That Associated Press story displaying a graph alleged to be part of an Iranian computer simulation of a nuclear explosion — likely leaked by Israel with the intention of reinforcing the media narrative of covert Iranian work on nuclear weapons – raises serious questions about the International Atomic [...]]]>
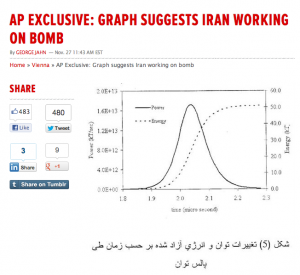 That Associated Press story displaying a graph alleged to be part of an Iranian computer simulation of a nuclear explosion — likely leaked by Israel with the intention of reinforcing the media narrative of covert Iranian work on nuclear weapons – raises serious questions about the International Atomic Energy Association’s (IAEA) claim that it has credible evidence of such modeling work by Iran.
That Associated Press story displaying a graph alleged to be part of an Iranian computer simulation of a nuclear explosion — likely leaked by Israel with the intention of reinforcing the media narrative of covert Iranian work on nuclear weapons – raises serious questions about the International Atomic Energy Association’s (IAEA) claim that it has credible evidence of such modeling work by Iran.
The graph of the relationship between energy and power shown in the AP story has now been revealed to contain absurdly large errors indicating its fraudulence.
Those revelations indicate, in turn, that the IAEA based its publication of detailed allegations of nuclear weapons-related Iranian computer modeling on evidence that should have been rejected as having no credibility.
Former senior IAEA inspector Robert Kelley, who has challenged the accuracy of IAEA reporting on Iran, told Lobe Log in an e-mail that “It’s clear the graph has nothing to do with a nuclear bomb.”
“The pretty, symmetrical bell shaped curve at the bottom is not typical of a nuclear explosion but of some more idealized natural phenomena or mathematical equation,” he said. “Clearly it is a student example of how to perform integrals to which someone has attached some meaningless numbers.”
Nuclear physicists Yousaf Butt and Ferenc Dalnoki-Veress also pointed out that the graph depicted by AP is not only so rudimentary and crude that it could have been done by an undergraduate student, but is based on a fundamental error of mind-numbing proportions.
The graph shown in the AP story plots two curves, one of energy versus time, the other of power output versus time. But Butt and Dalnoki-Veress noted that the two curves are inconsistent. The peak level of power shown in the graph, they said, is nearly a million times too high.
After a quick look at the graph, the head of the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Cal State Sacramento, Dr. Hossein Partovi, observed, “[T]he total energy is more than four orders of magnitude (forty thousand times) smaller than the total integrated power that it must equal!” Essentially, the mismatch between the level of total energy and total power on the graph is “more than four orders of magnitude”, which Partovi explained means that the level of energy is 40,000 times too small in relation to the level of power.
One alert reader of the account of the debunking of the graph at the Mondoweiss blog cited further evidence supporting Kelley’s observation that the graph shown by AP was based on an another graph that had nothing to do with nuclear explosions.
The reader noted that the notation “kT” shown after “energy” on the right hand scale of the graph does not stand for “kilotons” as Jahn suggested, but “Boltzmann constant” (k) multiplied by temperature (T). The unit of tons, on the other hand, is always abbreviated with a lower case “t”, he pointed out, so kilotons would be denoted as “kt”.
The reader also stated that the “kT” product is used in physics as a scaling factor for energy values in molecular-scale systems, such as a microsecond laser pulse.
The evidence thus suggests that someone took a graph related to an entirely different problem and made changes to show a computer simulation of a 50 kiloton explosion. The dotted line on the graph leads the eye directly to the number 50 on the right-hand energy scale, which would lead most viewers to believe that it is the result of modeling a 50 kiloton nuclear explosion.
The graph was obviously not done by a real Iranian scientist — much less someone working in a top secret nuclear weapons research program — but by an amateur trying to simulate a graph that would be viewed, at least by non-specialists, as something a scientist might have drawn.
Although AP reporter George Jahn wrote that officials who provided the diagram did so “only on condition that they and their country not be named”, the country behind the graph is not much of a mystery.
Blogger Richard Silverstein has reported that a “highly-placed Israeli source” told him the diagram “was stolen by the Mossad from an Iranian computer” using one of the various malware programs deployed against Iran.
Whether one chooses to rely on Silverstein’s reporting or not, it is clear that the graph is part of a longer stream of suspicious documents supposedly obtained by Israeli intelligence from inside Iran’s nuclear program and then given to the IAEA over the past few years.
