has credible evidence of such modeling work by Iran.
The graph of the relationship between energy and power shown in the AP story has now been revealed to contain absurdly large errors indicating its fraudulence.
Those revelations indicate, in turn, that the IAEA based its publication of detailed allegations of nuclear weapons-related Iranian computer modeling on evidence that should have been rejected as having no credibility.
Former senior IAEA inspector Robert Kelley, who has challenged the accuracy of IAEA reporting on Iran, told Lobe Log in an e-mail that “It’s clear the graph has nothing to do with a nuclear bomb.”
“The pretty, symmetrical bell shaped curve at the bottom is not typical of a nuclear explosion but of some more idealized natural phenomena or mathematical equation,” he said. “Clearly it is a student example of how to perform integrals to which someone has attached some meaningless numbers.”
Nuclear physicists Yousaf Butt and Ferenc Dalnoki-Veress also pointed out that the graph depicted by AP is not only so rudimentary and crude that it could have been done by an undergraduate student, but is based on a fundamental error of mind-numbing proportions.
The graph shown in the AP story plots two curves, one of energy versus time, the other of power output versus time. But Butt and Dalnoki-Veress noted that the two curves are inconsistent. The peak level of power shown in the graph, they said, is nearly a million times too high.
After a quick look at the graph, the head of the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Cal State Sacramento, Dr. Hossein Partovi, observed, “[T]he total energy is more than four orders of magnitude (forty thousand times) smaller than the total integrated power that it must equal!” Essentially, the mismatch between the level of total energy and total power on the graph is “more than four orders of magnitude”, which Partovi explained means that the level of energy is 40,000 times too small in relation to the level of power.
One alert reader of the account of the debunking of the graph at the Mondoweiss blog cited further evidence supporting Kelley’s observation that the graph shown by AP was based on an another graph that had nothing to do with nuclear explosions.
The reader noted that the notation “kT” shown after “energy” on the right hand scale of the graph does not stand for “kilotons” as Jahn suggested, but “Boltzmann constant” (k) multiplied by temperature (T). The unit of tons, on the other hand, is always abbreviated with a lower case “t”, he pointed out, so kilotons would be denoted as “kt”.
The reader also stated that the “kT” product is used in physics as a scaling factor for energy values in molecular-scale systems, such as a microsecond laser pulse.
The evidence thus suggests that someone took a graph related to an entirely different problem and made changes to show a computer simulation of a 50 kiloton explosion. The dotted line on the graph leads the eye directly to the number 50 on the right-hand energy scale, which would lead most viewers to believe that it is the result of modeling a 50 kiloton nuclear explosion.
The graph was obviously not done by a real Iranian scientist — much less someone working in a top secret nuclear weapons research program — but by an amateur trying to simulate a graph that would be viewed, at least by non-specialists, as something a scientist might have drawn.
Although AP reporter George Jahn wrote that officials who provided the diagram did so “only on condition that they and their country not be named”, the country behind the graph is not much of a mystery.
Blogger Richard Silverstein has reported that a “highly-placed Israeli source” told him the diagram “was stolen by the Mossad from an Iranian computer” using one of the various malware programs deployed against Iran.
Whether one chooses to rely on Silverstein’s reporting or not, it is clear that the graph is part of a longer stream of suspicious documents supposedly obtained by Israeli intelligence from inside Iran’s nuclear program and then given to the IAEA over the past few years.
Former IAEA Secretary General Mohammed ElBaradei refers in his memoirs to documents provided by Israel in 2009 “purportedly showing that Iran had continued with nuclear weapons studies until at least 2007.” ElBaradei adds that the Agency’s “technical experts” had “raised numerous questions about the documents’ authenticity”, and suggested that US intelligence “did not buy the “evidence” put forward by Israel” in its 2007 National Intelligence Estimate.
Jahn’s story indicates that this and similar graphs were the basis for the IAEA’s publishing charges by two unnamed states that Iran had done computer modeling that the agency said could only have been about nuclear weapons.
Jahn cites a “senior diplomat who is considered neutral on the issue” as confirming that the graph accompanying his story was one of “a series of Iranian computer-generated models provided to the IAEA by the intelligences services of member nations.”
Those “computer generated models” were discussed in the November 2011 report, which referred to “[i]nformation provided to the Agency by two Member States relating to modelling [sic] studies alleged to have been conducted in 2008 and 2009 by Iran….” The unnamed member states were alleging that the Iranian studies “involved the modelling [sic] of spherical geometries, consisting of components of the core of an HEU nuclear device subjected to shock compression, for their neutronic behaviour at high density, and a determination of the subsequent nuclear explosive yield.”
Nothing in that description of the alleged modeling is documented by the type of graph shown by the AP story.
The IAEA report concludes by saying, “The information also identifies models said to have been used in those studies and the results of these calculations, which the Agency has seen.”
