As everyone knows, prominent neo-conservatives have been spending weeks insisting that Chuck Hagel is an anti-Semite. The most toxic of these charges have, of course, been leveled by the Council on Foreign Relations’ mendacious Senior Middle East fellow Elliott Abrams in his now-infamous NPR interview a few evenings ago (which was [...]]]>
As everyone knows, prominent neo-conservatives have been spending weeks insisting that Chuck Hagel is an anti-Semite. The most toxic of these charges have, of course, been leveled by the Council on Foreign Relations’ mendacious Senior Middle East fellow Elliott Abrams in his now-infamous NPR interview a few evenings ago (which was taken apart by Lobelog alumnus Ali Gharib and which, I hear, is creating some major headaches for CFR president Richard Haass); the Wall Street Journal’s Bret Stephens in a particularly malodorous column; the Washington Post’s Jennifer Rubin’s regular rants; and Bill Kristol’s Weekly Standard, which launched the campaign almost a month ago with a quote from “a top Republican Senate aide” that warned: “Send us Hagel and we will make sure every American knows he is an anti-Semite.” (One wonders whether the source could have been Sen. Mark Kirk’s deputy chief of staff and AIPAC favorite, Richard Goldberg.) Of course, it’s long been a strategic neo-con goal to make criticism of Israel and its policies synonymous with anti-Semitism, so it’s no surprise that Hagel, who, for example, has been critical of Israeli settlements, should incur such attacks, as utterly ridiculous as virtually everyone who has worked with Hagel on Middle East issues (including former and current senior Israeli officials) has subsequently testified.
Neo-cons have long made sniffing out (as Stephens would probably put it) anti-Semites a specialty, although that skill has been deployed in a remarkably one-dimensional way, directed, as it has been, almost exclusively at “the left.” Aside from Adolph Hitler and his Nazis and, more recently, paleo-con Pat Buchanan, their olfactory sense appears to be blocked when inhaling through the right nostril. For example, they have largely absolved the Religious Right of anti-Semitism because of its love of Israel. (As Bill’s dad, Irving Kristol, opined about the more-anti-Jewish tendencies in Christian Zionist thought in Commentary back in 1982, “It’s their theology, but it’s our Israel.” And when Pastor John Hagee said in 2008 that the Nazi Holocaust was part of God’s plan to get Jews to move to Israel, neo-cons — and Abe Foxman – accepted his explanation without question.)
Much the same applied on the international front. Indeed, while the elder Kristol was arguing for a Judeo-Christian Zionist alliance at home back in the early 1980s, he and other leading neo-cons, notably Midge Decter, Jeane Kirkpatrick, and, yes, Elliott Abrams, too, were also busy defending really serious anti-Semities abroad. Even as they agitated effectively for the exodus of Jews from the Soviet Union, they conveniently averted their view from what was going on inArgentina, whose military junta — which enjoyed normal, even good relations with Israel — conducted its “dirty war” between 1976 until its fall shortly after its disastrous 1982 Falklands/Malvinas conflict withBritain. That war not only targeted Jews in disproportionate numbers, but was also known for treating those Jews who were “disappeared” into its clutches especially brutally — a fact that was well-documented as it happened but about which the neo-cons for several years had virtually nothing to say.
Consider the headline “Argentina Worried Over Anti-Semitism” that appeared in the July 7, 1977 edition of the New York Times. That article noted that:
[T]he complaints in the Jewish community include the leveling of anti-Semitic insults at and the physical abuse of Jews arrested by the security forces during investigations of subversive activities by left-wing guerrilla groups. In some cases, Jews have disclosed after being questioned and released that there were swastikas and pictures of Hitler in interrogation centers.
Earlier that year, two synagogues — one in central Buenos Aires– were firebombed, while pro-junta newspapers headlined lurid plots about the “Jewish-Marxist-Montonero conspiracy” against the country. In early 1980, Amnesty International published a lengthy report that included interviews of escaped detainees who testified that Jews were singled out for especially harsh treatment. Here’s a Jerusalem Post account quoting from the Amnesty report:
“From the moment they were kidnapped until they were included in a ‘transfer’ [a euphemism for being killed, usually taken by truck to helicopters, drugged, eviscerated, and thrown into the sea] they [the Jews] were systematically tortured. Some of them were made to kneel in front of pictures of Hitler and Mussolini to renounce their origins.”
