by Jim Lobe
Eli has a new blog post on The Nation’s website today that provides additional details about the curious — one is tempted to say incestuous — relationship between the staff of United Against Nuclear Iran (UANI) and the corporate interests of billionaire gold and silver investor, Thomas Kaplan. [...]]]>
by Jim Lobe
Eli has a new blog post on The Nation’s website today that provides additional details about the curious — one is tempted to say incestuous — relationship between the staff of United Against Nuclear Iran (UANI) and the corporate interests of billionaire gold and silver investor, Thomas Kaplan. It also provides more details about the relationship between UANI and Harvard’s Belfer Center, a major beneficiary of Kaplan’s largesse, which hired UANI’s president, Gary Samore, shortly after he stepped down as a top proliferation adviser to Obama in 2012 (some prominent faculty members also serve on the group’s advisory board). We excerpted Eli’s original Salon piece on UANI’s ties to Kaplan last Friday.
Eli’s latest is based on a recent filing by the plaintiff, Greek shipowner Victor Restis, in his pending defamation case against UANI. It adds new layers of intrigue to the alleged connections between UANI and Kaplan:
[Kaplan] got his start with help from the family of Leon Recanati, a Greek-Israeli entrepreneur whose family owns and still operates Overseas Shipholding Group (“OSG”), a rival shipping company to Enterprises Shipping and Trading. See Exs. 4, 5. OSG operates oil tankers that compete directly with Mr. Restis’ tanker company, Golden Energy Maritime Corp., whose initial public offering had to be abandoned in 2013 when Defendants launched their defamation campaign that is at the heart of this litigation. See Am. Compl. ¶ 97. OSG would stand to profit if Mr. Restis and his companies were no longer able to operate. Kaplan married Leon Recanati’s daughter Dafna Recanati and was introduced to Israeli investor Avi Tiomkin, by Dafna Recanati’s mother.
If this allegation is true — that Kaplan and/or the Recanati family stood to gain a competitive advantage by publicly charging (through UANI) that Restis and his companies were violating sanctions against Iran — then UANI’s failure to publicly disclose any and all of its ties to Kaplan would obviously constitute a serious ethical breach.
(This is not the only example of billionaire financiers allegedly trying to benefit from Iranophobia. As Charles Davis wrote for IPS a year ago, when the fight between Argentina and Paul Singer and other hold-out, or “vulture” bondholders of the country’s debt was getting relatively little media notice, Singer and his fellow-holdouts founded the American Task Force Argentina (ATFA), which has led a lavishly funded public relations and lobbying campaign against the Kirchner government, including a host of full-page ads in national and Capitol Hill newspapers, at least two of which assailed Argentina’s ties to Iran and suggested that Kirchner was engaged in a cover-up of Tehran’s alleged — and highly doubtful — role in the 1994 bombing of the Jewish community center in Buenos Aires. One even showed a photo of Kirchner alongside then-President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad with the headline, “A Pact with the Devil?” Singer, who has given millions of dollars to the Likudist Foundation for Defense of Democracies (FDD), stands to make tens of million dollars of dollars in profit if he and his other hedge-fund holdouts prevail in the case.)
In addition to the connections between Kaplan and UANI, which Eli had previously documented in his Salon article, the plaintiff’s filing alleges that UANI operates out of offices at Rockefeller Center. Those offices are provided rent-free by Continental Properties, whose managing director, Mark Fisch, co-funds an NYU fellowship with Kaplan, and whose staff member, Kim Hillman, has served as an UANI director. The filing also notes that UANI’s CEO, Mark Wallace, serves not only as CEO of Kaplan’s Tigris Financial Group as Eli reported last week, but also as an officer and/or director of at least five other Kaplan enterprises, as well. It concludes:
Wallace has not drawn a salary from UANI since 2009, so Wallace appears to be getting his financial benefit indirectly through UANI supporter Kaplan.
Read the rest of Eli’s piece here.
]]>by Francois Nicoulaud
“No deal is better than bad deal:” that’s the mantra that has been heard ad nauseam in the recent past and presented as self-evident of U.S. toughness in the negotiations over Iran’s nuclear program.
But is it really so? Of course, everybody knows what “no deal” means. It is [...]]]>
by Francois Nicoulaud
“No deal is better than bad deal:” that’s the mantra that has been heard ad nauseam in the recent past and presented as self-evident of U.S. toughness in the negotiations over Iran’s nuclear program.
But is it really so? Of course, everybody knows what “no deal” means. It is more difficult to discern at what point a deal becomes bad, rather than good, or even average. But plenty of experts are ready to help. A bad deal, they tell us, is a deal which would allow the Iranians to produce the material necessary for a bomb in less than six months. A bad deal is a deal which would not clarify once and for all what kind of research the Iranians have been pursuing in the past for manufacturing a nuclear explosive device. A bad deal is a deal which would allow the Iranians to pursue their ballistic missile program. And so on… One ends up understanding that any deal less than perfect would amount to an unacceptably bad deal.
But such an approach goes against any diplomatic process in which compromise and give and take are key notions. It leads to the conclusion that a perfect deal is a deal which does not have to be negotiated, a deal in which the winner takes all. And indeed, there are people who believe that non-proliferation is too important a question to be submitted to any kind of compromise. It deserves only perfect deals.
History, though, does not confirm this approach. The mother of all non-proliferation agreements, the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), concluded in 1968, was in each and all its articles one big compromise. A few countries were allowed to develop nuclear arsenals, others not. The countries that agreed to forsake any military nuclear ambitions were allowed to bring their nuclear capabilities up to the thin red line beyond which could start the manufacturing of an explosive nuclear device. Nobody was happy at the result when the Treaty was signed and nobody is satisfied today by the state of affairs that has developed since.
Thus, the NPT was a deeply imperfect agreement, and indeed, a kind of bad deal. But would a “no deal” have been better? Obviously not. In a different field, the strategic arms limitation agreements concluded during and after the Cold War between the US and the USSR, later on Russia, and signed on the US side by Presidents Nixon, Carter, Reagan, George H.W. Bush, Obama… were certainly deeply imperfect. But, again, would “no deals” have been better?
Considering the Iranian negotiation, one could risk being provocative by saying that almost any deal (at least in the ambit of the current negotiation) could be better than no deal at all. No deal means the unchecked development of the Iranian program, the continuing increase of its enrichment capacities and stock of enriched uranium, the completion of a reactor of the plutonium-production type, and eventually the resumption of active research on engineering a nuclear device. By way of consequence, it would mean a growing tension between the international community and the Islamic Republic, possibly culminating in strikes on its nuclear facilities and in armed confrontation.
Compared to such a prospect, a far less-than-perfect agreement could appear indeed as highly desirable. Let us remember that international relations are nurtured by iterative and evolutionary processes. “Solve-all”, perfectly designed agreements, the epitome of which could well have been the Treaty of Versailles, seldom produce brilliant and lasting results. What is critical is to grab at the right moment the maximum of what is within reach. The art of diplomacy lies precisely in the ability to first discern, and then to join and knit together the extremes of what can be willingly accepted by the conflicting parties. It incorporates also the humility of leaving to others the task of solving at a later stage questions not yet fully addressed or wholly answered, in the knowledge that new circumstances created by an agreement will create new possibilities for progress. It keeps in mind that even an imperfect agreement, if faithfully implemented by the parties, can be a kind of confidence-building machine, opening the way to further advances. This is precisely what happened with the November 24 Joint Plan of Action between the P5+1 and Iran: that accord was transitory and therefore essentially imperfect, but it created the proper atmosphere for a more ambitious step forward.
Given the current state of the negotiations, how can these general considerations be translated into concrete terms? Let us limit ourselves to the most difficult point; that is, the acceptable level of Iranian enrichment activities. Here, the obvious line of compromise turns around capping them for a few years the present level of employed enrichment capacity – expressed in Separation Work Units (SWU) in order neutralize the consequences of the possible introduction of more efficient centrifuges. The figure to be retained would then be between 8,000 and 10,000 SWU per year.
