History, it is said, arrives first as tragedy, then as farce. First as Karl Marx, then as the Marx Brothers. In the case of twenty-first century America, history arrived first as George W. Bush (and Dick Cheney and Donald Rumsfeld and [...]]]>
History, it is said, arrives first as tragedy, then as farce. First as Karl Marx, then as the Marx Brothers. In the case of twenty-first century America, history arrived first as George W. Bush (and Dick Cheney and Donald Rumsfeld and Paul Wolfowitz and Douglas Feith and the Project for a New America — a shadow government masquerading as a think tank — and an assorted crew of ambitious neocons and neo-pundits); only later did David Petraeus make it onto the scene.
It couldn’t be clearer now that, from the shirtless FBI agent to the “embedded” biographer and the “other other woman,” the “fall” of David Petraeus is playing out as farce of the first order. What’s less obvious is that Petraeus, America’s military golden boy and Caesar of celebrity, was always smoke and mirrors, always the farce, even if the denizens of Washington didn’t know it.
Until recently, here was the open secret of Petraeus’s life: he may not have understood Iraqis or Afghans, but no military man in generations more intuitively grasped how to flatter and charm American reporters, pundits, and politicians into praising him. This was, after all, the general who got his first Newsweek cover (“Can This Man Save Iraq?”) in 2004 while he was making a mess of a training program for Iraqi security forces, and two more before that magazine, too, took the fall. In 2007, he was a runner-up to Vladimir Putin for TIME’s “Person of the Year.” And long before Paula Broadwell’s aptly named biography, All In, was published to hosannas from the usual elite crew, that was par for the course.
You didn’t need special insider’s access to know that Broadwell wasn’t the only one with whom the general did calisthenics. The FBI didn’t need to investigate. Even before she came on the scene, scads of columnists, pundits, reporters, and politicians were in bed with him. And weirdly enough, many of them still are. (Typical was NBC Nightly News anchor Brian Williams mournfully discussing the “painful” resignation of “Dave” — “the most prominent and best known general of the modern era.”) Adoring media people treated him like the next military Messiah, a combination of Alexander the Great, Napoleon, and Ulysses S. Grant rolled into one fabulous piñata. It’s a safe bet that no general of our era, perhaps of any American era, has had so many glowing adjectives attached to his name.
Perhaps Petraeus’s single most insightful moment, capturing both the tragedy and the farce to come, occurred during the 2003 invasion of Iraq. He was commanding the 101st Airborne on its drive to Baghdad, and even then was inviting reporters to spend time with him. At some point, he said to journalist Rick Atkinson, “Tell me how this ends.” Now, of course, we know: in farce and not well.
Here was the odd thing: none of David Petraeus’s “achievements” outlasted his presence on the scene. Still, give him credit. He was a prodigious campaigner and a thoroughly modern general. From Baghdad to Kabul, no one was better at rolling out a media blitzkrieg back in the U.S. in which he himself would guide Americans through the fine points of his own war-making.
Where, once upon a time, victorious commanders had to take an enemy capital or accept the surrender of an opposing army, David Petraeus conquered Washington, something even Robert E. Lee couldn’t do. Until he made the mistake of recruiting his own “biographer” (and lover), he proved a PR prodigy. He was, in a sense, the real life military version of F. Scott Fitzgerald’s Jay (“the Great”) Gatsby, a man who made himself into the image of what he wanted to be and then convinced others that it was so.
In the field, his successes were transitory, his failures all too real, and because he proved infinitely adaptable, none of it really mattered or stanched the flood of adjectives from admirers of every political stripe. In Washington, at least, he seemed invincible, even immortal, until it all ended in a military version of Dallas or perhaps previews for Revenge, season three.
His “fall from grace,” as ABC’s nightly news labeled it, was a fall from Washington’s grace, and his tale, like that of the president who first fell in love with him, might be summarized as all-American to fall-American.
Turning the Lone Superpower Into the Lonely Superpower
David Petraeus was a Johnny-come-lately in respect to Petraeus-ism. He would pick up the basics of the imperial style of that moment from his models in and around the Bush administration and apply them to his own world. It was George W. and his guys (and gal) who first dreamed the dreams, spent a remarkable amount of time “conquering Washington,” and sold their particular set of fantasies to themselves and then to the American people.
They were the original smoke-and-mirrors crew. From the moment, just five hours after the 9/11 attacks, that Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld — in the presence of a note-taking aide – urged planning to begin against Saddam Hussein’s Iraq (“Go massive. Sweep it all up. Things related and not…”), the selling of an invasion and various other over-the-top fantasies was underway.
First, in the heat of 9/12, the president and top administration officials sold their “war” on terror. Then, after “liberating” Afghanistan and deciding to stay for the long run, they launched a massive publicity campaign to flog the idea that Saddam Hussein had weapons of mass destruction and was linked to al-Qaeda. In doing so, they would push the image ofmushroom clouds rising over American cities from the Iraqi dictator’s nonexistent nuclear program, and chemical or biological weapons being sprayed over the U.S. East Coast by phantasmal Iraqi drones.
Cheney and Rice, among others, would make the rounds of the talk shows, putting the heat on Congress. Administration figures leaked useful (mis)information, pressed the CIA to cherry-pick the intelligence they wanted, and even formed their own secret intel outfit to give them what they needed. They considered just when they should roll out their plans for their much-desired invasion and decided on September 2002. As White House Chief of Staff Andrew Card infamously explained, “From a marketing point of view, you don’t introduce new products in August.”
They were, by then, at war — in Washington. Initially, they hardly worried about the actual war to come. They were so confident of what the U.S. military could do that, like the premature Petraeuses they were, they concentrated their efforts on the homeland. Romantics about U.S. military power, convinced that it would trump any other kind of power on the planet, they assumed that Iraq would be, in the words of one of their supporters, a “cakewalk.” They convinced themselves and then others that the Iraqis would greet the advancing invaders as liberators, that the cost of the war (especially given Iraq’s oil wealth) would be next to nothing, and that there was no need to create a serious plan for a post-invasion occupation.
In all of this, they proved both masters of public relations and staggeringly wrong. As such, they would be the progenitors of an imperial tragedy — a deflating set of disasters that would take the pop out of American power and turn the planet’s “lone superpower” into a lonely superpower presiding over an unraveling global system, especially in the Greater Middle East. Blinded by their fantasies, they would ensure a more precipitous than necessary American decline in the first decade of the new century.
Not that they cared, but they would also generate a set of wrenching human tragedies: first for the Iraqis, hundreds of thousands of whom became casualties of war, insurgency, and sectarian strife, while millions more fled into exile; then there were the Afghans, who died attendingweddings, funerals, even baby-naming ceremonies; and, of course, tens of thousands of U.S. soldiers and contractors, who died or were injured, often grievously, in those dismal wars; and don’t forget the inhabitants of post-Katrina New Orleans left to rot in their flooded city; or the millions of Americans who lost jobs, houses, even lives in the economic meltdown of 2008, a disaster that emerged from a set of globe-spanning financial fantasies and snow jobs that Bush and his crew encouraged and facilitated.
 They were the ones, in other words, who took a mighty imperial power already in slow decline, grabbed the wheel of the car of state, put the peddle to the metal, and like a group of drunken revelers promptly headed for the nearest cliff. In the process — they were nothing if not great salesmen — they sold Americans a bill of goods, even as they fostered their own dreams of establishing a Pax Americana in the Greater Middle East and aPax Republicana at home. All now, of course, down in flames.
They were the ones, in other words, who took a mighty imperial power already in slow decline, grabbed the wheel of the car of state, put the peddle to the metal, and like a group of drunken revelers promptly headed for the nearest cliff. In the process — they were nothing if not great salesmen — they sold Americans a bill of goods, even as they fostered their own dreams of establishing a Pax Americana in the Greater Middle East and aPax Republicana at home. All now, of course, down in flames.
In his 1987 Princeton dissertation, David Petraeus wrote this on perception: “What policymakers believe to have taken place in any particular case is what matters — more than what actually occurred.” On this and other subjects, he was certainly no dope, but he was a huckster — for himself (given his particular version of self-love), and for a dream already going down in Iraq and Afghanistan. And he was just one of many promoters out there in those years pushing product (including himself): the top officials of the Bush administration, gaggles of neocons, gangs of military intellectuals, hordes of think tanks linked to serried ranks of pundits. All of them imagining Washington as a battlefield for the ages, all assuming that the struggle for “perception” was on the home front alone.
Producing a Bedside Manual
You could say that Petraeus fully arrived on the scene, in Washington at least, in that classic rollout month of September (2004). It was then that the three-star general, in charge of training Iraq’s security forces, gave a president in a tight race for reelection a little extra firepower in the domestic perception wars. Stepping blithely across a classic no-no line for the military, hewrote a well-placed op-ed in the Washington Post as General Johnnie-on-the-spot, plugging “tangible progress” in Iraq and touting “reasons for optimism.”
Given George W. Bush’s increasingly dismal and unpopular mission-unaccomplished war and occupation, it was like the cavalry riding to the rescue. It shouldn’t have been surprising, then, that the general, backed and promoted in the years to come by various neocon warriors, would be the military man the president would fall for. Over the first half of the “surge” year of 2007, Bush would publicly cite the general more than 150 times, 53 in May alone. (And Petraeus, a man particularly prone toward those who idolized him — see: Broadwell, Paula — returned the favor.)
But there was another step up the ladder of perception that would make him the perfect neocon warrior. While commanding general at Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, in 2005-2006, he also became the “face” of a new doctrine. Well, actually, a very old and particularly dead doctrine that went by the name of counterinsurgency or, acronymically, COIN. It had been part and parcel of the world of colonial and neocolonial wars and, in the 1960s, became the basis for the U.S. ground war and “pacification” program in South Vietnam — and we all know how that turned out.
Amid the greatest defeat the U.S. had suffered since the burning of Washington in 1814, counterinsurgency as a doctrine was left for dead in the rubble of Vietnam. With a sigh of relief, the military high command turned back to the task of stopping Soviet armies-that-never-would from pouring through Germany’s Fulda Gap. Even in the military academies they ceased to teach counterinsurgency — until Petraeus and his team disinterred it, dusted it off, polished it up, and turned it into the military’s latest war-fighting bible. Via a new Army and Marine field manual Petraeus helped to oversee, it would be presented as the missing formula for success in the Bush administration’s two flailing, failing invasions-cum-occupations on the Eurasian mainland.
It would gain such acclaim, in fact, that the University of Chicago Press would publish it as a trade paperback on July 4, 2007. Already back in Baghdad filling the role of Washington’s savior, the general, who had already written a foreward for that “paradigm shattering” manual, would flog it with this classic blurb: “Surely a manual that’s on the bedside table of the president, vice president, secretary of defense, 21 of 25 members of the Senate Armed Services Committee, and many others deserves a place at your bedside too.”
And really, you know the rest. He would be sold (and, from Baghdad, sell himself) to the public the same way Saddam’s al-Qaeda links and weapons of mass destruction had been. He, too, would be rolled out as a product — our “surge commander” — and soon enough become the general of the hour, and Iraq a success story for the ages. Then, appointed CENTCOM commander, the military man in charge of Washington’s two wars, by Bush, he made it out of town before it became fully apparent that his successes in Iraq would leave the U.S. out on its ear a few years down the line.