A watered-down report by the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights that came out shortly afterwards confirmed that Jewish detainees were being singled out for especially cruel treatment by their captors.
Or, read this 1981 account of one prominent Jewish family’s ordeal by the extraordinarily courageous columnist for the Buenos Aires Herald, Mario del Carril, to get some notion of what was happening in Argentina:
“Before he died in exile — stripped of his citizenship — former Peronist economy minister Jose Ber Gelbard reported that his decision to take his whole extended family — 36 persons — out of Argentina in 1976 was prompted by the fact that a distant relative, a nephew that he might encounter once a year, had been tortured for no reason at all — unless the family connection to Gelbard can be considered a reason. This young man was found alive and nude in the street of a provincial city with a sign tied from his neck that read: ‘I am a Jewish pig.’ [Imagine if any of these things were happening in Iran today.]

Jacobo Timerman
The Carter administration, with its new emphasis on human rights, reacted to the repression quite strongly by U.S.historical standards. It downgraded ties with Buenos Aires; it cut bilateral assistance and opposed loans to the country from international financial institutions like the World Bank; and, through the persistent and public hectoring of the first human rights assistant secretary, Pat Derian, it pushed relentlessly for the release of some of the more prominent detainees, notably and fatefully newspaper publisher Jacobo Timerman, who was abducted by unknown assailants in April, 1977 and spent a year in a torture chamber and prison before being transferred to house arrest one year later and finally freed by a Supreme Court order in September, 1979, only to be immediately stripped of his citizenship by the junta which also expropriated his property and newspaper, and bundled him onto a plane bound for Israel. To its credit, the Anti-Defamation League (ADL) also spoke out strongly against the treatment of Jews by the regime during this period.
And what was the reaction of the neo-cons at the time to all this? They not only looked the other way; they actively criticized the Carter administration’s efforts, arguing, as Kirkpatrick did in her famous ”Dictatorships and Double Standards” essay in Commentary that Washington’s human-rights policy was dangerously naive, especially in the context of the global struggle between the West and the Soviet Union. In her view, one had to make a distinction between “traditional autocrats” — especially friendly ones — which, in her view, were far less threatening to human rights (they respect “habitual patterns of family and personal relations” as opposed to “totalitarian” regimes, especially of the Communist variety, which deny their subjects all rights and are incapable of internal reform). Pressing “friendly authoritarians” like Somoza in Nicaragua and the Shah in Iran to respect human rights too quickly and punishing them if they failed to do so were ultimately counter-productive in her view, both politically in terms of encouraging internal reform and strategically in terms of the greater contest with Moscow. As Ronald Reagan took power in January 1981, the notion that “friendly authoritarians” — be they the military junta in Argentina, or apartheid South Africa, or genocidal Guatemala — should be dealt with through positive incentives and “quiet diplomacy” became the guiding light for the new administration for which Kirkpatrick would serve as UN ambassador and Abrams initially as assistant secretary of state for international organizations, soon thereafter as assistant secretary for human rights, and ultimately as assistant secretary for Inter-American affairs.
Meanwhile, Timerman had written a book, Prisoner Without a Name, Cell Without a Number, which detailed his experience in exceptionally powerful terms. In addition to describing his own torture by electric shock (and the reaction of his torturers as they chanted in glee after each jolt, “Jew…Jew…Jew!…Jew”), he also addressed the fate of other victims, including entire families whose torture he personally witnessed or overheard.
“Of all the dramatic situations I witnessed in clandestine prisons, nothing can compare to those family groups who were tortured often together, sometimes separately but in view of one another. …The entire affective world, constructed over the years with utmost difficulty, collapses with a kick in the father’s genitals …or the sexual violation of a daughter. Suddenly an entire culture based on familial love, devotion, the capacity for mutual sacrifice collapses.” [Recall Kirkpatrick’s defense of authoritarian regimes based on their respect for “habitual patterns of family and personal relations.”]
Unfortunately for Ernest Lefever, Reagan’s first pick for the human rights post and a man who fully embraced Kirkpatrick’s theories and many other highly questionable ideas, the English-language edition of Timerman’s book came out just as his confirmation hearings were about to begin. Until that moment, U.S. mainstream media had paid amazingly little attention to what had been going on in Argentina, but the book made such a splash, and Reagan’s repudiation of Carter’s human-rights policy had been so stark, that when Timerman himself showed up to witness and comment on the hearings, the military junta, its torture chambers, and its anti-Semitic — not to say neo-Nazi — inclinations, suddenly became front-page news and the focus of long-delayed attention to the nature of the Argentine regime.