For this, the Iranians have to admit that they do not need to develop an enrichment capacity on an industrial scale (about 50,000 SWU per year and over) as long as do not break ground on the main structures of their future nuclear power plants. And they should take advantage of this interval to develop more productive and more secure centrifuges than the primitive, outdated model that forms the bulk of their present stock of working centrifuges. They also need to progress significantly in the technology of nuclear-fuel manufacturing in order to be ready in due time if they want to meet at least partially the needs of their future nuclear power plants.
On the other side, the West should consider the enormous political difficulty the Iranian government would face if it had to dismantle even part of the nation’s hard-won enrichment capacity. It is true that accepting the preservation of this capacity at its present level would open the theoretical risk of the Iranians quickly acquiring significant quantities of highly enriched uranium, thus opening the way to the bomb. But considering the self-destructive consequences of such a blatant breach of agreement, the risk is very limited indeed, and by all means much more limited than the risks raised by the absence of any deal. Is this risk really unmanageable for the coalition of the world’s most powerful countries, given the sophistication of their diplomatic, intelligence, and contingency-planning capacities? Of course, such a compromise could be easily depicted with equal vehemence as a bad deal on both sides. And that is why it is probably the right compromise, and a fair deal.
Photo: The P5+1 foreign ministers, with Iranian Foreign Minister Javad Zarif at United Nations Headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, November 24, 2013. Credit: State Department photo/Public Domain
]]>by Thomas Lippman
Has King Abdullah backed away from his longstanding refusal to have anything to do with an Iraqi government that includes Nouri al-Maliki? Reporters who were in Jeddah when Abdullah met with Secretary of State John F. Kerry Friday seemed to think so, based on a background briefing by the [...]]]>
by Thomas Lippman
Has King Abdullah backed away from his longstanding refusal to have anything to do with an Iraqi government that includes Nouri al-Maliki? Reporters who were in Jeddah when Abdullah met with Secretary of State John F. Kerry Friday seemed to think so, based on a background briefing by the ubiquitous “senior official.”
Abdullah reportedly said that he would urge Iraq’s Sunni Muslims to join a new, more inclusive government in Baghdad to help save the country from itself by fending off the radical Sunni Muslim forces known as the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria [ISIS]. These militants have overrun much of northern Iraq and are marching toward the capital. According to the senior official, Abdullah did not specifically say that any new government would have to exclude Maliki, whom he loathes and mistrusts, an apparent softening of his adamant position.
“It was clear,” the senior official told reporters after the Kerry-Abdullah meeting, “that the two shared a view that all of Iraq’s community should be participating on an urgent basis in the political process to allow it to move forward and that each—both the Secretary and King Abdullah in their conversations with Iraqi leaders—would convey that message directly to them.”
That could signal a willingness to recognize a new government headed by Maliki, but it could also mean the opposite – since Maliki is unlikely to be able to form a government that would have substantial Sunni representation, what Abdullah really wants is a government headed by someone else.
There is no doubt that the Saudi leadership regards ISIS as a threat to regional stability and a menace to themselves, but the king has long believed that Maliki is the cause of the problem in Iraq and cannot be part of the solution. In his view, Maliki is an Iranian agent whose exclusion of Sunni Muslims from positions of power is what motivates the ISIS rebels. Saudi Arabia’s foreign minister, Prince Saud al-Faisal, restated that view the day before Kerry met the king.
“Maliki is the one to blame,” he said, according to the Saudi Press Agency, because he “stirred up the sectarian fight” and encouraged sectarian militias to fight each other.
Prince Saud himself met with Kerry on Friday, along with the foreign ministers of Jordan and United Arab Emirates, and gave no indication that King Abdullah was reconsidering his position. On the contrary, a “senior official” told reporters, the Saudi position was “exactly” the same as what the kingdom has said publicly, which is that Maliki must go. “They talked about their concerns about the lack of inclusivity of the current leadership. That’s obviously a reference to Maliki, so…”
Because Saudi Arabia has supported a Sunni insurgency against the Iran-supported government in Syria, many analysts in the Gulf of suspect Saudi Arabia of also encouraging the ISIS uprising in Iraq. In both countries, Saudi Arabia would gain through the downfall of regimes aligned with Riyadh’s arch-rival, Iran, a Shiite state that supports Maliki’s Shiite-dominated government in Baghdad. King Abdullah’s belief that Maliki is an Iranian agent can only be reinforced by news reports this weekend that Iran is preparing to return to Iraq warplanes that it had refused to give back after defecting Iraqi pilots flew them there during the 1991 Gulf war.
Saudi Arabia has a nominal ambassador to the Maliki government, but he lives in Amman; the kingdom does not have an embassy in Baghdad, has offered no economic or military support to the Maliki government, and has not encouraged Saudis to do business in Iraq. Iraq does have an embassy in Riyadh. Diplomats who have served there say King Abdullah’s senior advisers all recognize that his refusal to engage with Iraq has been counter-productive because it has left the field of influence to Iran, but they have been unable to persuade the king to soften his position. He believes that Maliki lied to him when he pledged, upon taking office eight years ago, to run an inclusive government that would give a sense of dignity and responsibility to Iraq’s formerly dominant Sunnis, whose power vaporized with the fall of Saddam Hussein and the U.S.-orchestrated purge that followed.
The question facing King Abdullah now is whether the ISIS threat is sufficiently dangerous to Saudi Arabia to persuade him to accept a new Baghdad government run by Maliki, and cooperate with it – and possibly with Iran directly – to thwart the rebellion and preserve the unity of the Iraqi state.
The militias grouped under the ISIS name are ruthless, well-financed, and now quite well armed with U.S.-made weapons seized from the fleeing Iraqi army. Even so, they present no direct military threat to Saudi Arabia, which is not their primary target. What Riyadh fears is that radical jihadists, Saudi and otherwise, who have joined ISIS’s ranks will infiltrate Saudi Arabia and attempt to destabilize the kingdom through terrorism and guerrilla attacks. The Saudis, like the ISIS fighters, are Sunni Muslims, but to the extent that ISIS has an ideology it derives from that of al-Qaeda, which originated as a Saudi movement dedicated to bringing down the al-Saud monarchy.
On Thursday, King Abdullah ordered Saudi security forces to take “necessary measures” to defend the kingdom against ISIS. Whether “necessary measures” might mean acceptance of Nouri al-Maliki’s role on Iraq is not yet clear.
This article was first published by LobeLog and was reprinted here with permission. Follow LobeLog on Twitter and like us on Facebook
Photo: U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry meets with Saudi King Abdullah bin Abdulaziz Al-Saud in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, on June 27, 2014. Credit: State Department photo/ Public Domain
]]>by Marsha B. Cohen
One of the more remarkable aspects of the recent news coverage of Iraq — the Maliki government’s loss of control over the northern region of the country, the deadly confrontations taking place between Iraqi Shia and Sunnis, and the clashes between Kurds and the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIL [...]]]>
by Marsha B. Cohen
One of the more remarkable aspects of the recent news coverage of Iraq — the Maliki government’s loss of control over the northern region of the country, the deadly confrontations taking place between Iraqi Shia and Sunnis, and the clashes between Kurds and the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIL or ISIS) — is the absence of any mention of Israel.
Commonalities between the Kurdish quest for a long-denied state of their own and Israel’s struggle to survive in a sea of geopolitical enemies are ubiquitous in reports on the Kurdish struggle, both in the Israeli press and among Israel’s supporters abroad. Indeed, it’s not unusual to see Kurdish separatism invoked and idealized as a reflection of the quest to establish a Jewish state, underscored by imagined historical parallels between Jews and Kurds. For example, in an essay titled, “Surprising Ties between Israel and the Kurds,” in Middle East Quarterly’s Summer 2014 issue, Ofra Bengio, a senior research fellow specializing in Kurdish affairs at Tel Aviv University, points out several of these perceived parallels:
Both are relatively small nations (15 million Jews and 30 million Kurds), traumatized by persecutions and wars. Both have been leading life and death struggles to preserve their unique identity, and both have been delegitimized and denied the right to a state of their own. In addition, both are ethnically different from neighboring Arabs, Persians, and Turks, who represent the majority in the Middle East.