In other words, the only evidence that the IAEA had actually seen was the graphs of the alleged computer modeling, of which the graph shown in the AP story is alleged to be an example. But the fact that data on that graph has been credibly shown to be off by four orders of magnitude suggests that the Israeli claim of Iranian computer modeling of “components of the core of an HEU nuclear device subjected to shock compression” was completely fabricated.
Former IAEA Inspector Kelley also told Lobe Log that “We can only hope that the claim that the IAEA has relied on this crude hoax is false. Otherwise their credibility has been shattered.”
- Gareth Porter, an investigative historian and journalist specialising in U.S. national security policy, received the UK-based Gellhorn Prize for journalism for 2011 for articles on the U.S. war in Afghanistan.
]]>News and views relevant to US foreign policy for Sept. 11
“New intelligence on Iran nuke work”: The Associated Press reports that the International Atomic Energy Association (IAEA) has received intelligence from the United States, Israel and at least two other Western countries showing that Iran has “moved further toward the [...]]]>
News and views relevant to US foreign policy for Sept. 11
“New intelligence on Iran nuke work”: The Associated Press reports that the International Atomic Energy Association (IAEA) has received intelligence from the United States, Israel and at least two other Western countries showing that Iran has “moved further toward the ability to build a nuclear weapon”.
“Nuclear Mullahs, Continued”: Bill Keller responds to reader questions about his column that argues against a preemptive war on Iran’s nuclear program:
Q: You say that after an attack, Iran would have strong motivation to rebuild its nuclear facilities, this time faster and deeper underground. But the Israeli attacks on nuclear reactors at Osirak, Iraq, in 1981 and Al-Kibar, Syria, in 2007 were quite successful in keeping those countries non-nuclear.
A: First, Iran’s multiple facilities, well fortified (especially the centrifuges buried deep in the rock at Fordow, near Qom) present a much tougher target than the reactors in Iraq and Syria. Second, and more important, the Osirak attack, far from stopping Iraq’s nuclear ambitions, hastened them. After Israel bombed the reactor, Saddam Hussein launched an accelerated, covert program to manufacture nuclear weapons. When the First Gulf War ended his ambitions in 1991, that program was well underway. Experts disagree how far Saddam was from having a weapon (estimates ranged from six months to three years) but the Israeli strike in Iraq accomplished what many fear a strike in Iran would accomplish: it gave the nuclear weapons program new life. Third, Israel’s attack on the (suspected) nuclear reactor in Syria was kept secret for a long time, so that Syria did not feel obliged to undertake reprisals against the superior Israeli military. It’s inconceivable that Iran and the world would not know whom to hold responsible for an attack on its facilities, and Iranian leaders would have to lash back, if only to save face. Fourth, what ended Iraq’s nuclear ambitions was a full-scale military invasion in 1991 – followed by an (unnecessary and botched) occupation in 2003. No doubt, occupying Iran would solve the problem of its nuclear program. Anybody up for that?
“Former CIA Chief: Obama’s War on Terror Same as Bush’s, But With More Killing”: Wired reports that Michael Hayden has offered words of praise for President Obama’s counterterrorism agenda after initially criticizing the POTUS’s early comments against programs Hayden helped formulate under George W. Bush, such as the use of “enhanced interrogation” techniques and domestic wiretapping:
“But let me repeat my hypothesis: Despite the frequent drama at the political level, America and Americans have found a comfortable center line in what it is they want their government to do and what it is they accept their government doing. It is that practical consensus that has fostered such powerful continuity between two vastly different presidents, George W. Bush and Barack Obama, when it comes, when it comes to this conflict,” Hayden said Friday while speaking at the University of Michigan.
….
But Hayden, in a nearly 80-minute lecture posted on C-Span, said Obama came to embrace Bush’s positions. Both Bush and Obama said the country was at war. The enemy was al-Qaida. The war was global in nature. And the United States would have to take the fight to the enemy, wherever it may be, he said.
“The Deafness Before the Storm”: Vanity Fair’s Kurt Eichenwald delivers a bombshell report in the New York Times on the 11th anniversary of the September 11th attacks arguing that the Bush Administration had received multiple warnings prior to August 2001 from the CIA about Osama bin Laden’s intent and capabilities to attack US targets. According to Eichenwald, the White House dismissed the agency’s sources as agents “in” on a maskirovka directed by both Saddam Hussein and Bin Laden:
But some in the administration considered the warning to be just bluster. An intelligence official and a member of the Bush administration both told me in interviews that the neoconservative leaders who had recently assumed power at the Pentagon were warning the White House that the C.I.A. had been fooled; according to this theory, Bin Laden was merely pretending to be planning an attack to distract the administration from Saddam Hussein, whom the neoconservatives saw as a greater threat. Intelligence officials, these sources said, protested that the idea of Bin Laden, an Islamic fundamentalist, conspiring with Mr. Hussein, an Iraqi secularist, was ridiculous, but the neoconservatives’ suspicions were nevertheless carrying the day.