To make a long story short, Timerman’s book and the critical acclaim it received posed a major challenge to neo-con worldview both with respect to their cherished authoritarian/totalitarian dichotomy and their conviction that the greatest threat to Jews came from the left, rather than the right. (Indeed, Lefever’s nomination was quickly derailed, permitting the more diplomatic Abrams to take his place.) In more concrete terms, the neo-cons (and the Reagan administration in which they were ascendant) saw Argentina as a critical ally in the fight against the Soviet menace, especially in Central America where they had sent some of their torturers to help train and equip what, with the Reagan administration’s help, would become the anti-Sandinista contra army. Not only that, but the junta enjoyed very good relations with Israel, which, in the words of the Reagan State Department at the time, was “an important supplier of arms and military equipment toArgentina.” (This was cited in a memo to Congress as evidence that the junta could not be considered anti-Semitic and that “those outside Argentina who state that Argentine Jews and Soviet Jews are in the same situation do a grave disservice to Argentine Jews.”) In other words, the military junta was on our side, and here they were being exposed by Timerman as a bunch of sadistic neo-Nazi murderers, who decorated their torture chambers with banners of swastikas and giant photos of the Fuehrer himself.
So how did the neo-cons react, now that the junta’s anti-Semitism — real, Nazi-like anti-Semitism, not rhetorical denunciations about Jewish control of the media and the banks and the Protocol of the Elders of Zion, but serious, sadistic and murderous anti-Semitism that resulted in the most horrific treatment and killings of hundreds of Jewish people — had finally hit the headlines and captured the public attention in a way that it had escaped for the previous five years?
They attacked Timerman, of course. They didn’t accuse him of entirely fabricating his story, at least not publicly. (Chris Hitchens told me a few years ago that Irving Kristol had told him at a dinner party at the time that he really didn’t believe that Timerman had suffered anything like what he had described in the book.) But they — and by they, I’m referring specifically to the elder Kristol (“The Timerman Affair”, WSJ, May 29, 1981); Decter (“The Uses of Jacobo Timerman”, Contentions, August, 1981); another Journal columnist, Seth Lipsky (“A Conversation with Publisher Jacobo Timerman”, WSJ, June 4, 1981); and numerous NYT columns by William Safire — very much echoed what the Argentine regime itself had been saying: Timerman wasn’t abducted and tortured because he was a Jew, but because he had a business relationship with David Graiver, a shadowy financier suspected of funding the Montoneros (a notion thoroughly debunked by del Carril who noted in a 5 July 1981 Washington Post op-ed — “Reflections on Timerman” — that Graiver had a number of other business associates, including an archbishop and the secretary-general of the Organization of American States (OAS) who were not Jewish and never questioned, let alone kidnapped and tortured). Or that the military consisted of different “factions”, the more moderate of which — supposedly consisting of successive presidents of the junta (both of whom were later convicted of and imprisoned for crimes committed under their command, including the theft of babies of detained mothers who were murdered after giving birth) — had worked tirelessly to secure Timerman’s release and free other Jewish prisoners. Or that it was a chaotic period in which difficult decisions and extreme measures had to be taken. Or that anti-Semitism was never an official policy of the government. Or that Timerman was a leftist, not just an innocent victim (thus echoing Kirkpatrick’s remarks about the four U.S. churchwomen who were raped and killed close to San Salvador’s airport in December, 1980 — “The nuns were not just nuns. The nuns were political activists.”) Here’s how Kristol, the most influential of Timerman’s assailants, wound up his op-ed in the Journal:
The military regime inArgentina, for all its ugly aspects, is authoritarian, not totalitarian
Now that the Montonero terrorists have been crushed, theUnited Statesis using its influence to try to move the regime gradually toward greater liberalization. …[W]e are doing what we can to strengthen the more moderate and sensible elements in the army. The outlook of far from hopeless.