The idealized goals and strategies of sovereignty seeking Kurdish separatists are often contrasted with those of Palestinian Arabs, as illustrated by Victor Sharpe at the American Thinker:
…(A)fter the overthrow of Saddam Hussein, the Kurds displayed great political and economic wisdom. How different from the example of the Gazan Arabs who, when foolishly given full control over the Gaza Strip by Israel, chose not to build hospitals and schools, but instead bunkers and missile launchers. To this they have added the imposition of sharia law, with its attendant denigration of women and non-Muslims.
The Kurdish experiment, in at least the territory’s current quasi-independence, has shown the world a decent society where all its inhabitants, men and women, enjoy far greater freedoms than can be found anywhere else in the Arab and Muslim world — and certainly anywhere else in Iraq, which is fast descending into ethnic chaos now that the U.S. military has left.
For decades, Israel has been a silent stakeholder in northern Iraq, training and arming its restive Kurds. Massimiliano Fiore, a fellow at the Department of War Studies at King’s College London, cites a CIA document found in the US Embassy in Tehran and subsequently published, which reportedly attested that the Kurds aided Israel’s military in the June 1967 (Six Day) War by launching a major offensive against the Iraqi Army. This kept Iraq from joining the other Arab armies in Israel, in return for which, “after the war, massive quantities of Soviet equipment captured from the Egyptians and Syrians were transferred to the Kurds.” Former Mossad operative Eliezer Tsafrir has described in detail the decade of cooperation between 1965-75 of Israel’s Mossad and Iran’s SAVAK, the Shah’s secret police, in arming and training Iraqi Kurdish peshmerga forces. That cooperation ceased when, without warning, the Shah and Saddam Hussein made a secret deal that abruptly ended the Israeli-Iranian partnership in northern Iraq.
The First Gulf War in 1991 gave Kurds a safe haven with an unprecedented degree of autonomy in the no-fly zone enforced by the US-led Coalition. In oil-rich northern Iraq, Kurds held regional parliamentary elections in May 1992, establishing the Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG). Jacques Neriah, a retired colonel who served as foreign policy advisor to Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and as deputy head for assessment of Israeli military intelligence, explains in a 2012 report published by the Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs:
After the collapse of the Kurdish uprising of March 1991, which broke out after Saddam Hussein’s defeat by the U.S.-led coalition, Iraqi troops recaptured most of the Kurdish areas and 1.5 million Kurds abandoned their homes and fled to the Turkish and Iranian borders. It is estimated that close to 20,000 Kurds died from exhaustion, hunger, cold, and disease. On 5 April 1991, the UN Security Council passed Resolution 688, which demanded that Iraq end its measures against the Kurds and allow immediate access to international humanitarian organizations. This was the first international document to mention the Kurds by name since the League of Nations’ arbitration of Mosul in 1925.
A decade ago, Seymour Hersh called attention to Israel’s close ties with the Kurds. Hersh’s “Annals of National Security: Plan B“, published in the New Yorker is noteworthy, particularly in light of mounting criticism against the Obama administration’s handling of the current crisis. US officials interviewed by Hersh told him that by the end of 2003, “Israel had concluded that the Bush Administration would not be able to bring stability or democracy to Iraq, and that Israel needed other options.” One of those options was expanding Israel’s long-standing relationship with Iraqi Kurds and “establishing a significant presence on the ground in the semi-autonomous region of Kurdistan.” Although the reliability of Hersh’s sources was challenged at the time, they have been affirmed by more recent articles and reports. Neriah, writing in August 2012, cites numerous reports in the Israeli media about the activities of Israeli security and military personnel working for Israeli firms in Kurdistan:
According to Israeli newspapers, dozens of Israelis with a background in elite combat training have been working for private Israeli companies in northern Iraq, helping Kurds there establish elite antiterror units. Reports say that the Kurdish government contracted Israeli security and communications companies to train Kurdish security forces and provide them with advanced equipment.
Shlomi Michaels, an Israeli-American entrepreneur, and former Mossad chief Danny Yatom provided “strategic consultation on economic and security issues” to the Kurds, according to Neriah, although the Israeli government denied any official involvement.
Tons of equipment, including motorcycles, tractors, sniffer dogs, systems to upgrade Kalashnikov rifles, bulletproof vests, and first-aid items have been shipped to Iraq’s northern region, with most products stamped “Made in Israel.”The Kurds had insisted that the cooperation be kept secret, fearing that exposure of the projects would motivate terror groups to target their Jewish guests. Recent warnings that Al-Qaeda might be planning an attack on Kurdish training camps prompted a hasty exit of all Israeli trainers from the northern region. In response to the report, the Defense Ministry said: “We haven’t allowed Israelis to work in Iraq, and each activity, if performed, was a private initiative, without our authorization, and is under the responsibility of the employers and the employees involved.”
Laura Rozen, writing in Mother Jones in 2008, offered a less benign view of Michaels’ activities in Kurdistan. Besides promoting corruption through kickbacks, Michaels attempted to sell — for $1 million — a dossier to the CIA that would prove Saddam Hussein had met with Ukrainian officials in order to develop a covert chemical weapons program. Rozen also linked the 2005 AIPAC spy scandal to Israeli involvement in Kurdistan. In 2004, US intelligence agencies had heard rumors that Iranian agents planned to target Israeli and US personnel operating in northern Iraq. Larry Franklin, who worked for the Pentagon, had been caught leaking the intelligence to Washington hawks. That’s how he was was recruited by the FBI for a July 2004 sting operation that informed AIPAC officials about the alleged threat to Israelis operating in northern Iraq. Franklin pled guilty to leaking classified information and was sentenced to 12 years in prison.
In her Middle East Quarterly essay, Bengio also mentions many of Hersh’s claims about Israeli involvement in Kurdistan a decade earlier, which she cautiously avers “remain unproven,” drawing upon Neriah’s account of Michaels’ adventures (without naming names):
The Yedi’ot Aharonot newspaper published an exclusive regarding Israel’s training of peshmergas, the Kurdish paramilitary force. Another Israeli source mentioned the activities of an Israeli company in the construction of an international airport in Erbil in Iraqi Kurdistan. The same source revealed “For their part, Iraqi sources, especially Shiite ones, have published lists of scores of Israeli companies and enterprises active in Iraq through third parties.
Less than a year ago, Lazar Berman of the Times of Israel, under the optimistic headline, “Is a Free Kurdistan, and a New Israeli Ally, Upon Us?” quoted Kurdish journalist Ayub Nuri who argued that Kurds were “deeply sympathetic to Israel and an independent Kurdistan will be beneficial to Israel.” Fast forward a year later to Neriah’s article titled, ”The fall of Mosul could become the beginning of Kurdish quest for independence,” where he says nothing about the stakes for Israel. Would an increasingly independent Kurdistan continue to look to Israel as its patron?
Or will Kurdistan fully join an anti-ISIS Iraqi alliance, backed jointly, if discreetly, by Iran, with the approval of the US? Any scenario in which Iran is part of the solution, rather than the underlying problem, is a nightmare for Israel. “[W]e would especially not want for a situation to be created where, because both the United States and Iran support the government of (Iraqi Prime Minister Nuri) al-Maliki, it softens the American positions on the issue which is most critical for the peace of the world, which is the Iranian nuclear issue,” Yuval Steinitz, the Israeli minister of strategic affairs, told Reuters.
After so many decades of trying to make use of the Kurdish dream of independence as a narrative and nuisance against its enemies, Israel stands at the cusp of being the biggest loser in whatever comes next in strife-ridden Iraq.
