by Shireen T. Hunter
Throughout the recent handwringing about how the US and other Western countries failed to foresee the emergence of ISIS, one factor has been totally ignored, either intentionally or inadvertently: the impact of Washington’s hostility towards Iran, especially its persistent tendency to treat any anti-Iranian movement or idea in the Middle East as either good or the lesser evil compared to dealing with Tehran. This attitude has been coupled with a consistent unwillingness to support positive forces for change and reform in Iran; indeed, actually undermining them by insisting on their meeting preconditions that the West knows can’t be met due to Iran’s internal political dynamics. Significantly, this Western and especially American attitude predated any dispute over Iran’s nuclear program.
The first Western mistake followed the end of the Iran-Iraq war, the death of Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, and the coming to power of Ayatollah Akbar Hashemi Rafsanjani in 1989. Instead of taking advantage of Iran’s vulnerability at the time, as well as Rafsanjani’s efforts both to move Iran towards moderation and openness domestically and internationally and to reach out to the West to help him achieve these goals, the United States chose to put all of its eggs into Saddam Hussein’s basket and adamantly refused to acknowledge his many transgressions—against Iraq’s neighbors and own people—until his fateful 1990 invasion of Kuwait.
Nevertheless, with great difficulty—due to leftist opposition—Rafsanjani managed to secure Iran’s neutrality in the Persian Gulf War, a fact that facilitated US military operations. He also secured the release of the last of the Western hostages held in Lebanon. Yet, instead of encouraging the moderate political trends in Iran, the US under President George H. W. Bush embarked on a policy of containing Iran (soon to be replaced by the Clinton administration’s “dual containment” policy, which was then followed in 1996 by Congress’ enactment of the first oil sanctions against Iran at a time when Rafsanjani was actively encouraging American oil companies, notably Conoco, to invest). This policy of containment was first announced during a trip to Central Asia in 1992 by then-Secretary of State James Baker who declared containing Iran’s influence in the region would constitute a major goal of US policy.
Guided by this objective, the US subsequently bought into Pakistan’s argument that the Taliban would constitute a credible barrier to Iran’s influence in Afghanistan and, through it, in Central Asia as well. Hence Washington did not object to Pakistan’s arming and promoting the Taliban, a step that eventually led to the fall of the Afghan government of Burhaneddin Rabbani and Ahmad Shah Masood, two leaders who supported a version of Islam far more moderate than that of the Taliban. It is forgotten today that the Afghan civil war began with attacks by the Pakistan-based and more radical Islamists, first through Gulbuddin Hekmatyar, and, when Islamabad judged him to be too difficult to control, through the Taliban.
Even after the 1998 al-Qaeda bombings of US embassies in Nairobi and Dar es Salaam, followed by the 9/11 attacks and the US invasion of Afghanistan, which Iran directly and actively supported, Washington continued to rely on Pakistan as its key regional partner. Despite massive US aid, Islamabad actively—if covertly—undermined US strategy in Afghanistan while it scorned Iran’s offers to help stabilize the country.
Just as Washington ignored or rebuffed Rafsanjani’s efforts to moderate Iran’s domestic and international policies, it similarly declined to help his successor, President Mohammad Khatami, who promoted a tolerant and reformist Islam and a less confrontational approach to relations with the West and Iran’s neighbors. Thus, holding out for the best—namely, a secular, pro-western government in Tehran—the US lost the relatively good. And when Iran actively helped the US both to oust the Taliban and facilitate the transition that followed, it was rewarded by President George W. Bush with membership in the “axis of evil,” paving the way for new and ever more punitive sanctions.