It would become utterly hopeless, however, were we to “write off”Argentina– excommunicate it, so to speak, from the community of nations. Then the more extreme right-wing elements in the armed forces — the ones who illegally arrested and tortured Mr. Timerman — would surely take total power. One strongly suspects that there are many on the American left who would like to see this happen. The politics of polarization, in which the left crusades against the right under the banner of “human rights,” while the threat from the totalitarian left is altogether ignored, appeals to their ideological bias as well as to their self-righteous passions. One might almost say it is their secret agenda.” [You see: it's all the left's fault. Or, in Kirkpatrick-speak, "Blame the Left First."]

Ronald Reagan
So how did it work out? Well, the Reagan administration, presumably with the agreement of its new human rights czar, Abrams, soon lifted almost all the sanctions that the Carter administration had imposed against Argentina; worked with Buenos Aires to ease scrutiny of its record by the UN and Inter-American Human Rights Commission; cooperated and encouraged the junta to help build up the contra forces that were gathering in Honduras; expressed regret for all the liberal abuse the junta had taken under Carter, reassured Buenos Aires that more goodies would be forthcoming; even talked up the possibility of its inclusion in a South Atlantic Treaty Organization with South Africa, etc. — all in the service of strengthening the “more moderate and sensible elements” in the army.
And what did those “moderate and sensible elements” do in response? They invaded the Falklands/Malvinas, thus precipitating a war and a major split within the Reagan administration between Secretary of State Al Haig, who argued the U.S. had to provide some support – even if limited to intelligence — to its closest NATO ally, Britain, and the neo-cons led by Kirkpatrick who argued that Washington should remain neutral, presumably to ensure the survival of a “friendly authoritarian” regime whose help in Central America was considered important to the administration’s ambitions there. Indeed, as the Argentines were routed, the administration tried to broker a negotiated settlement that would save the junta’s face, but, as recently declassified British documents have revealed, Maggie Thatcher would have none of it. As for Kirkpatrick’s role in this, the British ambassador at the time, Nicholas Henderson, described the administration’s highest-ranking neo-con as “more fool than fascist” for her support of the junta. Utterly disgraced in the eyes of its public, the junta under which anti-Semitism had flourished, and hundreds of Jews had been tortured and killed, was out of power within months.
Did this experience change perceptions by the neo-cons about anti-Semitism on the right? There is certainly no evidence to suggest that it did, despite the enormous amount of documentation that has subsequently been adduced by Argentina’s 1984 Truth Commission (whose report was entitled, significantly, “Nunca Mas”) and the many subsequent trials against junta officials that followed over the following years – all of which vindicated what the early reports, Amnesty, and Timerman had written about.
Indeed, Abrams and the head of Reagan’s controversial “Office of Public Diplomacy”, Otto Reich (later George W. Bush’s first assistant secretary for Western Hemisphere affairs) worked tirelessly in the mid- to late-1980’s with the help of the Wall Street Journal’s editorial page and Norman Podhoretz’s Commentary magazine to tar the Sandinista government with the anti-Semitism brush (relying primarily on wealthy Jewish exiles who had strong financial ties to ousted dictator Anastasio Somoza and left the country when or soon after he did), despite the fact that the U.S. embassy in Managua “found no verifiable ground on which to accuse the GRN [the Sandinista government] of anti-Semitism,” according to a July 28, 1983, cable. Their goal was to rally support in the Jewish community, the great majority of which was strongly opposed to the Reagan administration’s policies inCentral America, behind arming the Nicaraguan contras.
Yet the strongest anti-Semitic statement issued by any prominent Nicaraguan figure during Sandinistas’ 11-year rule was unquestionably that of the anti-Sandinista and U.S.-backed Archbishop (later made Cardinal, in part at Washington’s urging, by Pope John Paul II) Miguel Obando y Bravo. In an October 1984 homily that was reprinted in the anti-Sandinista (and U.S.government-supported) La Prensa newspaper, he stated:
[T]he leaders ofIsrael…mistreated [the prophets], beat them, killed them. Finally as supreme proof of love, God sent his divine Son, but they …also killed him, crucifying him… The Jews killed the prophets and finally the Son of God. …Such idolatry calls forth the sky’s vengeance.”
The ADL protested the homily; the neo-cons, including Abrams and Reich, ignored it.
So, if you want to identify an anti-Semite, the last person to consult would be a neo-conservative.
Featured Photo: Pictures of some of the estimated 30,000 people who were “disappeared” during Argentina’s “Dirty War”. By “miss buenos ares” Flickr.