This article was first published by LobeLog. Follow LobeLog on Twitter and like us on Facebook.
]]>by Mitchell Plitnick
They were dueling op-eds, one in the New York Times and the other in the Jewish communal magazine, Tablet. The question being bandied between them was whether Israel is becoming a theocracy. Not surprisingly, both pieces missed the mark. It’s not theocracy but unbridled nationalism that is the threat [...]]]>
by Mitchell Plitnick
They were dueling op-eds, one in the New York Times and the other in the Jewish communal magazine, Tablet. The question being bandied between them was whether Israel is becoming a theocracy. Not surprisingly, both pieces missed the mark. It’s not theocracy but unbridled nationalism that is the threat in Israel.
The Times piece was authored by Abbas Milani, who heads the Iranian Studies program at Stanford University and Israel Waismel-Manor, a lecturer at Haifa University and visiting associate professor of political science at Stanford. Their thesis is that Iran and Israel are moving in opposite directions on a democratic-theocratic scale, and that they might at some point in the future pass each other. Milani and Waismel-Manor are certainly correct about the strengthening forces of secularism and democracy in Iran, along with a good dose of disillusionment and frustration with the revolutionary, Islamic government that Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini ushered in thirty-five years ago. But on Israel, they miss the mark by a pretty wide margin.
Waismel-Manor and Milani posit that the thirty seats currently held in Israel’s Knesset by religious parties shows growing religious influence on Israeli policies. But, as Yair Rosenberg at Tablet correctly points out, not all the religious parties have the same attitude about separation of religion and the state. Where Rosenberg, unsurprisingly, goes way off course is his complete eliding of the fact that the threat is not Israel’s tilt toward religion, but it’s increasingly radical shift toward right-wing policies, which are often severely discriminatory and militant.
Waismel-Manor and Milani collapse the religious and right-wing ideologies at play in the Israeli government. Rosenberg is right to counter this. There are currently three parties in the Knesset (Israeli parliament) which define themselves as religious parties: HaBayit HaYehudi (The Jewish Home), Shas, and United Torah Judaism (UTJ). Shas is the most explicitly dedicated, in ideology and practice, to a religious Jewish state. But it is currently in the opposition and has not seen much rise in its share of the electorate in quite a while. It is worth noting, as well, that Shas has generally been the most welcoming of all religious parties to a two-state solution, although its stance on an undivided Jerusalem is notoriously problematic.
UTJ is made up of two religious parties, which don’t always agree and sometimes split for a while and reunite later. But UTJ generally supports the status quo of religion in the state, and HaBayit Hayehudi, while ostensibly supporting a religious state, is much more focused on its radical nationalism. This is why Bennett, after some early difficulties, has found a way to work with secular parties like Yesh Atid and, most importantly, Avigdor Lieberman’s Yisrael Beiteinu (Israel, Our Home). Neither of those two parties, both major partners in the current coalition, could find common ground with UTJ or Shas.
That is very telling, because it illustrates where both the Times and Tablet op-eds go wrong. Rosenberg, who is also the editor of the Israel State Archives blog, is zealous in his determination to be a heroic “Defender of Israel” and in so doing he comes off as both snide and dishonest in his takedown of Waismel-Manor and Milani, despite the merits of his case. Surely so keen an observer of Israeli politics as Rosenberg claims to be could not have missed the thread that the two scholars detected but mis-identified in their piece. It is not theocracy that Israel is sliding toward, it is the passionate and often brutal oppression that extreme nationalism so often leads to. At the end of that road is fascism. And while Israel, despite some bombastic rhetoric of its fiercest critics, remains a long distance away from being fascist, the distance is not as great as it once was.
Rosenberg had the opportunity to issue an important corrective to the Times op-ed and grasp a teaching moment. Instead, he waved the Israeli flag and completely ignored the very real threat Israel’s increasingly right-wing body politic poses to the structures of democracy in Israel.
That threat is manifest in the ideologies and proposals of both Avigdor Lieberman of Yisrael Beiteinu and Naftali Bennett of HaBayit HaYehudi. I’ve explored in some detail the kind of future Bennett envisions; he is a leading champion of annexation of much of the West Bank. Lieberman, who is busily pushing stronger ties with Russia to increase Israel’s freedom of action, has repeatedly proposed such ideas as loyalty oaths for Palestinian citizens of Israel and the forced transfer of Arab areas of Israel to the Palestinian Authority. These, coupled with his general style and heavy-handed methods, have brought many people to describe him as a fascist.
But the threat doesn’t stop there, nor is it limited to the Palestinians on both sides of the Green Line. Various bills have been proposed to limit Israeli NGOs that work to support human rights, international law, and peace, many of which are staffed and supported by Israeli Jews. The bills have been directly targeting NGOs in these fields, not the right-wing ones which do not disclose their funding sources and operate in various shady ways.
And the effect is not limited to Lieberman’s and Bennett’s parties. The Likud, which has always been conservative and right-wing, has also seen a tilt in this same direction. Gone from the ranks of Likud are such party stalwarts as Dan Meridor and Benny Begin who, despite supporting settlement expansion and various hawkish positions, also stood firm by Israel’s democratic processes. They opposed the rightward march and now they’re gone.
Politicians like Meridor and Begin were able to stabilize Likud leaders like Benjamin Netanyahu in the face of rightward pressure, but those days have also passed. It is a mark of where Likud has gone that, not only did it form an electoral bloc with Lieberman in the last election, but an outspoken opponent of the creation of a Palestinian state, the son of Israel’s first Likud Prime Minister, Menachem Begin (who was, himself, once considered a terrorist by the British), Benny was considered too moderate for the Likud leadership.
Instead of right-wing leaders like Meridor and Begin, Likud features explicit opponents of democracy like Ze’ev Elkin, annexationists like Tzipi Hotovely and outright racists like Miri Regev. Here we find the common cause that Bennett and Lieberman find with Likud. Not religion, but the worst kind of nationalistic bigotry, one that leads to ongoing occupation outside the Green Line and increased institutionalized racism, whether you call it apartheid, segregation or whatever, inside.
Rosenberg merely wanted to demonstrate that the Times ran an op-ed that offered an inaccurate picture of Israel, hoping to strengthen the right-wing’s and center-right’s phony contention that the Times and other mainstream media treat Israel unfairly. He was right about Milani and Waismel-Manor mischaracterizing Israel. But rather than correct them with reality, he did it with pointless sarcasm and thereby perpetrated a lie by omission that is much more harmful to Israel.
The pull of Bennett and Lieberman has made Likud even more radically right-wing. It has made a party like Yesh Atid “centrist,” even though its leader kicked off his campaign in a settlement, claims to support a two-state solution while backing every second of Netanyahu’s obstructionism in peace talks, and proclaims repeatedly that Israel should not even discuss Palestinian refugees or dividing Jerusalem. That’s the new center in Israel.
And why wouldn’t it be, when the right-wing has pulled things so far from any kind of true moderation? That is the danger of where Israel is heading. It’s not theocratic, but it is repressive and a recipe for continued and escalated conflict. Milani and Waismel-Manor may have mid-identified the threat, but at least they acknowledge there is one. And it’s getting worse.
]]>by Marsha B. Cohen
Israeli academics have recently provided a case study of how Israel and Iran may say and do much the same thing, but Iran alone will be criticized for it.
In their latest Iran Pulse piece, headlined “Iran and the Ukraine Crisis,” Prof. Meir Litvak, head of Tel Aviv University’s [...]]]>
by Marsha B. Cohen
Israeli academics have recently provided a case study of how Israel and Iran may say and do much the same thing, but Iran alone will be criticized for it.
In their latest Iran Pulse piece, headlined “Iran and the Ukraine Crisis,” Prof. Meir Litvak, head of Tel Aviv University’s Alliance Center for Iranian Studies, and MA student Michelle Tabariai write, “As the crisis in the Ukraine unfolded since January 2014, Iran’s official position was cautious and seemingly neutral.”