The Fall of the American Empire (Writ Small)
Afghanistan followed as he maneuvered to box a new president, Barack Obama, into a new “surge” in another country. Then, his handpicked war commander General Stanley McChrystal, newly minted COIN believer, “ascetic,” and “rising superstar” (who wouldundergo his own Petraeus-like media build-up), went down in shame over nasty commentsmade by associates about the Obama White House. In mid-2010, Petraeus would take McChrystal’s place to save another president by bringing COIN to bear in just the right way. The usual set of hosannas — and even less success than in Iraq — followed.
But as with Saddam Hussein’s mythical WMDs, it seemed scarcely to matter when there was no there there. Even though Afghanistan’s two COIN commanders had visibly failed in a war against an under-armed, undermanned, none-too-popular minority insurgency, and even though the doctrine of counterinsurgency would soon be tossed off a moving drone and left to die in the Afghan rubble, Petraeus once again made it out in one piece. In Washington, he was still hailed as the soldier of his generation and President Obama, undoubtedly fearing him in 2012, either as a candidate or a supporter of another Republican candidate, promptly stashed him away at the CIA, sending him safely into the political shadows.
With that, Petraeus left his four stars behind, shed COIN-mode just as his doctrine was collapsing completely, and slipped into the directorship of a militarizing CIA and its drone wars. He remained widely known, in the words of Michael O’Hanlon of the Brookings Institution (praising Broadwell’s biography), as “the finest general of this era and one of the greatest in modern American history.” Unlike George W. Bush and crew who, despite pulling in staggering speaker’s fees and writing memoirs for millions, now found themselves in a far different set of shadows, he looked like the ultimate survivor — until, of course, books and “bedsides” resurfaced in unexpected ways.
In the Iraq surge moment, the liberal advocacy group MoveOn.org unsuccessfully tried to label him “General Betray Us.” Now, as his affair with Broadwell unraveled into the reality TV show of our moment, he became General Betray Himself, a figure of derision, an old man with a young babe, the “cloak-and-shag-her” guy (as one New York Post screaming headline put it).
So here you have it, the two paradigmatic figures of the closing of the “American Century”: the president’s son whose ambitions were stoked by Texas politics after years in the personal wilderness and the man who married the superintendent’s daughter and rose like a meteor in a military that could never win a war. In the end, as the faces of American-disaster-masquerading-as-success, neither made it out of town before shame caught up with them. It’s a measure of their importance, however, that Bush was finally put to flight by a global economic meltdown, Petraeus by the local sexual version of the same. Again, it’s history vs. farce.
Or think of the Petraeus version of collapse as a tryout for the fall of the American empire, writ very small, with Jill Kelley and Paula Broadwell as our Gibbons and the volume of email, including military sexting, taking the place of his six volumes. A poster general for American decline, David Petraeus will be a footnote to history, a man out for himself who simply went a bridge or a book too far. George W. and crew were the real thing: genuine mad visionaries who simply mistook their dreams and fantasies for reality.
But wasn’t it fun while it lasted? Wasn’t it a blast to occupy Washington, be treated as a demi-god, go to Pirate-themed parties in Tampa with a 28-motorcycle police escort, and direct your own biography… even if it did end as Fifty Shades of Khaki?
Tom Engelhardt, co-founder of the American Empire Project and author of The United States of Fear as well as The End of Victory Culture, his history of the Cold War, runs the Nation Institute’s TomDispatch.com. His latest book, co-authored with Nick Turse, is Terminator Planet: The First History of Drone Warfare, 2001-2050. You can see his recent interview with Bill Moyers on supersized politics, drones, and other subjects by clicking here.
[Note for TomDispatch Readers: A small bow to several sites that I always find particularly helpful: my daily companion Antiwar.com, Juan Cole’s invaluable Informed Comment blog, the always provocative War in Context run by Paul Woodward, and Noah Shachtman’sDanger Room at Wired magazine. (At that site, I particularly recommend Spencer Ackerman’s mea culpa for having been drawn into the cult of Petraeus. Scores of other journalists and pundits had far more reason to write such a piece -- and didn’t.) By the way, in case you think that, until recently, it wasn’t possible for anyone to see what is now commonly being written about the general, check out a piece I posted in 2008 under the title “Selling the President’s General.”]
Follow TomDispatch on Twitter @TomDispatch and join us on Facebook. Check out the newest Dispatch book, Nick Turse’s The Changing Face of Empire: Special Ops, Drones, Proxy Fighters, Secret Bases, and Cyberwarfare.
Copyright 2012 Tom Engelhardt
]]>On Oct. 19, the Wall Street Journal’s editorial board argued that Iran may be closer to a nuclear weapon than even Israeli estimates and that it could be producing a “crude “gun-type” bomb of the sort that leveled Hiroshima”. From “Tick-Tock Tehran“:
A report earlier this month from the Washington, [...]]]>
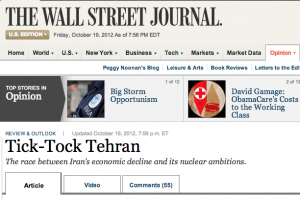 On Oct. 19, the Wall Street Journal’s editorial board argued that Iran may be closer to a nuclear weapon than even Israeli estimates and that it could be producing a “crude “gun-type” bomb of the sort that leveled Hiroshima”. From “Tick-Tock Tehran“:
On Oct. 19, the Wall Street Journal’s editorial board argued that Iran may be closer to a nuclear weapon than even Israeli estimates and that it could be producing a “crude “gun-type” bomb of the sort that leveled Hiroshima”. From “Tick-Tock Tehran“:
A report earlier this month from the Washington, D.C.-based Institute for Science and International Security (ISIS) warns that Tehran may be closer than even the Israelis think to enriching uranium to about 90%, the grade needed for a nuclear weapon. According to the ISIS study, the Iranians could combine their stockpiles of civilian- and medium-grade uranium to produce a bomb’s worth of 90% uranium in about two to four months.
That doesn’t put Iran within sight of a bomb, at least not yet. “Iran would need many additional months to manufacture a nuclear device suitable for underground testing,” the report says, “and even longer to make a reliable warhead for a ballistic missile.”
But this judgment assumes that Iran seeks to have a sophisticated nuclear weapon from the get-go, rather than a crude “gun-type” bomb of the sort that leveled Hiroshima, and which would be much simpler to produce. The judgment also assumes that Iran has no more enriched uranium than what the International Atomic Energy Agency reports it has. Yet Tehran has a record of nuclear deceit. Intelligence analysts shouldn’t assume that absence of evidence means evidence of absence.
In other words, be afraid, dear reader, be very afraid, because an Islamic Republic is intent on destroying you while everyone is looking the other way. Of course, this assessment has little to with facts. (It’s no secret, by the way, that the WSJ’s editorial board is hawkish on Iran and practically every other issue pertaining to US foreign policy. We’ve highlighted some examples here, here and here.) Indeed, so outrageous was the WSJ’s spin that ISIS, an anti-weapons proliferation institution with no reputation for being soft on Iran, was moved to respond:
The Wall Street Journal published an editorial on October 19, 2012 titled “Tick-Tock Tehran,” which referenced our recent ISIS report, Iran’s Evolving Breakout Potential. We would like to point out a central conclusion of our report, namely that the chance Iran will “break out” and build a nuclear weapon in the next year remains low. A straightforward method to help keep this probability low is to increase the frequency of International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) inspections of Iran’s main uranium enrichment plants. In addition, while we did not explicitly discuss this subject in our report, Iran is unlikely to build a gun-type nuclear weapon like the type that destroyed Hiroshima. If Iran decided to build a nuclear weapon, it would not be able to build a gun-type significantly faster than the other type of crude fission weapon, an implosion type that was used to destroy Nagasaki and has already been pursued by Iran, according to evidence assembled by the IAEA.
Iran can “currently break out in as little as 2-4 months”, note report authors David Albright, Christina Walrond, William Witt, and Houston Wood, but that could only occur if Iran made the decision to do so. While that likelihood remains low, an Iranian decision to breakout would be quickly detected:
Our estimates provide the length of time that Iran would need to produce enough weapon-grade uranium for a nuclear weapon, if Iran decided to do so. At this time, it is widely accepted that Iran has not made a decision to actually build a nuclear weapon, although it appears to be furthering its capability to make them.
Our estimate that Iran can currently break out in as little as 2-4 months provides adequate time for the United States to both detect and respond to the breakout before Iran accumulates enough weapon-grade uranium for one nuclear weapon. Because Iran fears a military response, it is unlikely to breakout. We assessed in our study that breakout times could reduce to about one month during the next year. But in all the scenarios we considered, the breakout would remain detectable to provide time for U.S. action. As a result, during at least the next year, our estimates support that the likelihood of an Iranian breakout will also be low.
And getting a weapon doesn’t mean you’ll be able to use it right away. ISIS states that Iran would need “many additional months” to produce a nuclear device suitable for testing and “even longer to make a reliable warhead for a ballistic missile.”
What did the WSJ base its WWII bomb-style assessment on? Clearly not expertise. ISIS’s response:
…The WSJ editorial offers a crude gun-type bomb of the type that destroyed Hiroshima as a way for Iran to save time in building the nuclear weapon, compared to building the conceptually more difficult implosion-type design. However, we assess that gun-type nuclear weapons are an unlikely choice for Iran and in any case will not save it a significant amount of time in fielding a nuclear device for an underground test aimed at establishing a nuclear weapon status or a deliverable nuclear weapon able to fit on a ballistic missile.
The biggest weakness of choosing a gun-type design is that Iran would need double the amount of weapon-grade uranium compared to that needed for an implosion-type design, increasing the time to breakout and accumulating sufficient weapon-grade uranium for one weapon from at least 2-4 months to at least 4-8 months.
But who needs facts when you sit on the editorial board of one of the most widely read newspapers in the world, right? Apparently from all the way up there, it’s easy to ignore telling recent history and the tragic consequences of a war that the US waged on false pretenses.
]]>By Dilip Hiro
via Tom Dispatch
The United States and Pakistan are by now a classic example of a dysfunctional nuclear family (with an emphasis on “nuclear”). While the two governments and their peoples become more suspicious and resentful of [...]]]>
By Dilip Hiro
via Tom Dispatch
 The United States and Pakistan are by now a classic example of a dysfunctional nuclear family (with an emphasis on “nuclear”). While the two governments and their peoples become more suspicious and resentful of each other with every passing month, Washington and Islamabad are still locked in an awkward post-9/11 embrace that, at this juncture, neither can afford to let go of.
The United States and Pakistan are by now a classic example of a dysfunctional nuclear family (with an emphasis on “nuclear”). While the two governments and their peoples become more suspicious and resentful of each other with every passing month, Washington and Islamabad are still locked in an awkward post-9/11 embrace that, at this juncture, neither can afford to let go of.
Washington is keeping Pakistan, with its collapsing economy and bloated military, afloat but also cripplingly dependent on its handouts and U.S.-sanctioned International Monetary Fund loans. Meanwhile, CIA drones unilaterally strike its tribal borderlands. Islamabad returns the favor. It holds Washington hostage over its Afghan War from which the Pentagon won’t be able to exit in an orderly fashion without its help. By blocking U.S. and NATO supply routes into Afghanistan (after a U.S. cross-border air strike had killed 24 Pakistani soldiers) from November 2011 until last July, Islamabad managed to ratchet up the cost of the war while underscoring its indispensability to the Obama administration.