]]>via IPS News
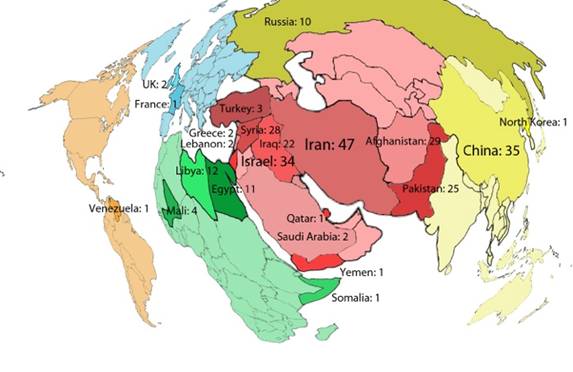
Graphic: The figures signify the number of times each country was mentioned in the Oct. 22 presidential debate. Credit: Zachary Fleischmann/IPS
U.S. strategy in the Greater Middle East, which has dominated foreign policy-making since the 9/11 attacks more than 11 years ago, similarly dominated the third and last debate between [...]]]>
via IPS News
Graphic: The figures signify the number of times each country was mentioned in the Oct. 22 presidential debate. Credit: Zachary Fleischmann/IPS
U.S. strategy in the Greater Middle East, which has dominated foreign policy-making since the 9/11 attacks more than 11 years ago, similarly dominated the third and last debate between President Barack Obama and Governor Mitt Romney Monday night.
The biggest surprise of the debate, which was supposed to be devoted exclusively to foreign policy and national security, was how much Romney agreed with Obama’s approach to the region.
His apparent embrace of the president’s policies appeared consistent with his recent efforts to reassure centrist voters that he is not as far right in his views as his primary campaign or his choice for vice president, Rep. Joe Ryan, would suggest.
The focus on the Greater Middle East, which took up roughly two-thirds of the 90-minute debate, reflected a number of factors in addition to the perception that the region is the main source of threats to U.S. security, a notion that Romney tried hard to foster during the debate.
“It’s partly because all candidates have to pander to Israel’s supporters here in the United States, but also four decades of misconduct have made the U.S. deeply unpopular in much of the Arab and Islamic world,” Stephen Walt, a Harvard international relations professor who blogs on foreignpolicy.com, told IPS.
“Add to that the mess Obama inherited from (George W.) Bush, and you can see why both candidates had to keep talking about the region,” he said.
But the region’s domination in the debate also came largely at the expense of other key regions, countries and global issues – testimony to the degree to which Bush’s legacy, particularly from his first term when neo-conservatives and other hawks ruled the foreign-policy roost, continues to define Washington’s relationship to the world.
Of all the countries cited by the moderator and the two candidates, China was the only one outside the Middle East that evoked any substantial discussion, albeit limited to trade and currency issues.
Romney re-iterated his pledge to label Beijing a “currency manipulator” on his first day in office, while Obama for the first time described Beijing as an “adversary” as well as a “partner” – a reflection of how China-bashing has become a predictable feature of presidential races since the end of the Cold War.
With the exception of one very short reference (by Romney) to Venezuelan President Hugo Chavez and another to trade with Latin America, Washington’s southern neighbours were completely ignored by the two candidates, as was Canada and all of sub-Saharan Africa, except Somalia and Mali where Romney charged that “al Qaeda-type individuals” had taken over the northern part of the country.
Not even the long-running financial crisis in the European Union (EU) – arguably, one of the greatest threats to U.S. national security and economic recovery – came up, although Romney warned several times that the U.S. could become “Greece” if it fails to tackle its debt problems.
Similarly, the big emerging democracies, including India, Brazil, South Africa, and Indonesia – all of which have been wooed by the Obama administration – went entirely unmentioned, although at least one commentator, Tanvi Madan, head of the Indian Project at the Brookings Institution, said Indians should “breathe a sigh of relief” over its omission since it signaled a lack of controversy over Washington’s relations with New Delhi.
Another key emerging democracy, Turkey, was mentioned several times, but only in relation to the civil war in Syria.
And climate change or global warming, which has been considered a national-security threat by U.S. intelligence agencies and the Pentagon for almost a decade, was a no-show at the debate.
“There was no serious discussion of climate change, the Euro crisis, the failed drug war, or the long-term strategic consequences of drone wars, cyberwar, and an increasingly ineffective set of global institutions,” noted Walt.