After the 2003 US invasion of Iraq, Tehran quietly put forward an offer for a comprehensive deal with the US not only to cooperate on efforts to stabilize Washington’s latest conquest, but also to address all outstanding issues between the two countries, from acceptance of Israel and Iran’s support for Hezbollah and Palestinian resistance groups to Iran’s nuclear program. The Bush administration did not even bother to respond. Moreover, fearful that Iran might become the unintended beneficiary of the Ba’ath regime’s removal, Washington essentially stood by as its regional Sunni allies worked to undermine the fledgling Shia-led government in Baghdad not only by denying it aid and formal diplomatic recognition, but also, in the case of some Gulf states, encouraging and supporting the burgeoning Sunni insurgency, including al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI), which did not hesitate to attack US personnel, as well as their Shia brethren. Ironically if predictably, Washington’s policy of ignoring Sunni extremists forced Iraq’s Shia government to move closer to Iran.
Of course, the unanticipated insurgency and the increasing sectarian violence that it fostered also derailed hopes by the Bush administration—especially its neoconservative faction—that its “success” in Iraq would lead to “regime change”—either through destabilization or an actual attack—as well. At the same time, however, the administration bought into the idea that the increasingly sectarian nature of the conflict could also be used to curb Iran’s influence, notably by forging a de facto alliance between Israel and the Sunni-led states against Tehran and what Jordan’s King Abdullah ominously called the “Shia Crescent.” Of course, not only did Washington’s acceptance and even promotion of this idea contribute to rising sectarian tensions and extremism throughout the region, but it also failed to produce any progress toward resolving the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Once again, rather than working with Iran to stabilize Iraq, which would have required exerting real pressure on its Sunni allies that were supporting the insurgency, containing Iran’s influence remained Washington’s overriding priority.
It was in this context that the so-called Arab Spring blossomed and, with it, renewed hopes in Washington to reshape the Middle East, if not by achieving “regime change” in Iran, then at least by weakening its regional influence, particularly in the Levant. Even as the Obama administration publicly depicted the movement as the dawn of open and democratic societies, its closest regional partners—to which Washington had so often and so counter-productively deferred in Iraq—saw it as a way to redress the region’s strategic balance that had been upset by the 2003 invasion and the empowerment of Iraq’s Shia majority.
As the movement progressed from Tunisia and Egypt to Libya and the (thwarted) pro-democracy movement in Bahrain, it eventually reached Syria and the minority Alawite regime of President Bashar al-Assad, Iran’s most important regional ally. While the Gulf states and Turkey led the charge against the regime, the US and much of the West were not far behind. Predictably, however, in its desire to see Assad overthrown and Iran weakened, the US and its allies largely ignored the steadily growing influence of groups such as al-Qaeda’s Syrian affiliate, Jabhat al-Nusra, and similar foreign-backed Sunni extremist groups whose violence toward Syrian Shias, Alawites, Alevis, and Christians has been exceeded only by AQI’s successor, the Islamic State (ISIS).
Thus, for the past 25 years or more, the West—especially the United States—has made containing Iran its overriding priority in the Gulf and has too often seen the Wahhabi/Salafi version of Islam and its violent offshoots as an effective counterweight to Iranian influence. In doing so, it has unintentionally helped create monsters like Saddam Hussein, Osama Bin Laden, Mullah Omar, and now Abu-Bakr al-Baghdadi.
This critique by no means absolves Iran, Syria, Shia militias, or Iraq’s Shia-led government of their own mistakes and crimes. They have their own not insignificant share of responsibility in creating the region’s current problems and conflicts. And they have to do their part if the region’s problems are to be resolved. But as great powers that claim the world’s moral and political leadership with the power to intervene at will in other countries, the US and other Western countries must be judged by higher standards.At the very least, they need to offer a coherent and positive vision of a functioning Middle East and South Asia.
This requires going beyond the platitudes about wanting to advance democracy and human rights.
While the Western powers do not have a clear vision of what kind of Middle East they want and even less how to achieve it, ISIS, al-Qaeda, and al-Nusra have their own regional plans, based on ethnic and sectarian cleansing as we have already seen in both Syria and Iraq.
In short, until the US and the West admit at least to themselves that they have made mistakes in the region in the last few decades, particularly in their efforts to isolate and weaken Iran, and learn from those mistakes and change course, their efforts at defeating extremism and stabilizing the region are bound to fail.