Of course, the Israeli government was also uncharacteristically quiet about the crisis in Ukraine, and has been almost silent about Russia’s takeover of Crimea. Only under pressure from Secretary of State John Kerry did the Israeli government issue its first and only official statement about the Russian incursion into Crimea on March 5 that was terse and subdued. “Israel is following developments in Ukraine with great concern for the well-being of all its citizens, and hopes the situation does not deteriorate to the point of loss of life,” said a statement released by Foreign Minister Avigdor Lieberman’s office. “Israel expects the crisis in Ukraine to be solved diplomatically and peacefully.”
“We have good and trusting relations with the Americans and the Russians, and our experience has been very positive with both sides,” Lieberman then told Israel’s Channel 9 TV. “So I don’t understand the idea that Israel has to get mired in this.”
Former Mossad Director Ephraim Halevy observes that “Israel’s most articulate spokespersons have sentenced themselves to complete silence over the issue, and this discipline is being kept in an unusually meticulous manner by the senior and less senior commentators in the Israeli media.”
The Iran Pulse analysis points out:
Iran did not participate in the UN General Assembly vote on March 27, which reaffirmed Ukraine’s territorial integrity and declared the Crimean referendum invalid. While seeking to preserve its alliance with Russia, it might have been wary of Russia’s unilateral measures in the Crimea.
Iran was indeed among two dozen states that did not vote in favor of the measure. So was Israel. Neither showed up for the vote.
Another excerpt from the Tel Aviv University critique:
…From the beginning of the protests in Kiev in January, the Iranian media adopted the Russian narrative, which described the movement as a product of Western plot.
Surprisingly, Litvak and Tabariai never mention Iranian rumors that Israeli operatives were involved in the ousting of Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovich in what appears to have been a rather curious game of propaganda poker between Israeli and Iranian press. On Feb. 16 Press TV cited unidentified Ukrainian sources who claimed a former Israeli army officer was “playing a leading role in the anti-government protests in the former Soviet Republic.” This unnamed Israeli was supposedly commanding 20 Ukrainian militants, and four other Israelis, who had served in the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) and “were recently reported to have taken part in opposition rallies in Ukraine’s capital, Kiev.” The Press TV report also claimed that “Ukrainian media said an Israeli tycoon provides financial support to the opposition in Ukraine, adding that Israel’s Mossad intelligence agency is one of the instigators of the unrest in the country.”
A week and a half later, Haaretz and The Times of Israel both published a Jewish Telegraphic Agency interview with “Delta,” a skull-cap wearing commander of a brigade he called the “Blue Helmets of Maidan,” which was fighting in the streets of Kiev. The pseudonymous “Delta” explained he’d been born in Ukraine, emigrated to Israel during the 1990s and served in the Israel Defense Forces. He returned to Ukraine several years ago and joined the protesters in November. He had been using his IDF acquired skills “to rise through the ranks of Kiev’s street fighters,” including “several fellow IDF veterans” engaging “in violent clashes with government forces.” Completing the circle, Press TV picked up the story on Mar. 1: “According to reports published by Haaretz and the Times of Israel on Friday, an Israeli army veteran identified as ‘Delta’ headed a street-fighting unit in Kiev.” There was no apparent glimmer of recognition that Press TV itself might have published the news that triggered the interview with “Delta.”
Write Litvak and Tabariai:
…Fars News, affiliated with the Revolutionary Guards, denounced the ousting of the president Viktor Yanukovych on February 22 as a “neo-Nazi-spearheaded coup” The new Ukraine, it warned, was governed by some ten “oligarchs” who were buying up media outlets and politicians, while the vast majority of the population will face a bleak future, which will include more European-demanded “austerity” (Fars, Mar. 16, 2014).
There has been no shortage of concerns expressed in the Israeli media about the widespread presence of neo-Nazis in Svoboda, the largest party in the Ukrainian opposition that brought down Yanukovych, or an equal number challenging such a claim. Israel’s official position is silence.
Mention “oligarchs” and Israelis get very nervous. A disproportionate percentage of both Russian and Ukrainian oligarchs are Jewish. Several fund the various Jewish organizations and foundations operating in Ukraine and Russia. One of them, the founder of what once was the Yukos oil empire, Mikhail Khordokovsky — once Russia’s richest man who lost the bulk of his wealth and spent a decade in prison due to his political rival, Vladimir Putin – joined the Ukrainian protestors in March, calling for the Russian people to overthrow Putin. A Ukrainian Jewish business tycoon, Vadim Rabinovich, recently announced his candidacy for president of Ukraine in the May elections. Rabinovich, founder of the All-Ukrainian Jewish Congress, is the owner and co-founder of Jewish News One and co-chair of the European Jewish Parliament. These developments, along with the calls from members of the US Congress, who are among Israel’s most energetic supporters, to arm Ukraine and sanction prominent Russian oligarchs are putting Israel in a very awkward position.
The Iran Pulse report notes that Iranian reformist media outlets “showed greater concern from a renewed outbreak of the Cold War and the repercussions of Russian use of force,” while hardliners focused more on the significance of the American failure vis-à-vis Russia”:
The reformist Sharq maintained that Russian military presence in the Crimea reveals the vulnerability and fragility of the international community in ensuring global security…(Sharq, March 3, 2014). Conversely, the conservative Khorasan asked rhetorically why Putin should respect international law while others fail to do so?…(Khorasan, March 3, 2014)
…More important, however, was the unanimous conclusion of the Iranian media that Western reactions to Russia’s measures exposed the weakness of the Western bloc and particularly the US’ declining power. Kayhan noted with satisfaction that “Putin’s agile reaction paralyzed Western response,” adding that “Western preference for economic sanctions and NATO’s contentment with issuing statements rather than acting against Russia’s military action show that the West is in a passive mode” (Kayhan, March 6, 2014).
On this point, right-wing Israelis have the most in common with their Iranian counterparts. Writing in the Sheldon Adelson-owned daily, Israel Today, Haim Shine argues for Israeli self-reliance, broadly hinting that the lesson of Ukraine for Israel is to never give up its nuclear weapons in exchange for pathetic promises of American protection.
Israel’s citizens know from their experience during the run-up to the Six-Day War what the Ukrainians are learning now — you cannot rely on Western nations. Treaties, agreements, promises and worthy guarantees are as flimsy as garlic skins just when you need them. The West is tired and weary. Its last strength rests on its lips alone…So how could Israel, in light of the circumstances, relinquish the very foundations of its security?!
This seems to be the predominant perspective in Israel, according to a head-shaking and somewhat dispirited opinion piece headlined “Israel Striking Obama, Rooting for Putin” by former Mossad head Ephraim Halevy in Y-Net on March 28:
Israel is not limiting its mocking criticism against Washington and its Middle Eastern policy: While Russia is described as a resolved, brave country engaging in a smart, shrewd and winning policy — the US is presented as hesitant, afraid, powerless, and therefore defeated.
The US president must envy his Russian rival for the respect he receives in Israel as opposed to the daily dose of scorn and alienation served to our “ally” time and again.
The Iranians can take pleasure in seeing America’s ally declare on a daily basis with hysterical cries of despair that Washington is going from bad to worse.
At least Iranian and Israeli hardliners can agree on something…
Photo: Delta, the nom de guerre of the Jewish commander of a Ukrainian street-fighting unit, is pictured in Kiev in late February 2014.