“Neither candidate offered a convincing diagnosis of the challenges we face in a globalised world, or the best way for the U.S. to advance its interests and values in a world it no longer dominates.”
Romney, whose top foreign-policy advisers include key neo-conservatives who were major promoters of Bush’s misadventures in the region, spent much of the debate repeatedly assuring the audience that he would be the un-Bush when it came to foreign policy.
“We don’t want another Iraq,” he said at one point in an apparent endorsement of Obama’s drone strategy. “We don’t want another Afghanistan. That’s not the right course for us.”
“I want to see peace,” he asserted somewhat awkwardly as he began his summation, suggesting that it was a talking point his coaches told him he must impress upon his audience before he left the hall in Boca Raton, Florida.
“Romney clearly decided he needed to head off perceptions of himself as a throwback to George W. Bush-era foreign policy adventurism, repeatedly stressing his desire for a peaceful world,” wrote Greg Sargent, a Washington Post blogger.
So strongly did he affirm most of Obama’s policies that, for those who hadn’t been paying close attention to Romney’s previous stands, the president’s charge that his rival’s foreign policy was “wrong and reckless” must have sounded somewhat puzzling.
As Obama was forced to remind the audience repeatedly, Romney’s positions on these issues have been “all over the map” since he launched his candidacy more than two years ago.
“I found it confusing, because he has spent much of the campaign season in some ways recycling Bush’s foreign policy, and, at least for one night, he seemed to throw the neo-cons under the bus,” said Charles Kupchan, a foreign policy specialist at the Council on Foreign Relations.
“Whether it was accepting the withdrawal timetable in Afghanistan, walking back a more aggressive stance on Syria, or basically agreeing with Obama’s approach on Iran, he seems to be stepping away from a lot of the positions he was taking just a few weeks ago,” he noted. “At this point, it’s impossible for voters to actually know what he thinks because he spent most of the campaign embracing a platform that was much further to the right.”
That Obama, who took the offensive from the outset and retained it for the next 90 minutes, won the debate was conceded by virtually all but the most partisan Republican commentators, with some analysts calling the president’s performance as decisive a victory as that which Romney achieved in the first debate earlier this month and which reversed his then-fading fortunes.
A CBS/Knowledge Networks poll of undecided voters taken immediately after the debate found that 53 percent of respondents thought Obama had won; only 23 percent saw Romney as the victor.
Whether that will be sufficient to reverse Romney’s recent gains in the polls – national surveys currently show a virtual tie among likely voters – remains to be seen.
Foreign policy remains a relatively minor issue in the minds of the vast majority of voters concerned mostly about the economy and jobs – one reason why, at every opportunity, Romney Monday tried, with some success, to steer the debate back toward those problems.
]]>Instead of highlighting the differences between some neocons and the Israeli right, Ross focuses [...]]]>
Instead of highlighting the differences between some neocons and the Israeli right, Ross focuses on the way neoconservatives try to have it both ways: promoting democracy (taking credit for Egypt as a after-effect of George W. Bush’s invasion of Iraq) and staunchly opposing figures like Mohammed ElBaradei and the Muslim Brotherhood. The contrast is between the “freedom crowd” and the “Islamophobes.”
Ross:
What accounts for this divide in neoconservative discourse? Nuances abound to be sure. For instance, while the case of Leon Wieseltier seems to be a horrified response to the fear that the Egyptian revolution bodes ill for Israel, a deeper pathology seems to be at work with the doctrinaire neoconservatives clustered around Commentary magazine. In a curious legacy of neoconservatism’s roots in Trotskyism, the neocon core seems to be characterized by a pathological insistence upon its internationalism, which leads them to their insistence that they are in fact witnessing the birth of a global democratic revolution. This also, it should be noted, seems to supersede any petty scores to be settled in defense of the Bush administration. Dana Perino amply covered that ground on Fox News, even to the point of embracing the Muslim Brotherhood.
On the other hand, the Anti-Islamist Scare that has gained full steam since the election of Obama appears to be a completely distinct phenomenon from historic neoconservatism, notwithstanding how opportunistically it has been embraced by figures like Bill Kristol and the Liz Cheney-led Keep America Safe. It is a phenomenon straight from the pages of Richard Hofstadter’s The Paranoid Style In American Politics. Whereas Hofstadter famously pointed to projection in the anti-Catholic Ku Klux Klan who “donned priestly vestments and constructed an elaborate hierarchy and ritual,” the backlash against the so-called Ground Zero Mosque—with its frank talk of “sacred ground”—reflected the desire to construct an American holy of holies.