At the heart of this acerbic relationship, however, is Pakistan’s arsenal of 110 nuclear bombs which, if the country were to disintegrate, could fall into the hands of Islamist militants, possibly from inside its own security establishment. As Barack Obama confided to his aides, this remains his worst foreign-policy nightmare, despite the decision of the U.S. Army to train a commando unit to retrieve Pakistan’s nukes, should extremists seize some of them or materials to produce a “dirty bomb” themselves.
Two Publics, Differing Opinions
Pakistan’s military high command fears the Pentagon’s contingency plans to seize its nukes. Following the clandestine strike by U.S. SEALs that killed Osama bin Laden in Abbottabad in May 2011, it loaded elements of its nuclear arsenal onto trucks, which rumbled around the country to frustrate any possible American attempt to grab its most prized possessions. When Senator John Kerry arrived in Islamabad to calm frayed nerves following Bin Laden’s assassination, high Pakistani officials insisted on a written U.S. promise not to raid their nuclear arsenal. He snubbed the demand.
Since then mutual distrust between the two nominal allies — a relationship encapsulated by some in the term “AmPak” — has only intensified. Last month, for instance, Pakistan became the sole Muslim country to officially call on the Obama administration to ban the anti-Islamic 14-minute video clip Innocence of Muslims, which depicts the Prophet Muhammad as a womanizer, religious fraud, and pedophile.
While offering a bounty of $100,000 for the killing of Nakoula Basseley Nakoula, an Egyptian-American Christian producer of the movie, Pakistan’s Railways Minister Ghulam Ahmad Bilour called on al-Qaeda and the Pakistani Taliban to be “partners in this noble deed.” Prime Minister Raja Ashraf distanced his government from Bilour’s incitement to murder, a criminal offense under Pakistani law, but did not dismiss him from the cabinet. The U.S. State Department strongly condemned Bilour’s move.
Pakistan also stood out as the only Muslim state whose government declared a public holiday, “Love the Prophet Muhammad Day,” to encourage its people to demonstrate against the offending movie. The U.S. Embassy’s strategy of disarming criticism with TV and newspaper ads showing President Obama and Secretary of State Hillary Clinton condemning “the content and the message” of the film failed to discourage protesters. In fact, the demonstrations in major Pakistani cities turned so violent that 23 protesters were killed, the highest figure worldwide.
 Taking advantage of the government’s stance, proscribed jihadist organizations made a defiant show of their continued existence. In Lahore, the capital of Punjab, the country’s largest province, activists from the banned Lashkar-e Taiba (Army of the Pure), whose leader Hafiz Saeed is the target of a $10 million bounty by Washington, led protesters toward the American consulate where perimeter defenses had been breached earlier in the week. In Islamabad, activists from the Sipah-e-Sahaba (Soldiers of the Prophet’s Companions), an outlawed Sunni faction, clashed with the police for hours in the course of a march to the heavily guarded diplomatic enclave.
Taking advantage of the government’s stance, proscribed jihadist organizations made a defiant show of their continued existence. In Lahore, the capital of Punjab, the country’s largest province, activists from the banned Lashkar-e Taiba (Army of the Pure), whose leader Hafiz Saeed is the target of a $10 million bounty by Washington, led protesters toward the American consulate where perimeter defenses had been breached earlier in the week. In Islamabad, activists from the Sipah-e-Sahaba (Soldiers of the Prophet’s Companions), an outlawed Sunni faction, clashed with the police for hours in the course of a march to the heavily guarded diplomatic enclave.
These outlawed organizations continue to operate with impunity in an environment that has grown rabidly anti-American. A June 2012 survey by the Washington-based Pew Research Center (PRC) found that 74% of Pakistanis consider the United States an enemy. By contrast, only 12% believe that U.S. aid helps solve problems in their country in a situation in which 89% describe their nation’s economic situation as “bad.”
The American public’s view of Pakistan is equally bleak. February polls byGallup and Fox News indicated that 81% of Americans had an unfavorable view of that country; just 15% held a contrary view, the lowest figure of the post-9/11 period (with only the remaining “axis of evil” states of Iran and North Korea faring worse).
Clashing Views on the War on Terror
Most Americans consider Pakistan an especially unreliable ally in Washington’s war on terror. That it provided safe haven to bin Laden for 10 years before his violent death in 2011 reinforced this perception. Bin Laden’s successor, Ayman Zawahiri, is widely believed to be hiding in Pakistan. So, too, are Mullah Muhammad Omar and other leaders of the Afghan Taliban.
It beggars belief that this array of Washington’s enemies can continue to function inside the country without the knowledge of its powerful Inter-Services Intelligence directorate (ISI) which reputedly has nearly 100,000 employees and informers. Even if serving ISI officers are not in cahoots with the Afghan Taliban, many retired ISI officers clearly are.
The rationale for this, top Pakistani officials say privately, is that the Afghan Taliban and the allied Haqqani Network are not attacking targets in Pakistan and so pose no threat to the state. In practice, these political-military entities are being sustained by Islamabad as future surrogates in a post-American Afghanistan. Their task is to ensure a pro-Islamabad government in Kabul, immune to offers of large-scale economic aid from India, the regional superpower. In short, it all boils down to Washington and Islamabad pursuing clashing aims in war-ravaged Afghanistan and in Pakistan as well.
The Pakistani government’s multifaceted stance toward Washington has wide public support. Popular hostility toward the U.S. stems from several interrelated factors. Above all, most Pakistanis view the war on terror from a radically differently perspective than Americans. Since its primary targets have been the predominantly Muslim countries of Afghanistan and Iraq, they equate it with an American crusade against Islam.
While U.S. pundits and politicians invariably cite the $24 billion in assistance and military aid Washington has given Islamabad in the post-9/11 period, Pakistanis stress the heavy price they have paid for participating in the Washington-led war. “No country and no people have suffered more in the epic struggle against terrorism than Pakistan,” said President Asif Ali Zardari at the United Nations General Assembly last month.
His government argues that, as a result of joining the war on terror, Pakistan has suffered a loss of $68 billion over the past decade. A widely disseminated statistic at home, it includes estimated losses due to a decline in foreign investments and adverse effects on trade, tourism, and businesses. Islamabad attributes all this to the insecurity caused by the terrorist acts of local jihadists in response to its participation in Washington’s war. Then there are the roughly 4,000 Pakistani military fatalities suffered during post-9/11 operations against terror groups and other homegrown militants — significantly higher than all allied troops killed in Afghanistan. Some 35,000 civilians have also died or suffered injuries in the process.
Drones Fuel Popular Rage
During a September address to the Asia Society in New York, Foreign Minister Hinna Rabbani Khar was asked for an explanation of the rampant anti-American sentiment in her country. She replied with a single word: “drones.” At any given time, CIA drones, buzzing like wasps and armed with Hellfire missiles, circle round the clock over an area in Pakistan’s tribal zone, their high-resolution cameras recording movements below. This fills people on the ground with unending terror, being unable to guess when and where the missiles will be fired.
A June Pew Research Center survey shows that 97% of Pakistanis familiar with the drone attacks held a negative view of them. “Those who are familiar with the drone campaign also overwhelmingly (94%) believe the attacks kill too many innocent people,” states its report. “Nearly three-quarters (74%) say they are not necessary to defend Pakistan from extremist organizations.” (In stark contrast, a February Washington Post-ABC News poll found that 83% of Americans — and 73% of liberal Democrats — support Obama’s drone onslaught.)
A recent anti-drone “march” by a nine-mile long motorcade from Islamabad to the border of the South Waziristan tribal agency was led by Imran Khan, head of the Movement for Justice political party. Joined by protesters from the U.S.and Britain, it was a dramatic reminder of the depth of popular feeling against the drones. By refraining from forcibly entering South Waziristan in defiance of an official ban, Khan stayed within the law. And by so doing, he enhanced his already impressive 70% approval rating and improved the chances of his party — committed to ending Islamabad’s participation in Washington’s war on terror — to achieve a breakthrough in the upcoming parliamentary election.
Unlike in Yemen, where the government has authorized the Obama administration to stage drone attacks, Pakistani leaders, who implicitly accepted such strikes before the Pentagon’s gross violation of their country’s sovereignty in the bin Laden killing, no longer do so. “The use of unilateral strikes on Pakistan territory is illegal,” said Foreign Minister Khar. Her government, she explained, needed to rally popular backing for its campaign to quash armed militant groups, and the drones make that impossible. “As the drones fly over the territory of Pakistan, it becomes an American war and the whole logic of this being our fight, in our own interest, is immediately put aside and again it is a war imposed on us.”
Underlying the deployment of a drone, helicopter, or jet fighter to hit a target in a foreign country is an updated version of the Vietnam-era doctrine of “hot pursuit,” which ignores the basic concept of national sovereignty. Pakistani leaders fear that if they do not protest Washington’s continued use of drones for “targeted killings” of Pakistan-based individuals selected in the White House, their arch-rival India will follow suit. It will hit the camps in Pakistan allegedly training terrorists to destabilize Indian Kashmir. That is one of the ongoing nightmares of Pakistan’s senior generals.
The Nuclear Conundrum
Since India would be the prime target of any nuclear-armed extremists, the Indian government dreads the prospect of Pakistan’s nukes falling into such hands far more than President Obama. The alarm of both Delhi and Washington is well justified, particularly because Pakistan’s arsenal is growingfaster than any on Earth — and the latest versions of nukes it’s producing are smaller and so easier to hijack.
Over the past five years, Pakistani extremists have staged a series of attacks on sensitive military installations, including nuclear facilities. In November 2007, for example, they attacked Sargodha airbase where nuclear-capable F-16 jet aircraft are stationed. The following month a suicide bomber targeted a Pakistani Air Force base believed to hold nuclear weapons at Kamra, 37 miles northwest of Islamabad. In August 2008, a group of suicide bombers blew up the gates to a weapons complex at the Wah cantonment containing a nuclear warhead assembly plant, leaving 63 people dead. A further assault on Kamra took place in October 2009 and yet another last August, this time by eight suicide bombers belonging to the Pakistani Taliban.
Given Pakistan’s dependence on a continuing supply of U.S.-made advanced weaponry — essential to withstand any onslaught by India in a conventional war — its government has had to continually reassure Washington that the security of its nuclear arsenal is foolproof. Its leaders have repeatedly assured their American counterparts that the hemispheres containing nuclear fuel and the triggers for activating the weapons are stored separately under tight guard. This has failed to allay the anxieties of successive American presidents. What disconcerts the U.S. is that, despite contributing hundreds of millions of dollars to underwrite programs to help Pakistan secure its nuclear arms, it does not know where many of these parts are stored.
This is not going to change. The military planners in Islamabad correctly surmise that Delhi and Washington would like to turn Pakistan into a non-nuclear power. At present, they see their nuclear arsenal as the only effective deterrent they have against an Indian aggression which, in their view, theyexperienced in 1965. “We developed all these nukes to use against India,” said an unnamed senior Pakistani military officer recently quoted in the London-based Sunday Times Magazine. “Now they turn out to be very useful in dealing with the U.S.”
In short, Pakistan’s military high command has come to view its nuclear arsenal as an effective deterrent not only against its traditional adversary, India, but also its nominal ally in Washington. If such thinking solidifies as the country’s military doctrine in the years following the Pentagon’s withdrawal from Afghanistan, then Pakistan may finally find itself removed from Washington’s list of non-NATO allies, ending the dysfunctional nuclear family of international politics. What that would mean in global terms is anyone’s guess.