]]>by Jasmin Ramsey
The title of this post is a quote from Shaul Bakhash, a George Mason University professor who moderated a panel discussion, “Iran, the Next Five Years: Change or More of the Same?“ at the Wilson Center today. “In a way, we’ve been here before,” said the esteemed scholar, referring [...]]]>
by Jasmin Ramsey
The title of this post is a quote from Shaul Bakhash, a George Mason University professor who moderated a panel discussion, “Iran, the Next Five Years: Change or More of the Same?“ at the Wilson Center today. “In a way, we’ve been here before,” said the esteemed scholar, referring to the presidencies of centrist leader Hashemi Rafsanjani and Mohammad Khatami, when the country was perceived as moving towards openness at home and abroad. But while Iranian President Hassan Rouhani’s administration includes individuals with past ties to those movements, Bakhash says the conservatives “remain the strongest political body in Iran”.
While nothing can stay the same forever, many people worried (some still do) that the Islamic Republic would continue down a path of conservatism verging on radicalism before the surprise presidential election of Rouhani in June 2013. Since Rouhani took over from Mahmoud Ahmadinejad — whose former conservative allies couldn’t effectively unite in time to support another conservative into the presidency — those worries have changed. Now the question on everyone’s mind is: can Rouhani successfully navigate Iran’s contested political waters in his quest to implement foreign, economic and social policy reforms?
A lot depends on Iran’s 2016 parliamentary elections, according to panelist Bernard Hourcade, an expert on Iran’s social and political geography. “Elections matter In Iran”, said Hourcade, echoing Farideh Farhi. What happened in 2009 (when large groups of Iranians protested the election of Mahmoud Ahmadinejad and were violently repressed) proved that “elections have become a major political and social item in [Iranian] political life.”
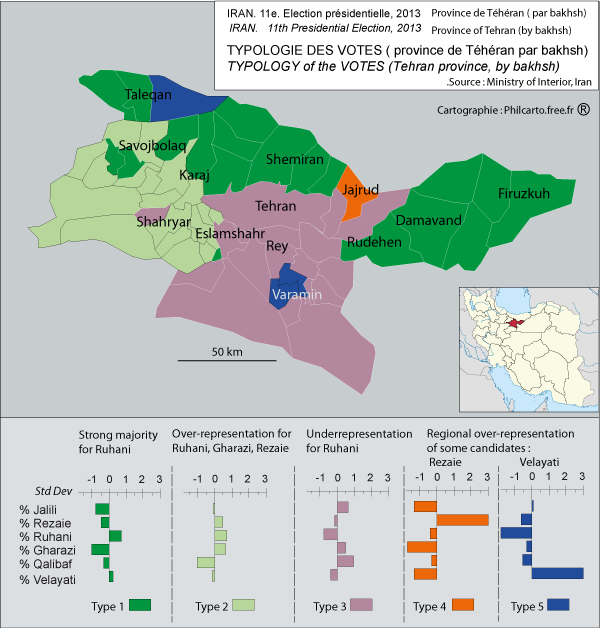 Hourcade uses official data to back up that point. Most interestingly, he shows that due to population migration patterns, the most important political divisions no longer exist between Iranian cities and villages, but between city centers and suburbs. Consider, for example, the typology of presidential votes for Rouhani in Tehran province. Hourcade’s diagram shows that while Rouhani had strong support in the northern part of Shemiran, he didn’t get a majority in central Tehran. Why that occurred is more difficult to answer, according to Hourcade, due to limited data resources.
Hourcade uses official data to back up that point. Most interestingly, he shows that due to population migration patterns, the most important political divisions no longer exist between Iranian cities and villages, but between city centers and suburbs. Consider, for example, the typology of presidential votes for Rouhani in Tehran province. Hourcade’s diagram shows that while Rouhani had strong support in the northern part of Shemiran, he didn’t get a majority in central Tehran. Why that occurred is more difficult to answer, according to Hourcade, due to limited data resources.
How political divisions play out in Iran’s upcoming parliamentary elections, which could give Iran’s currently sidelined conservatives more power, will also impact the Majles’ (parliament’s) reaction to the potential comprehensive deal with world powers over Iran’s nuclear program.
In other words, even if Iran’s rock star Foreign Minister can negotiate a final deal with the P5+1 (the U.S., Britain, France, China, and Russia plus Germany) that Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei approves, Iran’s parliament still has to ratify it, and if conservatives who oppose Rouhani dominate the majles, we may have another problem on our hands.
There were many other important points offered by Hourcade and his co-panelists, including Roberto Toscano, Italy’s former ambassador to Iran. He noted that former President Mohammad Khatami didn’t have the same chances as Rouhani because he was “too much out of the mainstream”. Rouhani, a centrist cleric and former advisor to Ayatollah Khamenei, wouldn’t have won the presidency without pivotal backing by both Khatami and Rafsanjani. So, as Toscano argues, Rouhani is in the mainstream (for now). But whether he and his allies will be able to maintain support from these important players moving forward, especially in 2016, will seriously influence whether he, like Khatami and Rafsanjani will be ultimately sidelined, or achieve a presidential legacy in Iran like nothing we’ve seen before.
Photo: Iranian President Hassan Rouhani walks by former Presidents Mohammad Khatami and Hashemi Rafsanjani following his June 2013 presidential vicotry. Credit: Mehdi Ghasemi/ISNA
]]>by Mitchell Plitnick
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s trip to the United States has ended in an unprecedented failure. On the Palestinian front, the Iranian front and the domestic US front, Netanyahu’s efforts last week ran badly aground. Let’s review the categories.
Iran
Netanyahu himself illustrated his greatest failure: his attempt to [...]]]>
by Mitchell Plitnick
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s trip to the United States has ended in an unprecedented failure. On the Palestinian front, the Iranian front and the domestic US front, Netanyahu’s efforts last week ran badly aground. Let’s review the categories.
Iran
Netanyahu himself illustrated his greatest failure: his attempt to divert the conversation about Iran by making a big show of intercepting a ship carrying rockets, ostensibly, according to Israel, headed for the Gaza Strip. Bemoaning the lack of global outrage that he had hoped would sabotage the talks between Iran and world powers on the nuclear issue, Netanyahu told the Israeli cabinet upon his return that: “”The goal of seizing the arms ship was to expose Iran’s true face. I say this in order to bring it to the attention of Ms. Ashton, who is now visiting Tehran, and I wish to ask her whether she asked her hosts about the shipment of weapons to terrorist organizations.”
In fact, there are very serious questions about the incident that are not being raised. It may be best that they’re not, because it is a reflection of the minor impact the incident has thus far had on the talks with Iran. The timing of the Israeli intercept was obviously staged to coincide with Netanyahu’s visit to the US to speak at the annual AIPAC conference and to meet with US President Barack Obama. As Amir Rappaport points out, the operation was being planned for months and was carried out far outside of Israeli waters, so the timing was no accident.
The plan fails in its very conception, though. At no point did Iran agree to stop its support for Hezbollah and Hamas in order to pursue these talks, nor did anyone expect them to. But other questions can be raised here as well. Was this, as Netanyahu alleges, Iran showing its “true face” as it masquerades behind the apparent moderation of Hassan Rouhani and Javad Zarif or was it, as many observers suspect, an attempt by Iranian hardliners to undermine the efforts of the moderates? Indeed, there is some question as to whether the weapons were even intended for Gaza.
It is also odd that weapons from Syria are brought to Iran to be smuggled all the way back to Gaza; the point of the Iran-Syria connection is for such flows to run in the opposite direction, although this could, perhaps, be explained by the ongoing civil war in Syria. In part, that explanation is connected to increased Israeli surveillance of Syrian munitions. That, however, raises the question of why Iran, knowing how closely Israel is watching Syria, would engage in such an operation now.
There are many questions about this incident, not the least of which is the veracity of Israel’s version of events, absent any proof they have made public about the weapons’ destination; they could have been heading for Hamas, to Islamic Jihad (as Israel claims) in Gaza, to anti-government militias in Egypt, to groups in Sudan… There is a lot here that is unclear at best in the Israeli version of events, although certainly nothing to prove that any part of it is untrue.