…
“The U.S. is not the target of a disinformation campaign by Usama Bin Laden,” the daily brief of June 29 read, using the government’s transliteration of Bin Laden’s first name. Going on for more than a page, the document recited much of the evidence, including an interview that month with a Middle Eastern journalist in which Bin Laden aides warned of a coming attack, as well as competitive pressures that the terrorist leader was feeling, given the number of Islamists being recruited for the separatist Russian region of Chechnya.
“Iraqi Spokesman: Al-Hashemi Is ‘Connected Directly’ To Terrorists”: Al-Monitor interviews Iraqi Government spokesman Ali Aldabbagh on the in absentia death sentence against the country’s Vice President Tareq al-Hashemi and the ongoing oil revenues dispute between Baghdad and the Kurdish north. The wide-ranging interview also touched on Iran-Iraq relations, including an oblique reference to reports that the US is pressuring Iraq to do more to undermine Iranian assistance to the Syrian regime:
]]>Al-Monitor: The US has asked Iraq to inspect Iranian planes flying to Syria to prevent arms and material from reaching the Syrian government. Is this a reasonable request? Will the government of Iraq consider doing so?
Aldabbagh: The US never asked [us] to do so, but it is our commitment not to allow the flow of arms or fighters to both parties in Syria. We had informed the Iranians that Iraq will never [allow the] use [of] its airspace to do so. Iraq is ready to be part of international efforts to stop any arms to Syria. We protect our borders from [allowing the flow of] any equipment or fighters to or from Syria. Iraq is totally committed to these principles. The US had satisfied with Iraq measures toward Syria.
Al-Monitor: How do you assess Iraq-Iran relations? Does your relationship with Iran complicate your ties with the United States, as in the case of Syria?
Aldabbagh: Never, on the contrary. The US understands that Iraq should maintain good relations with Iran, as we [have] been mediating between them. Even with the Syrians, we differ on some issues with US, while we agree and have the same ideas on some Syrian aspects. Such differences never affect our relations — the US respects Iraq sovergnity [sic] in building relations with others.
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) report made public Thursday reveals that Iran has actually reduced the amount of 20-percent enriched uranium available for any possible “breakout” to weapons grade enrichment over the last three months rather than increasing it.
Contrary to the impression conveyed by most news media coverage, [...]]]>
 The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) report made public Thursday reveals that Iran has actually reduced the amount of 20-percent enriched uranium available for any possible “breakout” to weapons grade enrichment over the last three months rather than increasing it.
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) report made public Thursday reveals that Iran has actually reduced the amount of 20-percent enriched uranium available for any possible “breakout” to weapons grade enrichment over the last three months rather than increasing it.
Contrary to the impression conveyed by most news media coverage, the report provides new evidence that Iran’s enrichment strategy is aimed at enhancing its bargaining position in negotiations with the United States rather than amassing such a breakout capability.
The reduction in the amount of 20-percent enriched uranium in the Iranian stockpile that could be used to enrich to weapons grade is the result of a major acceleration in the fabrication of fuel plates for the Tehran Research Reactor, which needs 20-percent enriched uranium to produce medical isotopes.
That higher level enriched uranium has been the main focus of U.S. diplomatic demands on Iran ever since 2009, on the ground that it represents the greatest threat of an Iranian move to obtain a nuclear weapon capability.
When 20-percent uranium is used to make fuel plates, however, it is very difficult to convert it back to a form that can enriched to weapons grade levels.
When data in the Aug. 30 IAEA report on the “inventory” of 20-percent enriched uranium is collated with comparable data in the May 25 IAEA report, it shows that Iran is further from having a breakout capability than it was three months earlier.
The data in the two reports indicate that Iran increased the total production of 20-percent enriched uranium from 143 kg in May 2012 to 189.4 kg in mid-August. But the total stockpile of 20-percent enriched uranium that could be more easily enriched to weapons grade – and which has been the focus of U.S. diplomatic demands on Iran ever since 2009 – fell from 101 kg to 91.4 kg during the quarter.
The reduction in the stockpile available for weapons grade enrichment was the result of the conversion of 53.3 kg of 20-percent enriched uranium into fuel plates – compared with only 43 kg in the previous five months.
Iran was thus creating fuel plates for its medical reactor faster than it was enriching uranium to a 20-percent level.
But although that reduction of the stockpile of enriched uranium of greatest concern to the United States was the real significance of the new report, it was not conveyed by the headlines and leads in news media coverage. Those stories focused instead on the fact that production of 20-percent enriched uranium had increased, and that the number of centrifuges at the underground facility at Fordow had doubled.