The West cannot get all that it desires in the region, because political engineering has its limits. But if it embarks on a strategy of conflict resolution—fostering regional cooperation, instead of fighting it; and promoting compromise instead of complete capitulation by Iran or any other local power—its interests and those of the region will be better served. Until such a strategy is adopted and seriously implemented, however, every day that passes will make it that much harder to end the violence in the Middle East and encourage compromise and reconciliation. The same is equally true for the regional players. By pursuing maximalist goals they will all end up losers.
]]>by Jasmin Ramsey
The title of this post is a quote from Shaul Bakhash, a George Mason University professor who moderated a panel discussion, “Iran, the Next Five Years: Change or More of the Same?“ at the Wilson Center today. “In a way, we’ve been here before,” said the esteemed scholar, referring [...]]]>
by Jasmin Ramsey
The title of this post is a quote from Shaul Bakhash, a George Mason University professor who moderated a panel discussion, “Iran, the Next Five Years: Change or More of the Same?“ at the Wilson Center today. “In a way, we’ve been here before,” said the esteemed scholar, referring to the presidencies of centrist leader Hashemi Rafsanjani and Mohammad Khatami, when the country was perceived as moving towards openness at home and abroad. But while Iranian President Hassan Rouhani’s administration includes individuals with past ties to those movements, Bakhash says the conservatives “remain the strongest political body in Iran”.
While nothing can stay the same forever, many people worried (some still do) that the Islamic Republic would continue down a path of conservatism verging on radicalism before the surprise presidential election of Rouhani in June 2013. Since Rouhani took over from Mahmoud Ahmadinejad — whose former conservative allies couldn’t effectively unite in time to support another conservative into the presidency — those worries have changed. Now the question on everyone’s mind is: can Rouhani successfully navigate Iran’s contested political waters in his quest to implement foreign, economic and social policy reforms?
A lot depends on Iran’s 2016 parliamentary elections, according to panelist Bernard Hourcade, an expert on Iran’s social and political geography. “Elections matter In Iran”, said Hourcade, echoing Farideh Farhi. What happened in 2009 (when large groups of Iranians protested the election of Mahmoud Ahmadinejad and were violently repressed) proved that “elections have become a major political and social item in [Iranian] political life.”
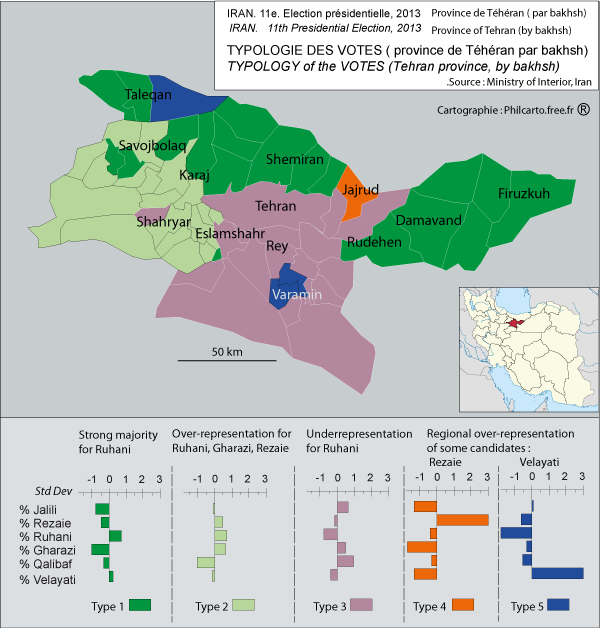 Hourcade uses official data to back up that point. Most interestingly, he shows that due to population migration patterns, the most important political divisions no longer exist between Iranian cities and villages, but between city centers and suburbs. Consider, for example, the typology of presidential votes for Rouhani in Tehran province. Hourcade’s diagram shows that while Rouhani had strong support in the northern part of Shemiran, he didn’t get a majority in central Tehran. Why that occurred is more difficult to answer, according to Hourcade, due to limited data resources.