But what is clear is that the response from the United States and Europe is considerably less than Netanyahu had hoped for. No one believes this shows Iran’s “true face” because no one ever believed that engagement on the nuclear issue by itself was going to change Iran’s position and policy vis–à–vis Israel. What can do that, as Zarif has strongly indicated, is an agreement that the Palestinians clearly accept. So, where are we with that?
Palestinians and the Kerry peace plan
Netanyahu didn’t have much to say about peace with the Palestinians, but what little he did say was a clear attempt to negate any possibility of success on the part of US Secretary of State John Kerry. His very first remark to the fawning crowd at the AIPAC conference was a greeting “from Jerusalem, the eternal, undivided capital of Israel and the Jewish people.” Not surprisingly, this did not sit well outside the hall of sycophants at AIPAC. His only other substantive statement was a call on Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas to recognize Israel as a “Jewish state,” something neither Jews nor Israelis can even agree to a definition of and that everyone knows is a non-starter for Abbas.
This demand is a threadbare attempt to get the Palestinians to acknowledge, before an agreement, that they have no claim to a return of refugees (fair for Israel to try to win in talks if they want, but unreasonable to demand as a precondition, as Israel generally has), that Palestinian citizens of Israel must be content with second-class status and most of all, that the Zionist historical narrative is more legitimate than the Palestinian one. No leader of any people would ever agree to such a thing, and Netanyahu is well aware of this.
But outside of the lock-step supporters of Israel in AIPAC and their fellow travelers to the right of that organization, no one is buying into this demand even though its crucial for Netanyahu. For months now, it has been getting clearer and clearer that Kerry’s efforts were likely to fail and much of what both Netanyahu and Abbas have been doing and saying has been geared toward escaping blame, especially US blame, for this likely failure. Bibi needs the demand for recognition of a “Jewish state” to be seen as reasonable, but he’s not winning the battle.
“The level of mistrust is as large as any level of mistrust I’ve ever seen, on both sides,” Kerry told a House of Representatives Appropriations Committee hearing on Wednesday. With Netanyahu now back in Israel and Abbas slated to come to Washington next week, this is a clear statement of pessimism from the one man who, whatever the reality of the talks, has insisted on maintaining a show of optimism. The prospect of failure is becoming more certain, but thus far, Netanyahu has failed to gain the upper hand in escaping blame, as Ehud Barak did with Bill Clinton in 2000.
The US domestic audience
On the US front, the situation is unprecedented. The good wishes most US citizens hold for Israel remain steady, indicating the same widespread support for Israel’s security that has always existed. But the war-weary United States is withdrawing into itself and the diminishing support for Israeli policies is a reflection of this. However, that’s far from the only cause of the new situation Israel finds itself in.
Relationships between Israeli leaders and US presidents have varied. Barack Obama is not the first to have a rocky relationship with an Israeli Prime Minister. Jimmy Carter and George H.W. Bush did not always get on well with Menachem Begin and Yitzhak Shamir, respectively. On the other hand, Bill Clinton was practically a groupie for Yitzhak Rabin and had a very warm relationship with his political successor, Ehud Barak. Similarly, George W. Bush called Ariel Sharon a mentor, and continued to get along famously with Sharon’s successor, Ehud Olmert. Yet through all these relationships, bad and good, Israel always maintained warm ties with both major US parties. AIPAC prided itself for decades on its bi-partisan reach.
Netanyahu has severely damaged that bipartisanship. From his deep ideological connection to US neoconservatives, to his barely hidden meddling in US electoral politics, he has alienated Democrats. Those Democrats remain dedicated to Israel’s security, or, in some cases, to AIPAC-directed campaign contributions. But with his repeated attempts to draw the United States into deepening conflict and possibly war with Iran, Netanyahu has forced Democrats to choose between their constituents and AIPAC. That’s a battle AIPAC would never win, but Netanyahu seemed to believe that AIPAC could do anything. For all those who accused John Mearsheimer and Stephen Walt of demonizing “Jewish power” in their book on the Israel lobby, it seems it was Netanyahu who imagined an omnipotent lobby for his country in the US and wildly overestimated their power.
While Bibi spoke to AIPAC and other US audiences, article after article — in the Huffington Post, Foreign Policy, the Washington Examiner, Israel’s YNet, and other sites – proclaimed AIPAC’s diminishing influence. It really isn’t surprising. Bibi has tried to increase US involvement in the Middle East at a time when most in the US, despite being willing to continue to fund Israel and help it out at the United Nations, want to reduce our involvement in the region. And, while Bibi can talk the talk of the US right-wing, most Jews in the United States are liberals. With voices who support the rights of Palestinians as equal to Israelis gaining prominence, US Jews are looking for ways to reconcile their liberalism with their support of Israel in a way they have not had to in the past. Bibi is trying to push them back to the old narratives, and they aren’t working.
What if Netanyahu fails?
That’s a reasonable question. Right now, there is no serious challenger to Netanyahu on the horizon, but that can change if his bungling of the US relationship becomes more of a problem for the average Israeli. The challenge could come from the right, as Avigdor Lieberman is trying to position himself to make a run at the Prime Minister’s office. But if failure with the Palestinians and with the US is at issue, Lieberman wouldn’t be the answer, and no one more moderate than Bibi is currently poised to make any kind of challenge.
Still, it is now much more likely that the peace talks are going to collapse at the end of April. Netanyahu won’t be directly blamed by the Obama administration, but if they do think it is his fault they can easily communicate that in Israel and Europe, with profound consequences for Netanyahu. Meanwhile, more and more of Europe is turning against Israel’s increasingly right-wing and rejectionist policies. That could cost Bibi dearly.
Failure might not only harm AIPAC, but it could seriously harm more moderate groups in the US like J Street. If the two-state solution appears unrealistic, J Street will have little to hang their hats on. And without the moderate alternative, US support, apart from the annual military aid, is likely to diminish as well. Unfortunately, without a Palestinian strategy to take advantage of this changing state of affairs (beginning with unifying their body politic), it’s not going to lead to better days. And such does not seem to be forthcoming.
Bibi’s gone back home now. But his trip here was notable for how much was at stake and how badly he did with it.
]]>by Mitchell Plitnick
It’s a busy week for Secretary of State John Kerry. On Monday, he received Israel’s top two negotiators, Tzipi Livni and Isaac Molho. Then he packed his bags and headed off to the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland. Kerry will have any number of important tasks in Davos, [...]]]>
by Mitchell Plitnick
It’s a busy week for Secretary of State John Kerry. On Monday, he received Israel’s top two negotiators, Tzipi Livni and Isaac Molho. Then he packed his bags and headed off to the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland. Kerry will have any number of important tasks in Davos, but perhaps the highest profile of them will be a sideline meeting with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. These meetings, it is said, are meant to “bridge the gaps between Israel and the Palestinians.”
If anyone was holding out hope that these talks were anything more than a sham, those words should end such hopes. The framing of the United States bridging the gap between Israel and the Palestinians belies the reality of Israeli anger and Palestinian disappointment bordering on feelings of betrayal in terms of the US’ relationship with both sides. Let’s just look at where things stand.
President Barack Obama, it was reported last weekend, sees “less than a fifty-fifty chance” that a deal can be struck between Israel and the Palestinians. That’s what he told David Remnick of The New Yorker. It leaves a lot of space, and given Obama’s general subscription to the Realist school of foreign policy, one has to think he believes it to be much, much less than fifty-fifty. Remnick’s interview with Obama was a number of weeks back; it’s fair to believe that events since then have driven Obama’s estimate even farther down.
Last week, Israeli Defense Minister Moshe Ya’alon came out with as brazen an insult as can be recalled by a top Israeli official directed at a major US official, rudely describing Kerry as “obsessive and messianic.” The insult itself, exceptional as it was, was highlighted by the fact that Netanyahu did not rebuke his Defense Minister for insulting Israel’s patron. That sent a strong message about where Israel stands, and it could hardly have been missed within the context of Israel’s having recently raised the bar for even a framework agreement yet again.
