by Mohammad Ali Shabani
Most headlines on Iran’s launch of uranium-related sites on April 9th — its National Day of Nuclear Technology — linked it to the diplomatic deadlock in Kazakhstan. Tehran was regarded as pursuing escalation, perhaps in frustration with the situation. But was this really the case?
To answer [...]]]>
by Mohammad Ali Shabani
Most headlines on Iran’s launch of uranium-related sites on April 9th — its National Day of Nuclear Technology — linked it to the diplomatic deadlock in Kazakhstan. Tehran was regarded as pursuing escalation, perhaps in frustration with the situation. But was this really the case?
To answer this question, one needs to consider what Iran has previously done on this anniversary, the significance of the Islamic Republic’s new sites and its escalatory options.
The government of Mahmoud Ahmadinejad launched the National Day of Nuclear Technology in 2006. This was part of the push for a harder stance on the nuclear issue after the breakdown of talks with European powers, during which Iran voluntarily agreed to freeze enrichment-related activities.
As part of the first festivities in 2006, Iran announced that it would — in defiance of a UN Security Council warning — enrich uranium on an industrial scale. A total of 164 centrifuges at Natanz started to spin, churning out uranium enriched below 5%.
During the past seven years, the Islamic Republic has largely used its Nuclear Technology day to unveil new achievements, both for domestic and foreign audiences. As the occasion has repeatedly coincided with nuclear diplomatic developments, it has often been used to signal Iranian attitudes.
In 2007, Iran used the anniversary to announce that it had crossed the Western red line of 3,000 operational centrifuges. Back then, David Albright, head of the Institute for Science and International Security, asserted that “Ahmadinejad is trying to demonstrate facts on the ground and negotiate from a stronger position.”
The year after, Iran used the occasion to announce that it would begin installing 6,000 centrifuges and alluded to the testing of a new generation of centrifuges. Then in 2009, Ahmadinejad inaugurated the country’s first Fuel Manufacturing Plant in the central city of Isfahan. The Islamic Republic also said its number of centrifuges had increased to 7,000.
In 2010, as the UN Security Council convened to discuss fresh sanctions, Iran unveiled new “third-generation” centrifuges, said to have separation power six times that of first-generation centrifuges. Iran also declared that “considerable” uranium reserves had been found in Yazd province. That year, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) reported that Iran had 8,610 centrifuges installed, of which 3,772 were operating.
In 2011, after dialogue over Iran’s production of 19.75%-enriched uranium had broken down, it opted to simply praise past achievements. Apart from this, it announced the resumption of fuel reloading at the Bushehr power plant. And last year, after the escalation of Western sanctions, Iran announced that local scientists had produced fuel for the Tehran Research Reactor containing uranium enriched to 19.75%.
This year, Iran announced on the anniversary that it had opened two uranium mines and a yellowcake processing plant named after an assassinated nuclear scientist. What’s the significance of these sites?
In terms of capacity, the yellowcake facility is insignificant. Its stated output of 60 tons a year is less than one third of what’s needed to fuel the Bushehr atomic power plant. Moreover, the discovery of the uranium deposits, which are now being extracted, was first announced years ago. Along the same line, the head of the Atomic Energy Organization of Iran had announced in February 2012 that the mines would be operational in about a year, that is, right around this time.
The most important fact to keep in mind, however, is that Iran has for a long time been projected to be close to exhausting its limited supply of yellowcake. Without feedstock to inject into its centrifuges at Natanz (in gaseous form), Iran’s uranium enrichment — at least to 3.5% — would grind to a halt.
In short, the new sites unveiled on April 9th are designed to ensure the status quo.
There are other factors which also signify Iran’s pursuit of the status quo rather than escalation. For example, considering the many powerful escalatory options in its possession — wider use of new-generation centrifuges, expansion of operations at Fordow, increases in enrichment levels and construction of long-promised, new enrichment sites — the announcements this year seem geared towards signaling restraint to a foreign audience without appearing empty-handed in front of a domestic public facing unprecedented sanctions.