Former IAEA Secretary General Mohammed ElBaradei refers in his memoirs to documents provided by Israel in 2009 “purportedly showing that Iran had continued with nuclear weapons studies until at least 2007.” ElBaradei adds that the Agency’s “technical experts” had “raised numerous questions about the documents’ authenticity”, and suggested that US intelligence “did not buy the “evidence” put forward by Israel” in its 2007 National Intelligence Estimate.
Jahn’s story indicates that this and similar graphs were the basis for the IAEA’s publishing charges by two unnamed states that Iran had done computer modeling that the agency said could only have been about nuclear weapons.
Jahn cites a “senior diplomat who is considered neutral on the issue” as confirming that the graph accompanying his story was one of “a series of Iranian computer-generated models provided to the IAEA by the intelligences services of member nations.”
Those “computer generated models” were discussed in the November 2011 report, which referred to “[i]nformation provided to the Agency by two Member States relating to modelling [sic] studies alleged to have been conducted in 2008 and 2009 by Iran….” The unnamed member states were alleging that the Iranian studies “involved the modelling [sic] of spherical geometries, consisting of components of the core of an HEU nuclear device subjected to shock compression, for their neutronic behaviour at high density, and a determination of the subsequent nuclear explosive yield.”
Nothing in that description of the alleged modeling is documented by the type of graph shown by the AP story.
The IAEA report concludes by saying, “The information also identifies models said to have been used in those studies and the results of these calculations, which the Agency has seen.”
In other words, the only evidence that the IAEA had actually seen was the graphs of the alleged computer modeling, of which the graph shown in the AP story is alleged to be an example. But the fact that data on that graph has been credibly shown to be off by four orders of magnitude suggests that the Israeli claim of Iranian computer modeling of “components of the core of an HEU nuclear device subjected to shock compression” was completely fabricated.
Former IAEA Inspector Kelley also told Lobe Log that “We can only hope that the claim that the IAEA has relied on this crude hoax is false. Otherwise their credibility has been shattered.”
- Gareth Porter, an investigative historian and journalist specialising in U.S. national security policy, received the UK-based Gellhorn Prize for journalism for 2011 for articles on the U.S. war in Afghanistan.
]]> An online NBC report by Robert Windrem published on Friday goes into explicit technical detail about the military hardware that will be brought to bear in an Israeli attack on Iran:
An online NBC report by Robert Windrem published on Friday goes into explicit technical detail about the military hardware that will be brought to bear in an Israeli attack on Iran:
Israel has both medium and intermediate range Jerichos. The medium-range Jericho I would not have the range to reach many Iranian targets but the intermediate-range Jericho II’s, capable of hitting targets 1,500 miles away, would have no problem. The Jerichos would be equipped with high explosives, not nuclear warheads. Asked if the Jericho would have the accuracy and the explosive power to take out a hardened bunker of the sort believed to be protecting Iran’s most-sensitive underground nuclear facilities, one official replied, “You would be surprised at their accuracy” and that the high explosives involved is a special mix of chemical explosives that could conceivably penetrate the Iranian fortifications.Missile attacks would be coordinated with fighter-bomber attacks (presumably the Israelis’ extended-range F-15I Strike Eaglet) as well as drone strikes. The fighter bombers would use what one official described as “high-low, low-high” flight paths — high first to increase fuel efficiency, then low for most of the trip to evade radar, then climbing high again as the weapons are released in what is known as a “flip toss” on the target. The Israelis would be prepared to lose aircraft if necessary, the officials said.
Windrem amalgamates and synthesizes the views of various unidentified “US and Israeli officials” about a more than likely Israeli attack on Iran in the next several months into a tidy and digestible question-and-answer format. One question he neither asks nor answers is whether Israel is actually capable of successfully carrying out a winner-take-all high tech attack on Iran that could destroy or (more likely) delay the development of Iran’s budding nuclear program, at minimal costs–financial, environmental or in casualties–to itself and anyone else except Iran.
Whether it’s due to technical glitches or human error, military hardware doesn’t always function the way it’s supposed to. A mysterious Yasour helicopter crash on July 26, 2010, during a training exercise in the Carpathian Mountains of Romania was, according to Jerusalem Post military analyst, Yaakov Katz:
…a blow to the IAF’s image and raises two serious questions – first, whether the transport helicopter, which has been in IAF service for over 40 years, is still a reliable and sturdy aircraft, and second, if this is what happens during a regular training exercise in Romania, what will happen in a future IAF long-range operation.