Dilip Hiro, a TomDispatch regular, is the author of 33 books, the most recent being Apocalyptic Realm: Jihadists in South Asia (Yale University Press, New Haven and London). To listen to Timothy MacBain’s latest Tomcast audio interview in which Hiro discusses the embattled Pakistan-U.S. relationship, click here or download it to your iPod here.
Follow TomDispatch on Twitter @TomDispatch and join us on Facebook.
Copyright 2012 Dilip Hiro
]]>The rising specter of terrorism in Syria shows that by clinging to power and refusing to implement meaningful reforms, Arab autocrats in Syria, Bahrain, and elsewhere are indirectly contributing to the resurgence of terrorism in their societies. Arab protests started peacefully, but almost in every country regime repression and torture ultimately pushed [...]]]>
 The rising specter of terrorism in Syria shows that by clinging to power and refusing to implement meaningful reforms, Arab autocrats in Syria, Bahrain, and elsewhere are indirectly contributing to the resurgence of terrorism in their societies. Arab protests started peacefully, but almost in every country regime repression and torture ultimately pushed popular revolts toward violence.
The rising specter of terrorism in Syria shows that by clinging to power and refusing to implement meaningful reforms, Arab autocrats in Syria, Bahrain, and elsewhere are indirectly contributing to the resurgence of terrorism in their societies. Arab protests started peacefully, but almost in every country regime repression and torture ultimately pushed popular revolts toward violence.
This cynical calculus allowed Arab autocrats to claim that protests were directed from the outside and resistance was the work of terrorist groups. In Egypt and Tunisia, regimes fell while popular protests were still peaceful.
In Yemen and Libya, regimes refused to leave and instead used bloody repression. While they failed to quell protests, some opposition groups were forced to militarize. In Bahrain and Syria, regimes have changed the narrative from human rights and reform to sectarianism, using the divide and rule approach. Their self-fulfilling prophecy of terrorism has come to pass because of their conscious policy to discredit the opposition and shore up their legitimacy.
While successful in the short-run, this policy is destined to fail in the long run. Domestic terrorist groups that could emerge from the opposition would not only target regime assets; they will go after U.S. and other western economic interests and personnel in those countries.
In Bahrain, for instance, Sunni vigilantes and even some government officials are encouraged by elements within the ruling family to direct their anger against Americans for their perceived support of pro-reform dissidents. Some regime conservatives increasingly view the Americans, the Shia majority, and Iran as an unholy alliance undermining the Khalifa rule.
The recently appointed minister of information Samira Rajab is anti-Shia, anti-American, and a fan of Saddam Hussein. She blames foreign media and outside provocateurs for the problems in her country—a similar narrative to that of the Assad regime in Syria.
The traditional faction within the Bahraini ruling family, including the Prime Minister, is turning to Saudi Arabia for support. The king and his son the crown prince Salman are committed to an independent and more inclusive country. Unfortunately, they have been marginalized by the older members of the family council and their younger xenophobic Sunni supporters.
By inviting Bahrain’s crown prince to Washington last week, the administration was sending a signal to the conservative faction that it still supports the king and his son and their plan to seek meaningful dialogue with the opposition. The other part of Washington’s message is that the resumption of some arms shipments that were halted after last year’s uprising applied to the coast guard and would not be used against the Bahraini people. It gave Salman something to take back, but indirectly signaled to the old guard that the young prince, not his great uncle, is the preferred interlocutor with Washington. Of course, to save face the old guard has touted the release of the arms as a sign that they are still in Washington’s graces.
It’s clear that Saudi Arabia is trying to expand its hegemony over the rest of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), beginning with Bahrain. The Prime Minister Khalifa and his supporters within the ruling family no longer seem to care about the sovereignty of Bahrain or its historically liberal tradition. Their main concern is their own survival. In the 1980s I wrote a book on the GCC and highlighted some of the challenges that would face the organization down the line. I’m afraid, it’s coming home to roost.
If the proposed Saudi-Bahraini federation is concluded, Bahrain would cease to exist as an independent state and would become a province under Saudi suzerainty. The Saudis and their Khalifa quislings would expand their repression of the Shia community and Sunni human rights activists in the name of fighting Shia and Iran. The opposition will likely arm, and domestic terrorist groups would emerge in both countries.
In Syria, human rights protests similarly started peacefully but have been forced to defend themselves with arms confiscated from the military and obtained from the outside. The Assad regime continues to kill and torture civilians. Like Bahrain, Assad is blaming foreign provocateurs and terrorists for the bloodshed. The regime’s acceptance of the Kofi Annan plan is a rouse to placate the international community and buy the regime more time.
The Annan plan is doomed to fail because the regime views the domestic situation as a zero-sum game. It believes its survival can only be assured through continued repression and control. Negotiating with the opposition is a fantasy that Assad cannot afford to indulge in if his Alawite minority rule is to survive.
Since 9/11 Arab autocrats have cooperated closely on counterterrorism with the US and other western countries. At the same time, they branded domestic dissidents and pro-democracy activists as radicals and urged western governments not to fret over their harsh tactics against their citizens.
Arab regimes mistakenly thought that autocracy, not democracy, was critical for fighting terrorism and that Western support for human rights in Arab countries would dilute such an effort. Because Arab autocrats were pliant partners, western governments, unfortunately, became addicted to autocracy, which in turn helped autocrats become more entrenched.
Arab rulers seem to forget that many non-Western democracies, including Muslim Indonesia and Turkey, also have been strong partners with western governments in fighting terrorism. The fall of the dictators in Egypt, Tunisia, Yemen, and Libya would not preclude these countries from fighting terrorism.
Arab Islamic autocrats co-operate in the fight against terrorism to preserve their rule; whereas democracies do so to protect their societies and way of life.
Washington and other Western capitals should make it clear to the remaining Arab dictators, in word and in deed that the game is up. They must implement genuine political reform or step aside. The world cannot tolerate a resurgence of terrorism because of their repressive rule and sectarian politics.
Dr. Emile Nakhleh is the former director of the CIA Political Islam Strategic Analysis Program, a Research Professor at the University of New Mexico and a National Intelligence Council Associate. He is the author of A Necessary Engagement: Reinventing America’s Relations with the Muslim World and Bahrain: Political Development in a Modernizing Society.
]]>By Dilip Hiro
Posted by Tom Dispatch
The following ingredients should go a long way to produce a political thriller. Mr. M, a jihadist in an Asian state, has emerged as the mastermind of a terrorist attack in a neighboring country, [...]]]>
By Dilip Hiro
Posted by Tom Dispatch
The following ingredients should go a long way to produce a political thriller. Mr. M, a jihadist in an Asian state, has emerged as the mastermind of a terrorist attack in a neighboring country, which killed six Americans. After sifting through a vast cache of intelligence and obtaining a legal clearance, the State Department announces a $10 million bounty for information leading to his arrest and conviction. Mr. M promptly appears at a press conference and says, “I am here. America should give that reward money to me.”
A State Department spokesperson explains lamely that the reward is meant for incriminating evidence against Mr. M that would stand up in court. The prime minister of M’s home state condemns foreign interference in his country’s internal affairs. In the midst of this imbroglio, the United States decides to release $1.18 billion in aid to the cash-strapped government of the defiant prime minister to persuade him to reopen supply lines for U.S. and NATO forces bogged down in the hapless neighboring Islamic Republic of Afghanistan.
Alarmingly, this is anything but fiction or a plot for an upcoming international sitcom. It is a brief summary of the latest development in the fraught relations between the United States and Pakistan, two countries locked into an uneasy embrace since September 12, 2001.
Mr. M. is Hafiz Muhammad Saeed, a 62-year-old former academic with a tapering, hennaed beard, and the founder of the Lashkar-e Taiba (the Army of the Pure, or LeT), widely linked to several outrageously audacious terrorist attacks in India. The LeT was formed in 1987 as the military wing of the Jammat-ud Dawa religious organization (Society of the Islamic Call, or JuD) at the instigation of the Pakistani army’s formidable intelligence agency, Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI). The JuD owes its existence to the efforts of Saeed, who founded it in 1985 following his return to his native Lahore after two years of advanced Islamic studies in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, under the guidance of that country’s Grand Mufti, Shaikh Abdul Aziz bin Baz.
On its formation, the LeT joined the seven-year-old anti-Soviet jihad in Afghanistan, an armed insurgency directed and supervised by the ISI with funds and arms supplied by the CIA and the Saudis. Once the Soviets withdrew from Afghanistan in 1989, the Army of the Pure turned its attention to a recently launched anti-Indian jihad in Indian-administered Kashmir and beyond. The terrorist attacks attributed to it range from the devastating multiple assaults in Mumbai in November 2008, which resulted in 166 deaths, including those six Americans, to a foiled attack on the Indian Parliament in New Delhi in December 2001, and a successful January 2010 attack on the airport in Kashmir’s capital Srinagar.
In January 2002, in the wake of Washington’s launching of the Global War on Terror, Pakistan formally banned the LeT, but in reality did little to curb its violent cross-border activities. Saeed remains its final authority. In a confession, offered as part of a plea bargain after his arrest in October 2009 in Chicago, David Coleman Headley, a Pakistani-American operative of LeT involved in planning the Mumbai carnage, said: “Hafiz Saeed had full knowledge of the Mumbai attacks and they were launched only after his approval.”
In December 2008, the United Nations Security Council declared the JuD a front organization for the banned LeT. The provincial Punjab government then placed Saeed under house arrest using the Maintenance of Public Order law. But six months later, the Lahore High Court declared his confinement unconstitutional. In August 2009, Interpol issued a Red Corner Notice, essentially an international arrest warrant, against Saeed in response to Indian requests for his extradition. Saeed was again put under house arrest but in October the Lahore High Court quashed all charges against him due to lack of evidence.
It is common knowledge that Pakistani judges, fearing for their lives, generally refrain from convicting high-profile jihadists with political connections. When, in the face of compelling evidence, a judge has no option but to order the sentence enjoined by the law, he must either live under guard afterwards or leave the country. Such was the case with Judge Pervez Ali Shah who tried Mumtaz Qadri, the jihadist bodyguard who murdered Punjab’s governor Salman Taseer for backing an amendment to the indiscriminately applied blasphemy law. Soon after sentencing Qadri to capital punishment last October, Shah received several death threats and was forced into self-exile.
Aware of the failures of the Pakistani authorities to convict Saeed, U.S. agencies seemed to have checked and cross-checked the authenticity of the evidence they had collected on him before the State Department announced, on April 2nd, its reward for his arrest. This was nothing less than an implied declaration of Washington’s lack of confidence in the executive and judicial organs of Pakistan.
Little wonder that Pakistani Prime Minister Yousaf Raza Gilani took umbrage, describing the U.S. bounty as blatant interference in his country’s domestic affairs. Actually, this is nothing new. It is an open secret that, in the ongoing tussle between Pakistani President Asif Ali Zardari and his bête noire, army chief of staff General Ashfaq Parvez Kayani, the Obama administration has always backed the civilian head of state. That, in turn, has been a significant factor in Gilani’s stay in office since March 2008, longer than any other prime minister in Pakistan’s history.
How to Trump a Superpower
Given such strong cards, diplomatic and legal, why then did the Obama administration commit itself to releasing more than $1 billion to a government that has challenged its attempt to bring to justice an alleged mastermind of cross-border terrorism?