“Nobody has put out the story that their stockpile is shrinking,” said Joe Cirincione, president of the Ploughshares Fund and a leading independent specialist on nuclear weapons policy, in an interview with IPS.
David Sanger and William Broad of the New York Times asserted in an Aug. 30 story that Iran had “doubled the number of centrifuges installed” at Fordow and had “cleansed” the site where the IAEA believed there had been nuclear weapons development work. The story made no reference to fuel plates or the effective stockpile of 20-percent enriched uranium.
A second story by Sanger and Jodi Rudoren on the same day, datelined Jerusalem, was even more alarmist and inaccurate. It declared that the nuclear programme was “speeding up” and that Iran was “close to crossing what Israel has said is its red line: the capacity to produce nuclear weapons in a location invulnerable to Israeli attack.”
Reuters and AP stories also focused on the doubling of centrifuges as the main message in the IAEA report, and Reuters also said Iran “seems to be struggling to develop more efficient nuclear technology that would shorten the time it would need for any atom bomb bid”.
The Washington Post headline said that Iran was “speeding up” uranium enrichment, and the lead said Iran had “substantially increased the production of a more enriched form of uranium in recent months”. But in the second paragraph, it added, somewhat cryptically, that Iran “appeared to take steps that would make it harder to use its uranium stockpile to make nuclear bombs”.
Only a few paragraphs later was it made clear that the lead was misleading, because the IAEA had found that Iran had “converted much of the new material to metal form for use in a nuclear research reactor.” It even quoted an unnamed Barack Obama administration officials said it could not be “further enriched to weapons-grade material….”
In fact the IAEA data showed that it had converted all of the uranium enriched to 20 percent during the quarter to fuel plates, and had converted some of the production from previous quarters as well.
The media reports of a doubling of the number of centrifuges at the underground facility at Fordow were also misleading. When the information is examined more carefully, it actually provides further evidence that Iran is not striving to amass the higher level uranium needed for a breakout capability but is maneuvering to prepare for a later negotiated settlement.
Although the IAEA report shows that the number of centrifuges in place in Fordow has increased from 696 to 2,140 over the past six months, it also makes it clear that the number of centrifuges actually operating has not changed during that period.
The reason for that striking anomaly in the deployment at Fordow does not appear to be technical problems with the centrifuges. The 1,444 centrifuges that are not operating were never even connected by pipes, as the Institute for Science and International Security (ISIS) observed in its Aug. 30 commentary on the report.
The noncommittal character of the deployment of centrifuges at Fordow suggests that Iran has not decided whether those 1,444 centrifuges are to be committed to 3.5-percent enrichment or to 20-percent enrichment.
The Obama administration appears to understand that this uncertainty about the purpose of the centrifuges is aimed at strengthening Iran’s diplomatic hand in future negotiations. “They have been very strategic about it,” a senior U.S. official told the New York Times just before the report was made public. “They are creating tremendous capacity, but they are not using it.”
The official added, “That gives them leverage, but they think it also stops short of creating the pretext for an attack.”
Cirincione agrees with that senior official’s analysis. “The Iranians are excellent chess players. They are moving their pieces very carefully,” he said. “They are continuing to enhance the value of their bargaining chips.”
The implication of the IAEA report, Cirincione believes, is that Iran is still maneuvering to position itself for a more advantageous agreement in future negotiations. “If you were the Iranians, why would you negotiate right now?” asked Cirincione. “You would want to wait for a better deal.”
In previous rounds of negotiations with Iran in 2012, the United States demanded an end to all 20-percent enrichment and even the closure of the Fordow facility but offered no alleviation of the harsh financial sanctions now being imposed on Iran.
*Gareth Porter, an investigative historian and journalist specialising in U.S. national security policy, received the UK-based Gellhorn Prize for journalism for 2011 for articles on the U.S. war in Afghanistan.
]]>The Washington Post reports, via AP‘s Nasser Karimi:
TEHRAN, Iran — Iran’s president on Sunday endorsed the idea of new talks with the international community over his country’s nuclear program, while warning that negotiations would fail if the West does not clearly come out against Israel’s suspected nuclear arsenal.
[...] In Washington, State Department spokesman P.J. Crowley said it was up to Iran to set a date.
“Iran says it is ready to talk,” Crowley said. “Now it needs to commit to a date. Iran knows the phone number. We are awaiting Iran’s formal response.”
The blog of neocon pundit David Frum excerpted a CNN report under the headline “Iran won’t budge on nukes.” Part of the FrumForum’s excerpt read:
Ahmadinejad said that Iran is ready to hold talks, but warned that his country won’t yield any of its international rights to peaceful nuclear energy development, according to the reports.
As a non-nuclear signatory to the Non-Proliferation Treaty, Iran is entitled to domestic nuclear enrichment and energy.
]]>