Examining this same divergence, Daniel Luban has a similar article up at IPS. He explores the evolution of neoconservatism on democracy promotion, which brings the current divide into focus and hints at some disingenuousness among the ‘pro-democracy’ crowd. (Elliott Abrams, Dan notes, supported undemocratic regimes in Latin America when the region was in his portfolio during the Reagan administration.)
Luban (with my links):
“The U.S. should make clear in an unambiguous way that a Muslim Brotherhood takeover of Egypt is a danger to American interests and could even lead to American intervention,” David Wurmser, former Vice President Dick Cheney‘s senior Middle East [adviser], told the “Forward”, the largest-circulation Jewish weekly, Thursday.
This ambivalence among neo-conservatives over Egypt may reflect a deeper ambivalence over democracy promotion. Both neo-conservatives and their critics often portray democracy promotion as the central tenet of the movement, but the historical record undercuts this portrayal.
The early tone of the movement regarding foreign policy was set by Jeane Kirkpatrick’s 1979 essay “Dictatorships and Double Standards,” which argued for supporting “friendly” authoritarian governments against their left-wing enemies. Kirkpatrick’s vision helped guide neo-conservative foreign policy throughout the 1980s, when neo-conservatives – notably including Elliott Abrams – helped prop up or defend military dictatorships throughout Latin America, and even apartheid South Africa, as Cold War allies against the Soviet Union.
While the movement became more explicitly committed to democracy promotion in recent decades, its democratisation efforts have unsurprisingly been far more focused on hostile, rather than friendly, regimes – left-wing governments during the Cold War; more recently, governments that are seen as antagonistic to either the U.S. or Israel.
When elections have brought enemies rather than allies into power – as occurred in 2006 when Hamas won Palestinian parliamentary elections – neo-conservatives have been among the first to call for punitive actions.
Thus, when John Bolton, the hawkish former U.S. ambassador to the UN, cited Jeane Kirkpatrick in a Thursday interview with Politico to argue that the U.S. should support Mubarak, he could stake a claim to being as much the legitimate heir of neo-conservatism as the anti-Mubarak neo-conservatives themselves.
I’m still figuring this all out for myself, but these two commentaries are certainly helpful. (I’m traveling next week, but hopefully will have time to blog some of my developing ideas.)
But I will note that on the point of Dan’s original post — the split between Israel and the neocons — I do view with skepticism some commentaries (most of which come from neocons) that tout the narrative of: ‘Look! Neocons are not in the thrall of the Likud.’ (As a rule, because of his history of dissembling, I take anything Abrams writes with a grain of salt.)
This line, from the horse’s mouth, is attacking a straw man. We neocon-watchers at this site, at least, have never said that U.S. neoconservatives take marching orders from Likud, but rather that neocons are closely aligned with the rightist Israeli party.
Furthermore, if a Democrat criticizes something done by the Democratic Party (as happens quite regularly), it would be specious to say, ‘Look! She is not a Democrat at all!’
Likewise, I don’t think that neocons are a monolith, and this split between them reveals so much because it is public, whereas neocons, a politically adept group, have usually displayed great messaging discipline.
Nonetheless, the neoconservative disagreements on this issue (both among themselves and with Likud) seem to show that the upheaval in Egypt is coming home to the U.S. discourse on Middle East policy. Here’s hoping the shift is productive.
]]>The Wall Street Journal: Richard Haass, president of the Council on Foreign Relations, writes that Afghanistan is costly and “a strategic distraction,” and that U.S. military resources could be better used by preparing for a conflict with North Korea and Iran. Haass says [...]]]>
The Wall Street Journal: Richard Haass, president of the Council on Foreign Relations, writes that Afghanistan is costly and “a strategic distraction,” and that U.S. military resources could be better used by preparing for a conflict with North Korea and Iran. Haass says an important factor is, “[T]he increased possibility of a conflict with a reckless North Korea and the continued possibility of a confrontation with Iran over its nuclear program. U.S. military forces must be freed up to contend with these issues.” While “total withdrawal is not the answer,” he concludes that “The perception that we are tied down in Afghanistan makes it more difficult to threaten North Korea or Iran credibly—and makes it more difficult to muster the forces to deal with either if necessary.”