Indeed, the Islamic Republic has little interest in escalating the situation at this point, especially as it faces its first presidential election since the disputed vote in 2009. The idea that Iran prefers to quietly kick the can down the road until it gets its house in order was also recently expressed by former top US non-proliferation official, Gary Samore.
Meanwhile, it could also be argued that the United States – or at least its Congress — is pursuing escalation.
Following the deadlock in Kazakhstan, US lawmakers have been pushing for fresh sanctions that would constitute something akin to an Oil-for-Food Program 2.0. The draft Senate bill states that the proposed embargo won’t be lifted until Iran releases political prisoners, respects the rights of women and minorities and moves toward “a free and democratically elected government.”
Moreover, last week, the National Council of Resistance of Iran (NCRI) — a front for the until recently terror-listed Mujahideen-e-Khalq Organization (MEK) — opened an official office one block away from the White House. The group was put on the State Department’s terror list by the Clinton Administration. In the past, the MEK was behind a series of killings and bombings in Iran — one of which led to the permanent paralysis of Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei’s right arm. The MEK, which sided with Saddam Hussein during the Iran-Iraq war, was also reportedly involved in the assassinations of Iranian nuclear scientists. Among these men is Darioush Rezaeinejad, whom the new yellowcake facility is named after.
The signal that’s being sent to decision-makers in Tehran, regardless of whether the Obama Administration approves of the MEK’s new office, is that the sanctions have little to do with their nuclear program. Combined with the wording of the proposed embargo, the situation ominously fits into Ayatollah Khamenei’s narrative that even a nuclear deal won’t be enough to roll back American pressure.
All things considered, one should be careful about linking Iran’s latest announcements about its nuclear achievements to the continued deadlock in talks with the 6 world powers, or viewing Iran’s actions as deserving of the escalation pursued by at least one of these powers.
It is becoming ever clearer that both Iran and the United States need to get their houses in order before they can move in the right direction. More than ever, cool heads need to prevail.
]]>By Robert Hunter
Former Secretary of State Henry Kissinger has written at length (Washington Post, November 18th – Job One Abroad: Iran) on Iran’s progress toward a military nuclear capability and, in brief, on what to do about it. His suggestion is for “a creative diplomacy, allied to [...]]]>
By Robert Hunter
![]()
![]()
 Former Secretary of State Henry Kissinger has written at length (Washington Post, November 18th – Job One Abroad: Iran) on Iran’s progress toward a military nuclear capability and, in brief, on what to do about it. His suggestion is for “a creative diplomacy, allied to a determined strategy.” But precisely what?
Former Secretary of State Henry Kissinger has written at length (Washington Post, November 18th – Job One Abroad: Iran) on Iran’s progress toward a military nuclear capability and, in brief, on what to do about it. His suggestion is for “a creative diplomacy, allied to a determined strategy.” But precisely what?
Historic parallels are always imprecise. But 40 years ago, the United States was in confrontation with the Soviet Union, in the midst of history’s most complex and potentially deadly arms race.
Yet the US government, matched by the Soviet Union, found ways to prevent a collective falling-off of the cliff of nuclear cataclysm.
1972 was notable for several developments, including the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty, which provides no precedent in today’s standoff with Iran. But a less-remembered diplomatic agreement does: the Incidents at Sea Agreement, whereby the two superpowers agreed on means to prevent a possible collision or other confrontation at sea from escalating to something far worse. Today, the parallel is in the Persian Gulf and more particularly, the Strait of Hormuz. All countries, including the US and Iran, have a vital interest in the free flow of commerce, especially oil commerce. All have an interest in reducing risks of unintended escalation. The risks are exacerbated by the heavy presence of US warships in the Gulf, although the plethora of US military power elsewhere in the region is surely sufficient to show resolve both to Teheran and to Gulf Arab states. The reported Iranian effort to shoot down a US drone last month could have escalated, had steady US nerves not prevailed.
As far as one knows, nothing akin to the Incidents at Sea Agreement has been proposed to Teheran, nor has its complementary interest of stability in Afghanistan, or its cooperative role in countering piracy in the Arabian Sea, been formally embraced.