The answer lies in what happened at two Pakistani border posts 1.5 miles from the Afghan frontier in the early hours of November 26, 2011. NATO fighter aircraft and helicopters based in Afghanistan carried out a two-hour-long raid on these posts, killing 24 soldiers. Enraged, Pakistan’s government shut the two border crossings through which the U.S. and NATO had until then sent a significant portion of their war supplies into Afghanistan. Its officials also forced the U.S. to vacate Shamsi air base, which was being used by the CIA as a staging area for its drone air war in Pakistan’s tribal areas along the Afghan border. The drone strikes are exceedingly unpopular – one poll found 97% of respondents viewed them negatively — and they are vehemently condemned by a large section of the Pakistani public and its politicians.
Furthermore, the government ordered a comprehensive review of all programs, activities, and cooperation arrangements with the U.S. and NATO. It also instructed the country’s two-tier parliament to conduct a thorough review of Islamabad’s relations with Washington. Having taken the moral high ground, the Pakistani government pressed its demands on the Obama administration.
 An appointed Parliamentary Committee on National Security (PCNS) then deliberately moved at a snail’s pace to perform the task on hand, while the Pentagon explored alternative ways of ferrying goods into Afghanistan via other countries to sustain its war there. By contrast, a vociferous campaign against the reopening of the Pakistani supply lines led by the Difa-e Pakistan Council (Defense of Pakistan), representing 40 religious and political groups, headed by Hafiz Saeed, took off. Its leaders have addressed huge rallies in major Pakistani cities. It was quick to condemn Washington’s bounty on Saeed, describing it as “a nefarious attempt” to undermine the Council’s drive to protect the country’s sovereignty.
An appointed Parliamentary Committee on National Security (PCNS) then deliberately moved at a snail’s pace to perform the task on hand, while the Pentagon explored alternative ways of ferrying goods into Afghanistan via other countries to sustain its war there. By contrast, a vociferous campaign against the reopening of the Pakistani supply lines led by the Difa-e Pakistan Council (Defense of Pakistan), representing 40 religious and political groups, headed by Hafiz Saeed, took off. Its leaders have addressed huge rallies in major Pakistani cities. It was quick to condemn Washington’s bounty on Saeed, describing it as “a nefarious attempt” to undermine the Council’s drive to protect the country’s sovereignty.
Meanwhile, the loss of the daily traffic of 500 trucks worth of food, fuel, and weapons from the Pakistani port of Karachi through the Torkham and Chaman border crossings into Afghanistan, though little publicized in U.S. media, has undermined the fighting capability of U.S. and NATO forces.
“If we can’t negotiate or successfully renegotiate the reopening of ground lines of communication with Pakistan, we have to default and rely on India and the Northern Distribution Network (NDN),” said a worried Lieutenant General Frank Panter to the Readiness Subcommittee of the Armed Services Committee of the U.S. House of Representatives on March 30th. “Both are expensive propositions and it increases the deployment or redeployment.”
The main part of the NDN is a 3,220-mile rail network for transporting supplies between the Latvian port of Riga and the Uzbek town of Termez (connected by a bridge over the Oxus River to the Afghan settlement of Hairatan). According to the Pentagon, it costs nearly $17,000 per container to go through the NDN compared to $7,000 through the Pakistani border crossings.
Moreover, U.S. and NATO are allowed to transport only “non-lethal goods” through the NDN.
Other military officials have warned that the failure to reopen the Pakistani routes could even delay the schedule for withdrawing American “combat troops” from Afghanistan by 2014. That would be bad news for the Obama White House with the latest Washington Post/NBC News poll showing that, for the first time, even a majority of Republicans believe the Afghan War “has not been worth fighting.” A CBS News/New York Times survey indicated that support for the war was at a record low of 23%, with 69% of respondents saying that now was the time to withdraw troops.
In the Pakistani capital, Islamabad, the PCNS finally published a list of preconditions that the U.S. must meet for the reopening of supply lines. These included an unqualified apology for the air strikes last November, an end to drone attacks, no more “hot pursuit” by U.S. or NATO troops inside Pakistan, and the taxing of supplies shipped through Pakistan. Much to the discomfiture of the Obama administration, a joint session of the National Assembly and the Senate called to debate the PCNS report took more than two weeks to reach a conclusion.
On April 12th, the Parliament finally unanimously approved the demands andadded that no foreign arms and ammunition should be transported through Pakistan. The Obama administration is spinning this development not as an ultimatum but as a document for launching talks between the two governments.
Even so, it has strengthened Prime Minister Gilani’s hand as never before. Furthermore, he has to take into account the popular support the Saeed-led Difa-e Pakistan Council is building for keeping the Pakistani border crossings permanently closed to NATO traffic. Thus, Saeed, a jihadist with a U.S. bounty on his head, has emerged as an important factor in the complex Islamabad-Washington relationship.
Squeezing Washington: The Pattern
There is, in fact, nothing new in the way Islamabad has been squeezing Washington lately. It has a long record of getting the better of U.S. officials by identifying areas of American weakness and exploiting them successfully to further its agenda.
When the Soviet bloc posed a serious challenge to the U.S., the Pakistanis obtained what they wanted from Washington by being even more anti-Soviet than America. Afghanistan in the 1980s is the classic example. Following the Soviet military intervention there in December 1979, the Pakistani dictator General Muhammad Zia ul-Haq volunteered to join Washington’s Cold War against the Kremlin — but strictly on his terms. He wanted sole control over the billions of dollars in cash and arms to be supplied by the U.S. and its ally Saudi Arabia to the Afghan Mujahedin (holy warriors) to expel the Soviets from Afghanistan. He got it.
That enabled his commanders to channel a third of the new weapons to their own arsenals for future battle against their archenemy, India. Another third were sold to private arms dealers on profitable terms. When pilfered U.S. weapons began appearing in arms bazaars of the Afghan-Pakistan border towns (as has happened again in recent years), the Pentagon decided to dispatch an audit team to Pakistan. On the eve of its arrival in April 1988, the Ojhiri arms depot complex, containing 10,000 tons of munitions, mysteriously went up in flames, with rockets, missiles, and artillery shells raining down on Islamabad, killing more than 100 people.
By playing on Ronald Reagan’s view of the Soviet Union as “the Evil Empire,” Zia ul-Haq also ensured that the American president would turn a blind eye on Pakistan’s frantic, clandestine efforts to build an atom bomb. Even when the CIA, the National Security Agency, and the State Department determined that a nuclear weapon assembled by Pakistan had been tested at Lop Nor in China in early 1984, Reagan continued to certify to Congress that Islamabad was not pursuing a nuclear weapons program in order to abide by a law which prohibited U.S. aid to a country doing so.
Today, there are an estimated 120 nuclear bombs in the arsenal of a nation that has more Islamist jihadists per million people than any other country in the world. From October 2007 to October 2009, there were at least four attacks by extremists on Pakistani army bases known to be storing nuclear weapons.
In the post-9/11 years, Pakistan’s ruler General Pervez Musharraf managed to repeat the process in the context of a new Afghan war. He promptly joined President George W. Bush in his Global War on Terror, and then went on to distinguish between “bad terrorists” with a global agenda (al-Qaeda), and “good terrorists” with a pro-Pakistani agenda (the Afghan Taliban). Musharraf’s ISI then proceeded to protect and foster the Afghan Taliban, while periodically handing over al-Qaeda militants to Washington. In this way, Musharraf played on Bush’s soft spot — his intense loathing of al-Qaeda — and exploited it to further Pakistan’s regional agenda.
Emulating the policies of Zia ul-Haq and Musharraf, the post-Musharraf civilian government has found ways of diverting U.S. funds and equipment meant for fighting al-Qaeda and the Taliban to bolster their defenses against India. By inflating the costs of fuel, ammunition, and transport used by Pakistan’s 100,000 troops posted in the Afghan-Pakistan border region, Islamabad received more money from the Pentagon’s Coalition Support Fund (CSF) than it spent. It then used the excess to buy weapons suitable for fighting India.
When the New York Times revealed this in December 2007, the Musharraf government dismissed its report as “nonsense.” But after resigning as president and moving to London, Musharraf told Pakistan’s Express News television channel in September 2009 that the funds had indeed been spent on weapons for use against India.
Now, the widely expected release of the latest round of funds from the Pentagon’s CSF will raise total U.S. military aid to Islamabad since 9/11 to $14.2 billion, two-and-a-half times the Pakistani military’s annual budget.
There is a distinct, if little discussed, downside to being a superpower and acting as the self-appointed global policeman with a multitude of targets. An arrogance feeding on a feeling of invincibility and an obsession with winning every battle blind you to your own impact and even to what might be to your long-term benefit. In this situation, as your planet-wide activities become ever more diverse, frenzied, and even contradictory, you expose yourself to exploitation by lesser powers otherwise seemingly tied to your apron strings.
Pakistan, twice during America’s 33-year-long involvement in Afghanistan made a frontline state, is a classic example of that. Current policymakers in Washington should take note: it’s a strategy for disaster.
Dilip Hiro, a TomDispatch regular, is the author of 33 books, the most recent being the just-published Apocalyptic Realm: Jihadists in South Asia (Yale University Press, New Haven and London).
Copyright 2012 Dilip Hiro
Reposted by arrangement with Tom Dispatch
By John Feffer
The United States has long styled itself a Pacific power. It established the model of counterinsurgency in the Philippines in 1899 and defeated the Japanese in World War II. It [...]]]>
Reposted by arrangement with Tom Dispatch
By John Feffer
The United States has long styled itself a Pacific power. It established the model of counterinsurgency in the Philippines in 1899 and defeated the Japanese in World War II. It faced down the Chinese and the North Koreans to keep the Korean peninsula divided in 1950, and it armed the Taiwanese to the teeth. Today, America maintains the most powerful military in the Pacific region, supported by a constellation of military bases, bilateral alliances, and about 100,000 service personnel.
It has, however, reached the high-water mark of its Pacific presence and influence. The geopolitical map is about to be redrawn. Northeast Asia, the area of the world with the greatest concentration of economic and military power, is on the verge of a regional transformation. And the United States, still preoccupied with the Middle East and hobbled by a stalled and stagnating economy, will be the odd man out.
Elections will be part of the change. Next year, South Koreans, Russians, and Taiwanese will all go to the polls. In 2012, the Chinese Communist Party will also ratify its choice of a new leader to take over from President Hu Jintao. He will be the man expected to preside over the country’s rise from the number two spot to the pinnacle of the global economy.
But here’s the real surprise in store for Washington. The catalyst of change may turn out to be the country in the region that has so far changed the least: North Korea. In 2012, the North Korean government has trumpeted to its people a promise to create kangsong taeguk, or an economically prosperous and militarily strong country. Pyongyang now has to deliver somehow on that promise — at a time of food shortages, overall economic stagnation, and political uncertainty. This dream of 2012 is propelling the regime in Pyongyang to shift into diplomatic high gear, and that, in turn, is already creating enormous opportunities for key Pacific powers.
WWashington, which has focused for years on North Korea’s small but developing nuclear arsenal, has barely been paying attention to the larger developments in Asia. Nor will Asia’s looming transformation be a hot topic in our own presidential election next year. We’ll be arguing about jobs, health care, and whether the president is a socialist or his Republican challenger a nutcase. Aside from some ritual China-bashing, Asia will merit little mention.
President Obama, anxious about giving ammunition to his opponent, will be loath to fiddle with Asia policy, which is already on autopilot. So while others scramble to remake East Asia, the United States will be suffering from its own peculiar form of continental drift.