That was done in the first week of 2014 when Netanyahu told a meeting of his Likud faction in the Knesset that he would never consent to withdraw from Hebron or Beit El, two settlements with historical religious significance to Jews, but exist well outside the settlement blocs that Israel has long assumed (along with the US) — despite a lack of Palestinian agreement — would remain under Israeli control in a deal. One can simply look at a map and see how even the most naïve and back-bending view of a two-state solution cannot possibly see an Israel in control of Hebron and Beit El allowing for a viable and contiguous Palestinian state.
All of this is added to the already unreasonable Israeli conditions of maintaining occupying forces in the Jordan Valley under a bogus pretext of security as the former head of the Mossad recently confirmed; and on Palestinian recognition of Israel as a Jewish State, something that is simply anathema to Palestinians, unprecedented in international relations and completely unnecessary for Israel. This leaves almost no foundation for Kerry to work with, no matter how dedicated he may be to bridging the two sides.
The Palestinians have raised other issues beyond these as well. Ongoing settlement construction, not only in the settlement blocs but crucially in the very much disputed areas of East Jerusalem, has been a major headache for the Palestinian negotiators. This is increasing pressure on the PA from within the West Bank and shifting a sizeable portion of Palestinian opinion from having lost faith in Abbas and his team to outright hostility toward them. That situation is certainly not about to abate. In response to European censure of Israel’s settlement project, Israeli Foreign Minister Avigdor Lieberman displayed remarkable hubris in summoning five European ambassadors to rebuke them for trying to stand up for international law and basic pragmatism in peacemaking. So Israel is getting only more aggressive about its settlement expansion.
The Palestinians also voiced their displeasure last week at an early outline of Kerry’s proposal, which they said made no mention at all of the right of return for Palestinian refugees or of Jerusalem’s status as the Palestinian capital. They are already preparing plans to return to pressing their case for statehood at the United Nations in the expectation that these talks will fail.
So what can Kerry do? It would seem very little. The Palestinians are under so much internal pressure that they are standing much more firmly than they have in past negotiations. Israel keeps moving the goalposts, despite already having set down conditions that no Palestinian leader could possibly meet. In order to create a bridge, there must be firm ground on either side to start building the two ends, and there seems to be far less common ground between Israel and the Palestinians than at any time since the two sides began negotiating two decades ago. There doesn’t seem to be a lot of ground for Kerry to stand on either.
No doubt, Kerry is hoping that he has some sway now over Netanyahu. The bill in the US Senate to increase sanctions and torpedo the fledgling diplomatic initiative between the P5+1 and Iran has stalled, at least for the moment, despite having gathered an appalling 59 co-sponsors. The preliminary agreement on Iran’s nuclear program has just gone into effect and so far is going well, while the US stood firm against Iran’s participation in the Geneva II peace conference regarding Iran’s ally, Syria. Having held the Iran issue at bay, Kerry may be thinking that his meeting with Netanyahu in Davos will be an opportunity to push Israel on the Palestinian issue and perhaps get Bibi to back off on some of the thorny issues. Kerry may well be hoping that if, for example, Netanyahu relented on Palestinian recognition of Israel as a Jewish state, the US may be able to convince the Palestinians to, for instance, accept a continued Israeli presence in the Jordan Valley.
Kerry may believe Netanyahu is particularly vulnerable right now, as he has heard from a group of 100 Israeli business leaders that he must reach a peace deal with the Palestinians because “the world is running out of patience and the threat of sanctions is rising.” He also heard from key coalition partner, Yair Lapid, head of the Yesh Atid party that he would quit Netanyahu’s government, threatening the governing coalition if the peace process did not get back on track.
But none of this is terribly likely to sway Netanyahu, even though it does represent more pressure to accommodate the peace talks than Bibi is accustomed to. And even if it does, it is highly unlikely that Mahmoud Abbas can afford to compromise on any of the current issues. If he allows a continued Israeli presence after an alleged “end to the occupation,” relents on Jerusalem, allows Israel to hold on to settlements outside the major blocs, or compromises on any of the issues that Netanyahu has brought to the fore in the last year, there is likely to be a major upheaval in the West Bank.
More likely, I think, is that Kerry is playing a carrot and stick game with Israel. He is smacking Bibi down for his arrogance on the peace process and his audacity in once again brazenly trying to play Congress against the Obama administration on Iran. His message in that case would be that if diplomacy with Iran is allowed to proceed apace, Kerry would allow Israel to maintain its intransigence unopposed after the April deadline for the current talks passes.
In either scenario, the Palestinians lose. There is no foundation for an agreement now between the two parties. The hope for a resolution lies not in this process, but in the growing threat of economic action along the lines of that which we’ve seen the Netherlands take recently coupled with renewed activism at the United Nations. Because above all else, it seems clear that Obama and probably Kerry as well understand that not only are the chances of success between Israel and the Palestinians “less than 50-50,” they are in fact about 50 points less.
]]>Nobel Peace Laureate Elie Wiesel took to the pages of the New York Times yesterday in a paid advertisement urging Congress to strengthen sanctions against Iran and, in apparent ignorance of the state of the current negotiations between Iran and P5+1, urged readers to “appeal to President Obama and Congress to [...]]]>
Nobel Peace Laureate Elie Wiesel took to the pages of the New York Times yesterday in a paid advertisement urging Congress to strengthen sanctions against Iran and, in apparent ignorance of the state of the current negotiations between Iran and P5+1, urged readers to “appeal to President Obama and Congress to demand, as a condition of continued talks, the total dismantling of Iran’s nuclear infrastructure and the regime’s public and complete repudiation of all genocidal intent against Israel.”
Never mind that Wiesel’s “demands” are supposed to be the goal of — rather than the preconditions for — the negotiations. Or that both the Obama administration and Iran’s Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif have clearly stated that passing new sanctions legislation could kill the sensitive diplomacy occurring between Tehran, Washington and the other P5+1 members.
Indeed, other than Elie Wiesel using his well-regarded name to support a plan whose likely impact will be to scuttle a nuclear deal with Iran (a deal that most Middle East experts believe would make both Israel and Western countries more secure) perhaps the most interesting part of the ad is buried at the bottom.
It reads: “Sponsored by Michael Steinhardt, Board of Governors, This World: The Values Network; co-founder Birthright Israel.”
Despite his understandably pro-Israel political leanings, Wiesel has repeatedly expressed support for a two-state solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and supported Obama’s efforts to negotiate such a deal.
After a meeting with Obama in 2010, Wiesel said, “The president is convinced that the peace process must continue. And we all agree of course. There is no substitute to peace among nations. Each side must understand that there is no absolute justice in the world, nor absolute peace in the world. One side must understand the other’s need for assurance for respect.”
Wiesel’s position, however, is not shared with his funder, hedge fund mogul Michael Steinhardt.
In an interview earlier this year with journalist and author Max Blumenthal, Steinhardt offered his own understanding of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Blumenthal: You know the occupation of Palestine has been going on for over 45 years and there are a lot of students organizing against it on campus?
Steinhardt: I think the idea of it being occupied isn’t exactly right either cause 45 years ago there was no Palestinian people.
Blumenthal: There’s no Palestinian people?
Steinhardt: There was none. So this is a new phenomenon.
Blumenthal: You’re saying they’re like an invented people.
Steinhardt: I think so.
Steinhardt is also a longstanding funder of the Foundation for Defense of Democracies, a hawkish think tank whose fellows frequently call for heightened sanctions against Iran and downplay the dangers of Israeli and/or U.S. military strikes against Iran’s nuclear facilities.
The 1986 Norwegian Nobel Committee cited Wiesel’s “practical work in the cause of peace” and his message “of peace, atonement and human dignity” when awarding him the Peace Prize. But Wiesel’s decision to throw his considerable moral weight behind an initiative to derail diplomacy with Iran and join forces with a man who engages in historical revisionism and denies Palestinian peoplehood is an odd turn for a person dedicated to human rights.
]]>