Katz went on to ask and answer the obvious question:
One might wonder why an Israeli helicopter was in Romania in the first place. The answer is that every long-range IAF operation today, wherever it may take place in the world including in Israel, takes into consideration ‘third-sphere threats’ like Iran, which are far from Israel.
On Nov. 10, 2010, two Israeli pilots were killed in the Negev Desert when their F15-I crashed. Last Sunday (Jan. 29) a state of the art Israeli Heron TP unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), also known as the Eitan, crashed in central Israel. No further reports have emerged to date regarding the cause of the disintegration of “the drone that can reach Iran,” believed to be the first such Israeli UAV crash of its kind.
The huge drone–the size of a Boeing 737, with a wingspan of 86 feet, and capable of carrying a one ton payload and reportedly capable of staying aloft for as long as 45 hours–went down near the Tel Nof Air Force Base not far from the town of Gedera in central Israel, about 20 miles southeast of Tel Aviv. According to the Associated Press, the Heron TP is “the largest unmanned aircraft in Israel’s military arsenal” and would “be featured prominently in any potential Israeli operation against Iran and its expanding nuclear program.” It can be aloft for as long as 45 hours, “making it capable of conducting a wide variety of missions.” Last September, Katz had reported that the Israeli Air Force’s claim that the deployment of the Heron TP by the end of 2011 would “boost its intelligence-gathering capabilities” and that “foreign reports” said the drone also had the ability to launch missiles.”
Early press reports about the downing of the UAV were inconsistent as to whether the UAV test flight was “routine” or “experimental.” A “flagship product” of Israeli Aircraft Industries, the Israeli business daily Globes assessed the cost of the downed UAV at $10 million. Y-Net cited the figure as $5 million, and Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty at $35 million. Israel is currently trying to market the drone to other countries and France recently decided to purchase Israeli Heron TPs instead of US Predator drones for use in NATO operations.
There hasn’t been much coverage of the investigation regarding the cause of the drone crash since it occurred. Initial reports stated that the cause was attributed to either human error or technical malfunction or some combination of the two. One possibility raised was that the one ton weight-bearing capability of the drone had been exceeded. (A GBU-28 “bunker buster” bomb weighs between 4500-5000 lbs.) Katz cited an explanation from military sources that the aircraft was flying with a new navigation component that might have disrupted the drone’s automatic flight systems. Yoav Zitun of Y-Net reported that a highly-advanced device on the wing was being tested during the drone’s flight.
Drones seem to offer the potential–and very real possibility–of wreaking enormous damage on an enemy from far away, with no military casualties to the country and with no loss of life to the military forces of the state launching the attack. On the other hand, UAVs don’t always reach their intended targets. Their “precision,” like that of a video game, depends upon the human hands on the controllers, and the choices made. These, in turn, are guided by the intelligence data they have available to them, at least some of which is gathered by UAVs.
The implications of last week’s crash of the Heron TP is a reminder that UAV technology, despite its increasing use, is far from perfect–a point that has received no discussion in the Israeli or global media. Presumably the fact that it is flawed is implicit. Nonetheless, the ramifications (and potential unintended consequences) of its deployment are staggering.
Iran (in case you were wondering) has its own UAV program, the domestically produced Kerrar. With an estimated range of 620 miles, a payload of 500 lbs. and a maximum speed of over 600 mph, the Kerrar is not (yet) capable of reaching Israel. This is good news for Israel for two reasons. The first–that Israel is out of reach–is a no-brainer. But there is another one too. An Israeli drone en route to Iran but shot down or otherwise crashing in Iraq or Bahrain might be declared to be Iranian, and be used as a pretext for war under international law.
What if, in the next test, an Israeli drone were to go further from its base but fall short of its target, causing widespread loss of life and property damage in Iraq, the Arabian peninsula, Turkey, or within Israel itself? If a malfunctioning Israeli drone en route to Iran were to crash and cause a disaster, would Israel accept responsibility, or would it point the finger at Iran, raising the specter and stakes of international retaliation? It might take days, weeks or months, possibly even years, for the truth to become known–long after a retaliatory strike had taken place.
Blogger Richard Silverstein has already suggested that last week’s crash was not that of a Heron TP but a Hezbollah drone targeting Israel. While Silverstein’s claim isn’t being taken seriously by anyone but himself and some of his readers (see Dimi Reider’s rejoinder on +972), it’s certainly within the range of possibility that a similar incident and accusation, coming from the lunatic right instead of the left, might be taken at face value, and drag the US into yet another war before the facts were even known.
Could the consequences of an Israeli attack on Iran that didn’t succeed be almost as bad–or even worse–than one that did?
]]>