Pyongyang Turns on the Charm
On April 15, 1912, in an obscure spot in the Japanese empire, a baby was born to a Christian family proud of its Korean heritage. The 100th anniversary of the birth of Kim Il Sung, North Korea’s founder and dynastic leader, is coming up next year. Ordinarily, such an event would be of little importance to anyone other than 24 million North Koreans and a scattering of Koreans elsewhere. But this centennial also marks the date by which the North Korean regime has promised to finally turn things around.
Despite its pretensions to self-reliance, Pyongyang has amply proven that it can only get by with a lot of help from its friends. Until recently, however, North Korea was not exactly playing well with others.
It responded in a particularly hardline fashion, for instance, to the more hawkish policies adopted by new South Korean President Lee Myung Bak, when he took office in February 2008. The shooting of a South Korean tourist at the Mount Kumgang resort that July, the sinking of the South Korean naval ship the Cheonan in March 2010 (Pyongyang still claims it was not the culprit), and the shelling of South Korea’s Yeonpyeong Island later that year all accelerated a tailspin in north-south relations. During this period, the North tested a second nuclear device, prompting even its closest ally, China, to react in disgust and support a U.N. declaration of condemnation. Pyongyang also managed to further alienate Washington by revealing in 2010 that it was indeed pursuing a program to produce highly enriched, weapons-grade uranium, something it had long denied.
These actions had painful economic consequences. South Korea cancelled almost all forms of cooperation. The North’s second nuclear test scotched any incipient economic rapprochement with the United States. (The Bush administration had removed North Korea from its terrorism list, and there had been hints that other longstanding sanctions might sooner or later be dropped as part of a warming in relations.)
Only the North’s relationship with China was unaffected, largely because Beijing is gobbling up significant quantities of valuable minerals and securing access to ports in exchange for just enough food and energy to keep the country on life support and the regime afloat. Between 2006 and 2009, an already anemic North Korean economy contracted, and chronic food shortages again became acute.
To these economic travails must be added political ones. The country’s leadership is long past retirement, with 70-year-old leader Kim Jong Il younger than most of the rest of the ruling elite. He has designated his youngest son, Kim Jeong Eun, as his successor, but the only thing that this mystery boy seems to have going for him is his resemblance to his grandfather, Kim Il Sung.
Still, North Korea seems no closer to full-scale collapse today than during previous crises — like the devastating famine of the mid-1990s. A thoroughly repressive state and zero civil society seem to insure that no color revolution or “Pyongyang Spring” is in the offing. Waiting for the North Korean regime to go gently into the night is like waiting for Godot.
But that doesn’t mean change isn’t in the air. To jumpstart its bedraggled economy and provide a political boost for the next leader in the year of kangsong taeguk, North Korea is suddenly in a let’s-make-a-deal mode.
 Kim Jong Il’s recent visit to Siberia to meet Russian President Dmitri Medvedev, for instance, raised a few knowledgeable eyebrows. Conferring at a Russian military base near Lake Baikal, for the first time in a long while the North Korean leader even raised the possibility of a moratorium on nuclear weapons production and testing. More substantially, he concluded a preliminary agreement on a natural gas pipeline that could in itself begin to transform the politics of the region. It would transfer gas from the energy-rich Russian Far East through North Korea to economically booming but energy-hungry South Korea. The deal could net Pyongyang as much as $100 million a year.
Kim Jong Il’s recent visit to Siberia to meet Russian President Dmitri Medvedev, for instance, raised a few knowledgeable eyebrows. Conferring at a Russian military base near Lake Baikal, for the first time in a long while the North Korean leader even raised the possibility of a moratorium on nuclear weapons production and testing. More substantially, he concluded a preliminary agreement on a natural gas pipeline that could in itself begin to transform the politics of the region. It would transfer gas from the energy-rich Russian Far East through North Korea to economically booming but energy-hungry South Korea. The deal could net Pyongyang as much as $100 million a year.
The North’s new charm offensive wouldn’t have a hope in hell of succeeding if a similar change of heart weren’t also underway in the South.
The Bulldozer’s Miscalculation
On taking office, the conservative South Korean president Lee Myung Bak, known as “the Bulldozer” when he headed up Hyundai’s engineering division, promised to put Korean relations on a new footing. Ten years of “engagement policy” with the North had, according to Lee, produced an asymmetrical relationship. The South, he insisted, was providing all the cash, and the North was doing very little in exchange. Lee promised a relationship based only on quid pro quos.
What he got instead was tit for tat: harsher rhetoric and military action. Ultimately, although the North made no friends below the 38th parallel that way, the new era of hostility didn’t help the Lee administration either. South Koreans generally watched in horror as a relatively peaceful relationship veered dangerously close to military conflict.
Lee’s ruling party suffered a loss in last April’s by-elections, and in August, he replaced his hardline “unification” minister with a more conciliatory fellow. Still insisting on an apology for the Cheonan sinking and the Yeonpyeong shelling, the ruling party is nevertheless looking for ways to restore commercial ties and again provide humanitarian assistance to the North. Since the summer, representatives from North and South have met twice to discuss Pyongyang’s nuclear program. Although the two sides haven’t made substantial progress, the stage is set for the resumption of the Six Party Talks between the two Koreas, Russia, Japan, China, and the United States that broke off in 2007.
Even if the opposition party doesn’t sweep the conservatives out of power in the 2012 elections, South Korea will likely abandon Lee’s tough-guy approach. In September, his likely successor as the ruling party candidate in 2012, Park Geun-Hye, openly criticized Lee’s approach in an article in Foreign Affairs that called instead for “trustpolitik.”
One project Park singled out for mention is an inter-Korean railroad line that would “perhaps transform the Korean Peninsula into a conduit for regional trade.” That’s an understatement. Restoring the line and hooking it up to Russia’s Trans-Siberian Railroad would connect the Korean peninsula to Europe, reduce the shipment time of goods from one end of Eurasia to the other by about two weeks, and save South Korea up to $34 to $50 per ton in shipping costs. Meanwhile, the natural gas pipeline, which South Korea approved at the end of September, could reduce its gas costs by as much as 30%. For the world’s second largest natural gas importer, this would be a major savings.
Serious economic steps toward Korean reunification are not just a dream, in other words, but good business, too. Even in the worst moments of the recent period of disengagement, it’s notable that the two countries managed to preserve the Kaesong industrial complex located just north of the Demilitarized Zone. Run by South Korean managers and employing more than 45,000 North Koreans, the business zone is a boon to both sides. It helps South Korean enterprises facing competition from China, even as it provides hard currency and well-paying jobs to the North. The railroad and the pipeline would offer similar mutual benefits.
According to conventional wisdom, North Korea has a single bargaining chip, its small nuclear arsenal, which it will never give up. But a real estate agent would look at the situation differently. What North Korea really has is “location, location, location,” and it finally seems ready to cash in on its critical position at the heart of the world’s most vital economic region.
The train line would bind the world’s two biggest economic regions into a huge Eurasian market. And the pipeline, coupled with green energy projects in China, South Korea, and Japan, might begin to wean East Asia from its dependency on Middle Eastern oil and thus on the U.S. military to secure access and protect shipping routes.
Thought of another way, these projects and others like them lurking in the Eurasian future are significant not just for what they connect, but what they leave out: the United States.
Out in the Cold
The Bush administration anticipated Lee Myung Bak’s approach to North Korea by chucking the carrot and waving the stick. By 2006, however, Washington had made a U-turn and was beginning to engage Pyongyang seriously. The Obama administration took another tack, eventually adopting a policy of “strategic patience,” a euphemism for ignoring North Korea and hoping it wouldn’t throw a tantrum.
It hasn’t worked. North Korea has plunged full speed ahead with its nuclear program. The U.S./NATO air campaign against Libya’s Muammar Gaddafi, who had given up his nuclear program to secure better relations with the West, only reinforced Pyongyang’s belief that nukes are the ultimate guarantor of its security. The Obama administration continues to insist that the regime show its seriousness about denuclearization as a precondition for resuming talks. Even though Washington recently sent a small amount of flood relief, it refuses to offer any serious food assistance. Indeed, in June, the House of Representatives passed an amendment to the agriculture bill that prohibited all food aid to the country, regardless of need.
Though the administration will likely send envoy Stephen Bosworth to North Korea later this year, no one expects major changes in policy or relations to result. With a presidential election year already looming, the Obama administration isn’t likely to spend political capital on North Korea — not when Republicans would undoubtedly label any new moves as “appeasement” of a “terrorist state.”
Obama came into office with a desire to shift U.S. policy away from its Middle Eastern focus and reassert America’s importance as a Pacific power, particularly in light of China’s growing regional influence. But the president has invested more in drones than in diplomacy, sustaining the war on terror at the expense of the sort of bolder engagement of adversaries that Obama hinted at as a candidate. In the meantime, the administration is prepared to just wait it out until the next elections are history — and by then, it might already be too late to catch up with regional developments.
After all, Washington has watched China become the top trading partner of nearly every Asian country. Similarly, the economic links between China and Taiwan have deepened considerably, a reality to which even that island’s opposition party must bow. The Obama administration’s recent decision not to upset Beijing too much by selling advanced F-16 fighter jets to Taiwan, opting instead for a mere upgrade of the F-16s it bought in the 1990s, is a clear sign of relative U.S. decline in the region, suggests big-picture analyst Robert Kaplan.
Then there’s the sheer cost of the U.S. military presence in the Pacific, which looks like a juicy target to budget cutters in Washington. Key members of Congress like Senators John McCain and Carl Levin have already signaled their anxiety about the high price tag of a planned “strategic realignment” in Asia that involves, among other things, an expansion of the U.S. military base in Guam and an upgrading of facilities in Okinawa. In response to a question about potential military cuts, new Deputy Secretary of Defense Ashton Carter has confirmed that reducing U.S. troops and bases overseas is “on the table.”
The future of East Asia is hardly a given, nor is an economic boom and regional integration the only possible scenario. Virtually every country in the region has hiked its military spending. Tension points abound, particularly in potentially energy-rich waters that various countries claim as their own. China’s staggering economic growth is not likely to be sustainable in the long term. And North Korea could ultimately decide to make do as an economically destitute but adequately strong military power.
Still, the trend lines for 2012 and after point to greater engagement on the Korean peninsula, across the Taiwan Strait, and between Asia and Europe. Right now, the United States, for all of its military clout, is not really part of this emerging picture. Isn’t it time for America to gracefully acknowledge that its years as the Pacific superpower are over and think creatively about how to be a pacific partner instead?
John Feffer is the co-director of Foreign Policy in Focus at the Institute for Policy Studies, writes its regular World Beat column, and will be publishing a book on Islamophobia with City Lights Press in 2012. His past essays, including those for TomDispatch.com, can be read at his website. To listen to Timothy MacBain’s latest Tomcast audio interview in which Feffer discusses the 2012 election season in Asia click here, or download it to your iPod here.
Copyright 2011 John Feffer
]]>[Note to Readers: Who hasn’t received one -- or 100 -- of those “Nigerian” letters offering you, in florid prose, millions of potential dollars and with nary a catch in sight? But who knew that the highest officials in Washington have been receiving [...]]]>
[Note to Readers: Who hasn’t received one -- or 100 -- of those “Nigerian” letters offering you, in florid prose, millions of potential dollars and with nary a catch in sight? But who knew that the highest officials in Washington have been receiving them as well -- and from our war zones rather than Africa. Today, TomDispatch.com is proud to release examples of such letters from a treasure trove of documents shown to us by the new website ScamiLeaks. (For unknown reasons, the British Guardian, the New York Times, and Der Spiegel all refused to take part in this process, and so it’s been left to TomDispatch to release a selection of them to the world.)