More broadly, by 1972 the US was fully committed to direct, bilateral talks with Moscow, which it still abjures, today, with Teheran, and has done for decades. Further, at the beginning of 1973, NATO and the Warsaw Pact began talks on Mutual and Balanced Force Reductions (MBFR), which recognized the risks of potential conventional force instabilities in a heavily-armed region — a good parallel with the vast overarming of all parties in the narrow confines, short-distances, and high performance weapons of the Persian Gulf region. That year the Conference on Security and Co-operation in Europe (CSCE) was also convened, resulting two years later in the Helsinki Final Act. Arguably, this agreement made a significant contribution to the eventual hollowing out of the Soviet empires (especially in Eastern Europe) and an end to the Cold War.
Collectively, this diplomacy became known as detente, one of the great successes of US diplomacy in the last half century.
All these efforts were premised on growing awareness, at a time of mutual hostility and risks of war that neither side could hope to escape unscathed, that each had to understand the other’s fears and take a major measure of responsibility for the other’s security. That was the essence of mutual deterrence (Mutual Assured Destruction). Obviously, even a nuclear-weapons-armed Iran would be no match for either the United States or Israel, each with its nuclear arsenal, but there would still be a form of mutual deterrence: in the sense that even a single Iranian nuclear weapon could threaten Israel’s very existence. Hence, pledges by both US presidential candidates to do whatever is needed to keep Iran from crossing a so-far imprecise “red line.”
Yet the United State has never been ready clearly to say that, even if Iran were to do everything that we want of it, we will recognize its legitimate security interests, much less offer it guarantees against attack, as the last Bush administration did with North Korea. Henry Kissinger sees that recognition not as something to be declared up front, as in the Cold War, but only after Iran “accepts enforceable verification.” Elementary strategy analysis and a vast history of statecraft argue that that course cannot succeed.
Kissinger is surely right that “Iran [needs to show] willingness to conduct itself as a nation-state, rather than a revolutionary religious cause.” And maybe Teheran would not respond positively, whatever we do. But in trying to move Iran in that direction and toward ending nuclear risks in the Middle East, there is clear precedent from the Cold War: intelligent US diplomacy, then crafted and led in major part by the National Security Advisor and later Secretary of State, Henry A. Kissinger.
- Robert Hunter, former US ambassador to NATO, was director of Middle East Affairs on the NSC Staff in the Carter Administration and in 2011-12 was Director of Transatlantic Security Studies at the National Defense University.
]]>The Truman National Security Project has created an interactive version of a war game with Iran. The goal is to highlight the costs of using the military option — financially massive and downright bad for US allies and forces in the region — on the Islamic Republic.
The game [...]]]>
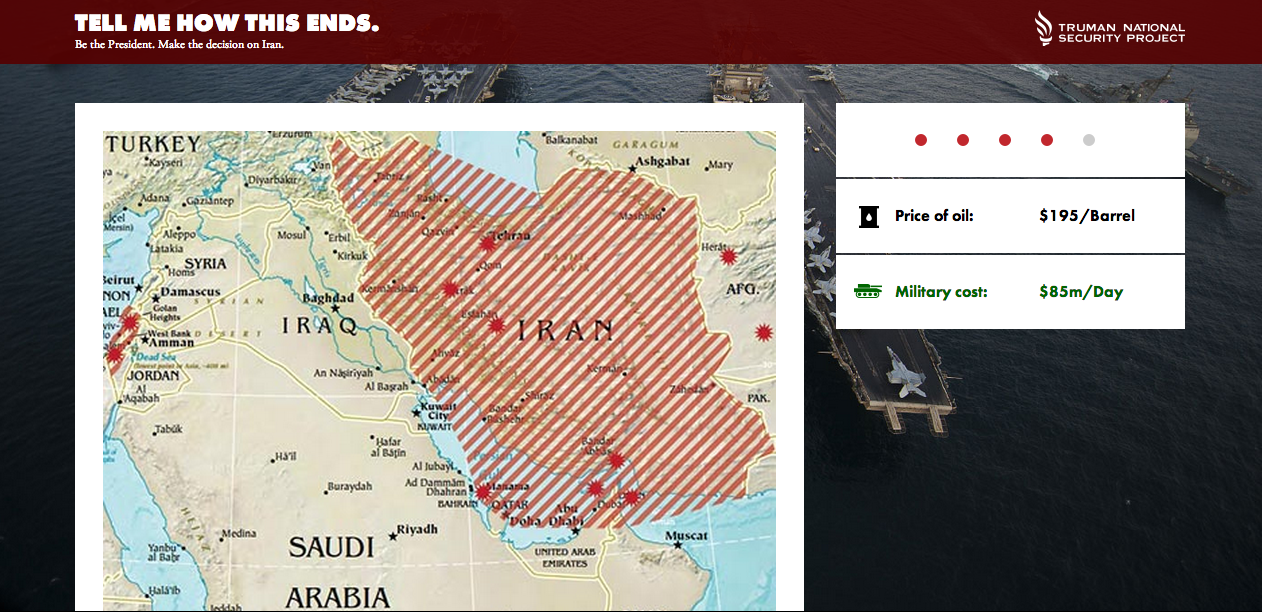 The Truman National Security Project has created an interactive version of a war game with Iran. The goal is to highlight the costs of using the military option — financially massive and downright bad for US allies and forces in the region — on the Islamic Republic.