New York Post: An editorial in NY’s Rupert Murdoch-owned tabloid picks up on the threats of an Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps general that Iran will retaliate for the assassinations of its nuclear scientists. “It may sound like an empty threat, or an unhinged response,” write the Post editors. “But the threat is dead serious — proof of how hellbent Iran is to split the atom.” They add: “For Iran, nukes are its foreign policy — along with the terror it exports to Iraq, Syria, Lebanon and the Gaza Strip.” They add the threat of nuclear war looms large if Iran gets the bomb: “An atomic Iran could launch traditional military and terrorist attacks and tie the world’s hands by threatening nuclear war when any nation moves to fight back. By then it won’t have to rattle its sabers — it can aim its nukes instead.”
Pajamas Media: Foundation for Defense of Democracies scholar Michael Ledeen writes that last week’s terror attack in Southeastern Iran wasn’t a terror attack at all, but was “against the symbols and enforcers of the Shi’ite regime: Revolutionary Guards, Basij, and Quds Force fighters.” Ledeen cites internal political wrangling and suggests that the regime is in a “death spiral.” He concludes by making a case for regime change as a means of “reverse linkage” in the most sweeping manner seen yet: “If only there were a Western leader with the prescience and courage to support the Greens, we would find many terrible problems a lot easier to manage: Iraq and Afghanistan would go better, the tyrant Chavez and his ‘Bolivarian’ Axis of Latin Evildoers would be weakened, and the misnamed ‘peace process’ might even have a chance.”
]]>I decided to visit my Nicaraguan friend who stays in a village called Fougamou, in central Gabon. So I looked up the nearest town, Lambaréné. It turned out to have a museum honouring Dr. Albert Schweitzer, who arrived there in 1913, built a hospital, and won a Nobel Peace Prize in 1952.
I [...]]]>

The Ogooué River seen from Dr. Schweitzer's home. Photo: M. Sayagues
I decided to visit my Nicaraguan friend who stays in a village called Fougamou, in central Gabon. So I looked up the nearest town, Lambaréné. It turned out to have a museum honouring Dr. Albert Schweitzer, who arrived there in 1913, built a hospital, and won a Nobel Peace Prize in 1952.
I had never been interested in him but it seemed like a truly off-the-beaten path museum, just my kind. But what sold me on Lambaréné was the name of its river: Ogooué. I HAD to see a river with such a wondrous name.
So I set off to Lambaréné on my way to Fougamou. Believe me, I was in the green heart of Africa. Green, as in rainforest.
I am glad I went. The river is awesome. The museum is charming. It preserves the old hospital and personal quarters from the 1920s as they were originally. Next is the modern hospital, which attends to 80,000 consultations and 6,000 hospitalized patients every year, and continues to practice what I believe was Schweitzer’s most creative medical idea: to welcome the African family, with place to wash, cook and sleep, in a hospital-cum-village.
True, the relatives provided – and still do – free labour. Also true, it is mostly women and girls who provide this free labour. In Gabon and elsewhere, caring for the sick and, increasingly, for the elderly, is women’s work.
In AIDS-ravaged Southern Africa, caring for the sick has put a burden on women and girls that is unthinkable to Western health consumers.
So huge, that the campaign Making Care Work Count lobbies governments for recognition and support of carers – who are subsidizing governments with their work, with little help, making up for woefully inadequate health budgets.
Notwithstanding the gender bias, to include the relatives in hospital design is much better than making them sleep on the street pavement, as I’ve seen in Luanda’s hospitals.
It also reflects a recognition that in Africa medicine must incorporate cultural and social meanings; that it can’t isolate the individual from the collective; that the meaning of disease is part of a bigger reality.

Yeyette and Joel Boko
I travelled from Libreville, 300 kms away, in a taxi-brousse. The first to get in was with Yeyette Boko. She was worried to tears about her husband, Joel Boko, who was in Lambaréné being treated for an ulcerous thigh. He needed a graft. So Yvette had wrestled a two-week leave from her employer to be with him.
She breezed into his room: “Mon chéri, I missed you so much!” They snuggled on the bed and called their four-year-old son, who was staying with an aunt in the capital.
Next day I visited again. Yeyette had cooked a hearty meal. He seemed stronger. They looked happy.

The old landing by the hospital-village.
Read about worldwide efforts to measure and pay women’s unpaid care work
]]>