Though we lack the staff of those papers, we have nonetheless done due diligence. We investigated each of the letters that follow and now believe that Hamid Karzai, the Afghan president, was never trapped in a Kabul airport bathroom, that “Iraqi parliamentarian” Sami Malouf does not exist, and that the letter writer who calls herself Serena Massoud could not be the lost granddaughter of the Afghan leader Ahmad Shah Massoud whom al-Qaeda operatives assassinated two days before the 9/11 attacks. Curiously enough, however, all the Washington or Pentagon scandals the letter writers mention involving lost, squandered, or stolen money turn out to be perfectly real. In fact, they represent one of the true scams of our time.
Below, then, are three of the letters we have chosen as representative from the enormous archive that ScamiLeaks will soon release to the world. We have touched none of them, not even to correct various obvious grammatical errors and misspellings. We have only added a small number of links not in the originals, so that readers can explore the corruption scandals the letter writers refer to. We do not know whether any of the Washington officials addressed responded to these letters or were taken in by them (as they evidently were by scam after scam in our war zones these last ten years).
Whatever you make of the three letters below, consider them collectively a little parable about the fallout from our now decade-old set of wars in the Greater Middle East. Tom]
***
To My Closest of Friends President and Professor Barack Obama,
I send this missive to you with deepest urgency. My embarrassment at importuning you in any way in your busy life is beyond expression. Please excuse my rushedness, but I, your friend and associate, Hamid Karzai, President of Afghanistan, have lost my wallet, passport, and Kabul Bank deposit book in the men’s room of Kabul International Airport.
It is to my dismay to discover, in addition, that the $31 billion in small bills I had secured within the sleeves of my chapan, thanks to your most generous heart and the reconstruction abilities of the American contractor, is now gone as well. Without it, I cannot return to the presidential palace.
Please let me ask whether you can at moment soonest respond at this email address and let me know that you are willing to deposit a new $33 billion in the Kabul Bank for me. I will then, of course, provide you with the necessary account numbers and transmission information. (Lest you would think me in any way dishonest, my dear friend, I hasten to point out that Kabul Bank is the shining light of Afghan Banking and the extra $2 billion above and beyond the lost $31 billion, are deeply necessary if I am to present alms on my way from the airport to the Palace.)
As we are the closest of companions, I reassure you immediately and in no uncertain terms that this money of yours, a mere pittance compared to what is surely available to the President of the United States, is Absolutely Safe in the Kabul Bank (whose small troubles will soon be straightened out) and will in no way be lost to you. If you remit the said sum to me with all due speed, I will return it to you with $2 billion in interest within the month. You have my sincerest promise of that.
Act with great haste, my erstwhile companion!
Your Friend and Associate in Need,
Hamid Karzai, President of Afghanistan
***
Attention: Secretary of the Treasury Timothy Gythner, Washington CD
From: Barrister Hammad al-Saad, First Assistant and Secretary to Parliamentarian Sami Malouf, Baghdad, Iraq
With due respect, Good News!
Thanks to a dead business associate who lacks all heirs, an accountant for my lawerly firm, Al-Azawi & Sons, has discovered an abandoned sum of $6.6 billion (SIX BILLION SIX HUNDRED THOUSAND DOLLARS) in U.S. bills in a deserted warehouse on the outskirts of Baghdad owned by said dead associate. They are all shrink-wrapped $100 (ONE HUNDRED DOLLAR) bills with your Benjamin on the front cover. No one has claimed this money.
It has come to our attention that one of your Predecessors also lost $6.6 billion (SIX BILLION SIX HUNDRED THOUSAND DOLLARS) in shrink-wrapped $100 (ONE HUNDRD DOLLAR) bills with same Benjamin on cover, which were shipped to my country by C-130 cargo plane in 2003. In the discrepitude of Iraq at that moment, such a misplacement is not strange.
However, your loss of such moneys must weigh deeply on you. We wish to alleviate that weight and return to you the rightful sums. This can happen almost immediately. In order to ship Benjamin to you, we must, of course, avoid Iraqi customs, which is sorrowfully corrupt.
To do this we need a few small fees from you, esteemed Gythner, to grease other palms with friendship and hire such a plane as to return your sums. I, Barrister Hammad Al-Saad, will personally fly this money to you. This is 100% (ONE HUNDRED PERCENT) risk free!
Do not worry. You are in our thoughts momentarily. Please contact us to firm up details and to exchange pleasantries on necessary fees!
Yours Most Fully Sincerely and Honorably,
Hammad Al-Saad
***
To: David Petreaus, Director-General of the Central Intelligence Agency
From: Serena Massoud, Granddaughter of Ahmad Shah Massoud, the Lion of the Panjshi
My dearest,
I beg your indulgence, Kind General, I am the Lost Granddaughter of Ahmad Shah Massoud, the erstwhile, sadly al-Qaeda assassinated Lion of Panjshir. Mine is a dismal tale to tell and it is yours to be patient, I hope with utter nonindifference, while I explain.
Let me preface this dawn of the weighted heart by assuring you that it will be worth all your whiles. I, Serena Massoud, out of my full heart and deep love for America and the CIA, and You — I, a poor Afghan woman awash in her times, wish to return to you $125 million. This, you will agree, is part of the $360 million that, according to one of your most esteemed news sources, “has ended up in the hands of people the American-led coalition has spent nearly a decade battling: the Taliban, criminals, and power brokers with ties to both.”
I must beg your forgiveness. To explain how such fundings came almost into my own hands and how — with barely no effort on your part — you will get them back, I have a tangled tale to tell of a dark and stormy decade in my country whose breezes and gales buffeted me. But if I told it all to you, dear General, you would stumble into Incredulity.
Let me just state that, after many and various adventures of the terrible kind, I found myself, against my uttermost will, in the grips of marriage to Omar Fahim Dadulah, whom you would know as a War Lord. He was a man of Evil Incarnate and his treatment of yours truly was not to be described. He was, moreover, In League With the Taliban, and among those whom Navy Times so rightly describes as absorbing your moneys with obscure nefariousness of purpose.
Without straining your patience, My Darling Director-General, in the end he was expectably poisoned by the self-same proclaimed Taliban and, as death came upon him, called me to his bedside. He then informed me in tones too solemn to mistake of that fund of $125 million, the very dollars which you have slipped upon the Taliban in trucking fees and safety passes and the like, which he had hidden in a spot unmentionable and which he meant for me.
I beg of you, my dearest General, lend me a helping hand to assist me in claiming this money. Be my guardian, let me be your orphan ward, and receive the money in your account. Also promise to invest a small part of it for me in a lucrative business since I am still a young woman and make arrangements for me to come over to your country to further my education and secure a beloved citizenship permit.
I have seen the photos of you. Your chest of medals is the light of my day. It is with the most profound and sincerity that I make this gesture to you from deep within my loving soul. Your open heart has touched me. I eagerly await your tiptoed words.
Humbly Yrs and Only Yrs,
Serena Masoud
 [A Further Note: The “Nigerian” letter scam is, in its own way, remarkable. Smart grifters from another land generally pose as highly (or strategically) placed individuals, but also ignorant yokels and innocents with a minimalist grasp of over-the-top nineteenth-century English. It’s a highly skilled compositional con and it works, evidently to the tune of tens of millions of dollars yearly. If you want to explore how it operates, fleecing significant numbers of people, the Snopes.com website is most useful. (Click here.) For a wonderful older essay on the charms of those scam letters, check out Douglas Cruickshank’s “I crave your distinguished indulgence (and all your cash)” at Salon.com.
[A Further Note: The “Nigerian” letter scam is, in its own way, remarkable. Smart grifters from another land generally pose as highly (or strategically) placed individuals, but also ignorant yokels and innocents with a minimalist grasp of over-the-top nineteenth-century English. It’s a highly skilled compositional con and it works, evidently to the tune of tens of millions of dollars yearly. If you want to explore how it operates, fleecing significant numbers of people, the Snopes.com website is most useful. (Click here.) For a wonderful older essay on the charms of those scam letters, check out Douglas Cruickshank’s “I crave your distinguished indulgence (and all your cash)” at Salon.com.
If, on the other hand, you prefer to explore the scams Washington has been involved in these last endless years of war, you could start with Adam Weinstein’s recent Mother Jones piece “The All-Time Ten Worst Military Contracting Boondoggles.” The individual scams from this period are a dime a dozen (or rather, unfortunately, billions of dollars a dozen, making the “Nigerians” look like the rubes they aren’t). These would include, to mention just a few examples, that missing $31 to $60 billion in contractor waste and fraud in the Afghan and Iraq war zones; the $6.6 billion (evidently largely Iraqi oil money held in U.S. banks) that the Bush administration sent in pallets of shrink-wrapped bills to Iraq, and which then went missing-in-action; the $360 million in U.S. taxpayer dollars that, according to a special military task force, headed directly for the Taliban and other Afghan lovelies; the $65 billion that went into the development of the F-22, the most expensive fighter jet ever built not to be used -- since May, all of the F-22s in the U.S. fleet have been grounded indefinitely; and the more than $140 billion in contracts the Pentagon awarded to companies in 2010 without a hint of competitive bidding, up from $50 billion in 2001.
Believe me, the “Nigerians” have a great deal to learn from the Pentagon and from U.S. operations in the Greater Middle East, as do the real rubes in the larger scam of things, gullible American taxpayers!]
Tom Engelhardt, co-founder of the American Empire Project and the author of The American Way of War: How Bush’s Wars Became Obama’s as well as The End of Victory Culture, runs the Nation Institute’s TomDispatch.com. His latest book, The United States of Fear (Haymarket Books), will be published in November.
Copyright 2011 Tom Engelhardt
]]>By Karen J. Greenberg
As the 10th anniversary of 9/11 approaches, the unexpected extent of the damage Americans have done to themselves and their institutions is coming into better focus. The event that “changed everything” did turn out to change Washington in ways more startling than most [...]]]>
By Karen J. Greenberg
As the 10th anniversary of 9/11 approaches, the unexpected extent of the damage Americans have done to themselves and their institutions is coming into better focus. The event that “changed everything” did turn out to change Washington in ways more startling than most people realize. On terrorism and national security, to take an obvious (if seldom commented upon) example, the confidence of the U.S. government seems to have been severely, perhaps irreparably, shaken when it comes to that basic and essential American institution: the courts.
If, in fact, we are a “nation of laws,” you wouldn’t know it from Washington’s actions over the past few years. Nothing spoke more strikingly to that loss of faith, to our country’s increasing incapacity for meeting violence with the law, than the widely hailed decision to kill rather than capture Osama bin Laden.
Clearly, a key factor in that decision was a growing belief, widely shared within the national-security establishment, that none of our traditional or even newly created tribunals, civilian or military, could have handled a bin Laden trial. Washington’s faith went solely to Navy SEALs zooming into another country’s sovereign airspace on aT moonless night on a mission to assassinate bin Laden, whether he offered the slightest resistance or not. It evidently seemed so much easier to the top officials overseeing the operation — and so much less messy — than bringing a confessed mass murderer into a courtroom in, or even anywhere near, the United States.