The Truman National Security Project has created an interactive version of a war game with Iran. The goal is to highlight the costs of using the military option — financially massive and downright bad for US allies and forces in the region — on the Islamic Republic.
The game was developed in consultation with senior former defense department officials and military experts. Users are put in the shoes of the President who is given various modes of deployment for attacking Iran after it crosses his stated red line — acquisition of a nuclear weapon. Players are faced with quickly rising oil and military costs from the get-go, as well as retaliatory attacks against US forces and allies in the region. In sum, once the war has begun, it’s impossible to escape unscathed as harsh force will result in harsh responses from Iran and its proxies while de-escalation attempts will further endanger US interests and forces.
The game is informative and frightening, to say the least, and indicative of why the highest echelons of the Israeli and US defence establishments are hardly gung-ho about going to war with Iran, especially when striking its nuclear facilities will likely intensify Iran’s drive to go nuclear as former Secretary of Defense Robert Gates has argued, and only set back its program by 3-5 years at best
The website was launched on Friday and an accompanying television ad featuring US Army veteran Justin Ford will begin airing tonight during the national security presidential debate.
]]>
After a short and half-hearted attempt, the Obama administration, willingly or otherwise, fell into the trap of [...]]]>
]]>After a short and half-hearted attempt, the Obama administration, willingly or otherwise, fell into the trap of effectively continuing the Bush administration’s one-track policy of ratcheting up pressure in the hope that the Iranians will finally cry uncle. Meanwhile, hard-line Israeli influence on domestic US political dynamics prevents Obama from making do with existing draconian sanctions on Iran that more or less constitute economic warfare. Nothing he does is deemed sufficient; there is a consistent requirement for yet more measures to squeeze Iran yet further, and cease uranium enrichment that brings it closer to the status of a real or virtual nuclear state.
The problem with this approach is that the current Iranian leadership perceives itself as left with few options apart from responding to belligerent policies with belligerence of its own. It believes the Obama administration, despite protestations to the contrary, is like its predecessor: more interested in regime change and destabilization than resolving the nuclear issue. Hence, in its response, the Iranian leadership has made a calculated decision to demonstrate it will not be a passive recipient of decisions made by others. It has thus highlighted the costs of escalating sanctions, whether through threats to obstruct or shut down oil traffic through the Strait of Hormuz; permitting protestors to attack the British Embassy; or threatening to halt oil exports to European states before European sanctions against Iran’s Central Bank come into effect in July.
This escalating sanctions regime and threat scenario naturally increase the prospect of an accidental conflagration in the Persian Gulf, where both Iran and the US have a substantial military presence and lack sufficient means of communication. In short, the potential for this presumably controlled game of brinksmanship to spin out of control will continue to increase if the current round of negotiations fails to produce results.