Hourcade uses official data to back up that point. Most interestingly, he shows that due to population migration patterns, the most important political divisions no longer exist between Iranian cities and villages, but between city centers and suburbs. Consider, for example, the typology of presidential votes for Rouhani in Tehran province. Hourcade’s diagram shows that while Rouhani had strong support in the northern part of Shemiran, he didn’t get a majority in central Tehran. Why that occurred is more difficult to answer, according to Hourcade, due to limited data resources.
How political divisions play out in Iran’s upcoming parliamentary elections, which could give Iran’s currently sidelined conservatives more power, will also impact the Majles’ (parliament’s) reaction to the potential comprehensive deal with world powers over Iran’s nuclear program.
In other words, even if Iran’s rock star Foreign Minister can negotiate a final deal with the P5+1 (the U.S., Britain, France, China, and Russia plus Germany) that Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei approves, Iran’s parliament still has to ratify it, and if conservatives who oppose Rouhani dominate the majles, we may have another problem on our hands.
There were many other important points offered by Hourcade and his co-panelists, including Roberto Toscano, Italy’s former ambassador to Iran. He noted that former President Mohammad Khatami didn’t have the same chances as Rouhani because he was “too much out of the mainstream”. Rouhani, a centrist cleric and former advisor to Ayatollah Khamenei, wouldn’t have won the presidency without pivotal backing by both Khatami and Rafsanjani. So, as Toscano argues, Rouhani is in the mainstream (for now). But whether he and his allies will be able to maintain support from these important players moving forward, especially in 2016, will seriously influence whether he, like Khatami and Rafsanjani will be ultimately sidelined, or achieve a presidential legacy in Iran like nothing we’ve seen before.
Photo: Iranian President Hassan Rouhani walks by former Presidents Mohammad Khatami and Hashemi Rafsanjani following his June 2013 presidential vicotry. Credit: Mehdi Ghasemi/ISNA
]]>via IPS News
Iran’s June 14 presidential election results, announced the day after, was nothing less than a political earthquake.
The centrist Hassan Rowhani’s win was ruled out when Iran’s vetting body, the Guardian Council, qualified him as one of the eight candidates on May 21.
Furthermore, a first-round win [...]]]>
via IPS News
Iran’s June 14 presidential election results, announced the day after, was nothing less than a political earthquake.
The centrist Hassan Rowhani’s win was ruled out when Iran’s vetting body, the Guardian Council, qualified him as one of the eight candidates on May 21.
Furthermore, a first-round win by anyone in a crowded competition was not foreseen by any pre-election polling.
Until a couple of weeks ago, conventional wisdom held that only a conservative candidate anointed by Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei could win.
Few expected the election of a self-identified independent and moderate who was not well-known outside of Tehran.
And few thought participation rates of close to 73 percent were in the cards.
The expected range was around 60 to 65 percent, in favor of the conservative candidates who benefit from a solid and stable base of support that always comes out to vote.
But the move, a few days before the election by reformists and centrists — guided by two former presidents, Mohammad Khatami and Akbar Hashemi Rafsanjani — to join forces and align behind the centrist Rowhani proved successful and promises significant changes in the management and top layers of Iran’s various ministries and provincial offices.
Rowhani has also promised a shift towards a more conciliatory foreign policy and less securitized domestic political environment.
The centrist-reformist alliance occurred when, in a calculated action earlier this week, the reformist candidate Mohammadreza Aref withdrew his candidacy in favor of Rowhani, whose campaign slogan was one of moderation and prudence.
But the strong support for Rowhani, underwriting his first-round win, was made possible by an unexpected surge in voter turnout.
A good part of the electorate, disappointed by Iran’s contested 2009 election and the crackdown that followed, had become skeptical of the electoral process and whether their vote would really be counted.
They also questioned whether the holder of any elected office now could make a difference in the direction of the country.
Low voter turnout was the expectation. But with the centrist-reformist alliance, the mood of the country changed.