The decision to kill bin Laden on sight rather than capture him and bring him to trial followed hard on the heels of an ignominious Obama administration climb-down on its plan to try the “mastermind” of the 9/11 attacks, Khalid Sheikh Mohammed, or KSM, in a federal court in New York City. Captured in Pakistan in May 2003 and transferred to Guantanamo in 2006, his proposed trial was, under political pressure, returned to a military venue earlier this year.
Given the extraordinary record of underperformance by the military commissions system — only six convictions in 10 years — it’s hard to escape the conclusion that the United States has little faith in its ability to put on trial a man assumedly responsible for murdering thousands.
And don’t assume that these high-level examples of avoiding the court system are just knotty exceptions that prove the rule. There is evidence that the administration’s skepticism and faint-heartedness when it comes to using the judicial system risks becoming pervasive.
Pushing Guilt Before Trial
Needless to say, this backing away from courts of law as institutions appropriate for handling terrorism suspects began in the Bush-Cheney years. Top officials in the Bush administration believed civilian courts to be far too weak for the Global War on Terror they had declared. This, as they saw it, was largely because those courts would supposedly gift foreign terrorist suspects with a slew of American legal rights that might act as so many get-out-of-jail-free cards.
As a result, despite a shining record of terrorism convictions in civilian courts in the 1990s — including the prosecutions of those responsible for the 1993 attempt to take down a tower of the World Trade Center — President Bush issued a military order on November 13, 2001, that established the court-less contours of public debate to come. It mandated that non-American terrorists captured abroad would be put under the jurisdiction of the Pentagon, not the federal court system. This was “war,” after all, and the enemy had to be confronted by fighting men, not those sticklers for due process, civilian judges and juries.
The federal courts have, of course, continued to try American citizens and residents (and even, in a few cases, individuals captured abroad) in terror cases of all sorts — with an 87% conviction rate for both violent and non-violent crimes. In fact, 2010 was a banner year for terrorism prosecutions when it came to American citizens and residents, and 2011 is following suit. As could have been predicted, in the vast majority of these cases — all the ones that mattered — there were convictions.
 You might think, then, that the courts had proved their mettle against mounting criticism and distrust of a system said to be insufficiently harsh. And initially, Obama’s Department of Justice defended civilian courts as resilient and flexible enough to try terror cases.
You might think, then, that the courts had proved their mettle against mounting criticism and distrust of a system said to be insufficiently harsh. And initially, Obama’s Department of Justice defended civilian courts as resilient and flexible enough to try terror cases.
But that didn’t last. Recently, the Obama administration has reinforced a policy (begun under President Bush) which offers an ominous new twist on American justice: punishment before trial. It has, for example, relied upon various extreme methods of pre-trial isolation — including a version of restrictive orders known as Special Administrative Measures, or SAMs — that reek of punitiveness and have often caused severe psychological deterioration in suspects awaiting trial on terrorism charges. The most noteworthy case of this is Syed Fahad Hashmi’s. An American citizen arrested while studying in England, Hashmi had allowed an acquaintance, Mohammed Junaid Babar, to stay in his apartment for two weeks. Babar, who testified against Hashmi and was later released, allegedly had socks, ponchos, and raingear intended for al-Qaeda in his luggage and allegedly used Hashmi’s cell phone to call terrorist conspirators. Hashmi, accused of “material support” for al-Qaeda, was kept under SAMs for three years without trial — until he finally pled guilty.
The urge to punish before a verdict comes in reflects the same deep-seated conviction that the U.S. court system is simply not to be trusted to do its job. Two recent cases — that of whistleblowers Thomas Drake and Bradley Manning — illustrate how, in cases where national security is believed to be at stake, Obama-era pre-trial treatment has taken up the distrust of the courts, civilian or military, that characterized the Bush years.
Drake, an executive for the National Security Agency (NSA), became a whistleblower over what he considered mistaken policy decisions about an ill-performing data-sifting program which, among other things, he thought squandered taxpayer money. Subsequently, he revealed his disagreement with the agency’s warrantless wire-tapping program, which he believed overstepped legal boundaries. Charged initially with violating the Espionage Act and threatened with a draconian 35-year jail sentence, Drake finally pled this past June to a misdemeanor count of “exceeding the authorized use of a government computer.”
In Drake’s four-year saga, his pre-punishment took the form not of pre-trial detention but of the destruction of his livelihood. He was initially fired from the NSA and from the National Defense University position to which the NSA had assigned him. Once indicted in 2010, he was forced to resign from a subsequent teaching post at Strayer University. All told, the formal and informal hounding of Drake resulted in the loss of his jobs and pension, as well as $82,000 in legal costs. Ultimately, Drake was sentenced to a year’s probation and 240 hours of mandatory community service. By that time, he had been ruined financially and professionally, thanks to the government’s disparagement of him and the multi-year delay between its accusations and the lodging of formal charges against him. Drake now works at an Apple Store. In other words, well before the government took its chances in court, Thomas Drake was punished.
Another highly publicized case where punishment preceded trial has been the mistreatment of Army Private Bradley Manning while in military custody in a Marine brig in Quantico, Virginia, awaiting charges. The Obama administration believes he turned over a trove of secret military and State Department documents to the website WikiLeaks. Following his arrest, Manning was kept in subhuman conditions. He was forced to sleep naked and to strip for daily inspections, though as news about his situation generated bad publicity, he was eventually allowed to sleep in a “tear-proof” gown.
There is something deeply disturbing about the very different ways Manning and Drake were pre-punished by the government — both directly in the case of Manning and indirectly in the case of Drake — before being given due process of any kind. Like bin Laden’s killing, both cases reflect an unspoken worry in Washington that our courts will prove insufficiently ruthless and so incapable of giving the “obviously guilty” what they “obviously” deserve.
The Courts Take Notice
As it turns out, the judicial system hasn’t taken the government’s new attitude lying down. Various judges and juries have, in fact, shown themselves to be unfazed by both public and governmental pressures and have, in terror and national security cases, demonstrated signs of balance and of a concern for justice, rather than being driven by a blind sense of revenge.
In the past year, there has been an unprecedented number of high-profile terrorism trials. All have resulted in convictions, which have nonetheless not reflected the unstinting harshness that critics of court-centered counterterrorism insist upon. In the case of Ahmed Ghailani, the sole Guantanamo detainee to face trial in the nation’s criminal justice system, the jury, having done its work of assessing the evidence, acquitted the defendant on 284 of 285 counts, including all the murder charges associated with the 1998 bombings of the U.S. embassies in Kenya and Tanzania. On the single count on which he was convicted, however, Ghailani was given a life sentence without parole.
Meanwhile, a high-profile terrorism case — that of Tagawwur Rana — ended in a jury acquittal on its most serious charge. Rana had been accused of cooperating in the 2008 terrorist attacks in Mumbai, India, which resulted in the deaths of more than 160 individuals. The jury found Rana guilty of material support, but not of helping to coordinate the attack.
These cases and others like them have, of course, been fodder for all the usual critics who consider anything but a 100% conviction rate on all charges in all cases to be a sure sign not of the justice system’s strength, but of its fundamental weakness. And yet, such cases have showcased just how effectively the system still works, in a more nuanced way than in the previous near-decade, as well as in a subtler and more just way than Washington has managed to approximate over that same period. Despite the fears, pressures, and scare tactics that are entangled with all such terror cases, we now have living proof that juries can think for themselves, and guilt can be a partial matter, rather than a Washington slam-dunk.
Of late, federal judges on such cases also seem to have been signaling to the government’s representatives that they must be more restrained in their approach to national security cases, both in and out of court. In late June, for instance, during the sentencing of three of the men convicted of conspiring to bomb two synagogues in Riverdale, New York, and to launch a Stinger missile aimed at aircraft over Newburgh’s Air National Guard Base, Judge Colleen McMahon struck back at the government’s case. “I believe beyond a shadow of a doubt,” she said, “that there would have been no crime here except the government instigated it, planned it, and brought it to fruition. That does not mean that there was no crime. The jury concluded that you were not entrapped, and I see no basis to overturn their verdict.”
In the Drake case, Judge Richard Bennett was similarly distraught about the evident excesses in the government’s approach. At sentencing for the single minor count to which Drake agreed to plead, the judge bluntly refused to impose the $50,000 fine the prosecution was pushing for on the grounds that punishment had already been administered — prior to the court process. “There has been financial devastation wrought upon this defendant,” said Bennett, “that far exceeds any fine that can be imposed by me. And I’m not going to add to that in any way. And it’s very obvious to me in terms of some of the irritation I’ve expressed… not only my concern over the delay in this case… [but also the prosecution’s] inability to explain … the delay in this case… I think that somebody somewhere in the U.S. government has to say… that the American public deserves better than this.”
In the recent jury decisions, as in the growing expressions of judicial dissatisfaction, an optimist might find signs that the system is finally starting to right itself. On the other hand, a pessimist might come to the conclusion that the government will, in the future, simply put even more energy into avoiding the court system.
The bottom line is that the Obama administration, like its predecessor, defines success in terrorism prosecutions not by assessing whether or not due process and fair verdicts are administered, but solely in terms of what they deem proper punishment for those accused of violating national security — especially when doing so minimizes partisan political clashes. By refusing to rein in its evident distrust of the judicial system when it comes to national security, the government is perpetuating a legal landscape that, to this day, lies in the shadow of Osama bin Laden.
Karen Greenberg is the executive director of the New York University Center on Law and Security, a TomDispatch regular, and the author of The Least Worst Place: Guantanamo’s First One Hundred Days, as well as the editor of The Torture Debate in America.
Copyright 2011 Karen J. Greenberg
]]>Mubarak is clearly backed by the Americans. He took some moves after speaking with Obama and a visit by a former U.S. Ambassador to Egypt Frank Wisner (sp.?).
Mubarak, the army, the Americans and the Israelis are clearly on one side. That’s one camp. [...]]]>
Mubarak is clearly backed by the Americans. He took some moves after speaking with Obama and a visit by a former U.S. Ambassador to Egypt Frank Wisner (sp.?).
Mubarak, the army, the Americans and the Israelis are clearly on one side. That’s one camp. The people of Egypt (most of them now) are the other.
The Americans want Mubarak to stay on for longer while they look for a suitable successor that would be best for U.S. interests.
Mubarak’s tactic is to make Egyptians choose between “security”, that he supposedly provided over the past thirty years, or insecurity, vandalism, and chaos that he also is also providing now.
Mubarak, with the backing of his secret police force the Amn Dawla, is punishing the society in general for going out against him. Right now, there’s a battle going on by police officers and Mubarak supporters, many of them work for businessmen allied with the regime, and the protesters who are calling for his ouster.
His punishment for the people also includes blocking off roads, essentially making the cost of transportation much higher now. That translates as higher food prices and shortages of literally almost everything.
We had a huge dose of insecurity over the past few days. I had to take my own family out of Cairo after constant gun shots all night long in the city of 6th October which is some 30 kilometers south-east of Cairo.
This will backfire. Some people got scared which means the fear tactic he used over the past 30 years worked again. But many too have turned even further against him. His tactics are clearly so low and some say even “devious”. There will be lots of blood. But the word I hear is that is going to be worth it. Egyptians will be liberated not just from Mubarak but his backers as well.
The U.S. looks set to lose another country in the Middle East for backing Mubarak and trying to buy more time to get another of their men in power.
]]>