Serious debate began everywhere, including in homes, streets, shops and electronic media, about whether to vote or not.
As more and more people became convinced, Rowhani’s chances increased. Hope overcame skepticism and cynicism.
The case for voting centered on the argument that the most important democratic institution of the Islamic Republic — the electoral process — should not be abandoned easily out of the fear that it will be manipulated by non-elective institutions.
Abandoning the field was tantamount to premature surrender, it was argued.
Reformist newspaper editorials also articulated the fear that a continuation of Iran’s current policies may lead the country into war and instability.
Syria, in particular, played an important role as the Iranian public watched a peaceful protest for change in that country turn into a violent civil war through the intransigence of Bashar al-Assad’s government and external meddling.
The hope that the Iranian electoral system could still be utilized to register a desire for change was a significant motivation for voters.
Beyond the choice of Iran’s president, the conduct of this election should be considered an affirmation of a key institution of the Islamic Republic that had become tainted when the 2009 results were questioned by a large part of the voting public.
The election was conducted peacefully and without any serious complaints regarding the process.
Unlike the previous election, when the results were announced hurriedly on the night of the election, the Interior Ministry, which is in charge of conducting the election with over 60,000 voting stations throughout the country, chose to take its time to reveal the results piecemeal.
Other key individual winners of this election, beyond Rowhani, are undoubtedly former presidents Hashemi Rafsanjani and Khatami who proved they can lead and convince their supporters to vote for their preferred candidate.
Khatami in particular had to rally reformers behind a centrist candidate who, until this election, had not said much about many reformist concerns, including the incarceration of their key leaders, Mir Hossein Mussavi, his spouse Zahra Rahnavard, and Mehdi Karrubi.
Khatami’s task was made easier when Rowhani also began criticizing the securitized environment of the past few years and the arrests of journalists, civil society activists and even former government officials.
Meanwhile, Hashemi Rafsanjani, whose own candidacy was rejected by the Guardian Council, sees his call for moderation and political reconciliation confirmed by Rowhani’s win.
He rightly sensed that, despite the country’s huge economic problems — caused by bad management and the ferocious US-led sanctions regime imposed on Iran — voters understood the importance of political change in bringing about economic recovery.
Conservatives, on the other hand, proved rather inept at understanding the mood of the country.
They failed in their attempt to unify behind one candidate and ended up stealing votes from each other instead.
The biggest losers of all were the hardline conservatives, whose candidate Saeed Jalili ran on a platform that mostly emphasized resistance against Western powers and a reinvigoration of conservative Islamic values.
Although he was initially believed to be the the favored candidate due to the presumed support he had from Khamenei, he ended up placing third, with only 11.4 percent of the vote, behind the more moderate conservative mayor of Tehran, Mohammad Baqer Qalibaf.
The hardliners loss did not, however, result from a purge. It is noteworthy that other candidates besides Rowhani received approximately 49 percent of the vote overall.
While this election did not signal the hardliners’ disappearance, it did showcase the diversity and differentiation of the Iranian public.
Rowhani, as a centrist candidate in alliance with the reformists, will still be a president who will need to negotiate with the conservative-controlled parliament, Guardian Council and other key institutions such as the Judiciary, various security organizations and the office of Leader Ali Khamenei, which also continues to be controlled by conservatives.
Rowhani’s mandate gives him a strong position but not one that is outside the political frames of the Islamic Republic.
He will have to negotiate between the demands of many of his supporters who will be pushing for a faster rate of change and those who want to retain the status quo.
His slogan of moderation and prudence sets the right tone for a country wracked by 8 years of polarized and erratic politics.
But Rowhani’s promises constitute a tall order.
Whether he will be able to lower political tensions, help release political prisoners, reverse the economic downturn and ease the sanctions regime through negotiations with the United States remains to be seen.
But Iran’s voters just showed they still believe the elected office of the president matters and expect the person occupying that office to play a vital role in guiding the country in a different direction.
Photo Credit: Mohammad Ali Shabani
]]>